Difference between revisions of "FMM125 Network Settings"
(Created page with "__TOC__ ==Network settings== 400px|thumb|right|Network Settings <br> Device with external Quectel BG96 modem are named FMMxxx.<br> Quectel BG...") |
(Created page with "__TOC__ ==Network settings== 400px|thumb|right|Network Settings <br> Device with external Quectel BG96 modem are named FMMxxx.<br> Quectel BG...") |
(No difference)
| |
Latest revision as of 09:41, 3 April 2020
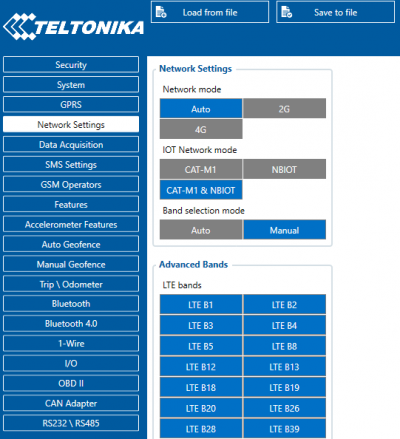
Main Page > Professional Trackers > FMM125 > FMM125 Network SettingsNetwork settings
Device with external Quectel BG96 modem are named FMMxxx.
Quectel BG96 has different connection sequence from firmware side compared to other modems.
Network settings method is called on these occasions:
1. Modem is initialized.
2. Configuration has changed.
3. Periodically every 60 seconds after startup.
On each network settings call changes are checked. Firmware sends configuration commands when they change. On device startup all these commands are always sent as we don’t know whether they have changed.
Geo bands
Quectel BG96 modem has 14 LTE network bands. According to Quectel each band can take up to 5 minutes to scan. To improve scan speed geographic bands have been implemented.
Geographic bands is a functionality that sets (changes) configuration bands according to device’s GPS location. Functionality is only active when band selection mode is “Auto”. It is run from network settings method (see above).
| Location | Abrevation | Bands set |
|---|---|---|
| United States of America | US | B2 B4 B12 B13 |
| Europe | EU | B3 B8 B20 |
| Korea | KR | B3 B5 |
| Australia | AU | B3 B28 |
| The Middle East | ET | B3 B8 B28 |
| Japan | JP | B1 B8 B18 B19 |
| China | CH | B1 B3 B5 B8 B26 B39 |
Operator connection
Device saves to memory last seen operator and its’ network type. When there is no operator attached, the device tries to attach to last seen operator on 4G IoT network mode. If the connection fails, device clears last seen operator from memory and starts new operator search. Same sequence happens when preferred operator is given (configured), but instead of clearing operator, device each time connecting first tries to connect to preferred operator.