TST100 System settings: Difference between revisions
m Protected "TST100 System settings" ([Edit=Allow only administrators] (indefinite) [Move=Allow only administrators] (indefinite)) |
Irmantas.K (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
|model=TST100 | |model=TST100 | ||
|device_group=MM | |device_group=MM | ||
|Data_protocol=false | |Data_protocol=false | ||
|PT_Power_on=false | |PT_Power_on=false | ||
|PT_Tracking_mode=false | |PT_Tracking_mode=false | ||
| Line 13: | Line 9: | ||
|GNSS_Fix_Holdout=false | |GNSS_Fix_Holdout=false | ||
|TAT100_show=false | |TAT100_show=false | ||
|Location_settings=false | |||
|AT_show=false | |||
|PT_show=false | |||
|TFT_can=false | |||
|TFT_show=false | |||
|GH_section=false | |||
|GH_TMT_section=false | |||
}} | }} | ||
[[Category:TST100 Configuration]] | [[Category:TST100 Configuration]] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:08, 10 July 2024
Main Page > E-Mobility Trackers > TST100 > TST100 Configuration > TST100 System settingsSystem Settings
Movement Source
User can select which source will be used to determine when vehicle is on stop or moving. When multiple are selected, if any of selected are active, Vehicle MOVING mode is used. Available movement source:
- Ignition: checks ignition settings which depends on Ignition Source settings;
- GNSS: movement detected if Fix position available and speed is bigger or equal to 5km/h;
- Accelerometer: movement detection depends on Accelerometer Delay Settings;
- CAN Speed: movement is detected if CAN speed retrieved from specific CAN protocol.
When multiple source are selected, if any of selected are active, Movement is detected.
Records settings
Here user can enable or disable records when GPS is not available (no GPS fix).
- After Position Fix - Device must have GPS fix and time to save/send records.
- After Time Sync - Device must have correct time to save/send records. Allows record sending with no coordinates.
- Always - Always save/send records. Allows record sending with no coordinates and no correct time.
LED Indication
User can turn on or off the indication LEDs.
GNSS Source settings
User can configure which GNSS system(s) to use.
User has a choice to use only one system between GPS, GLONASS, Galileo or Beidou and it is possible to choose two or three systems together. One exception is that you cannot combine BeiDou and GLONASS systems together.
Examples of non-configurable GNSS source combinations are:
- GLONASS + BeiDou;
- Galileo + GLONASS + BeiDou;
- GPS + GLONASS + BeiDou;
- GPS + Galileo + GLONASS + BeiDou.
List of configurable GNSS sources:
- GPS only;
- GPS + BeiDou;
- GPS + GLONASS;
- GPS + GLONASS + Galileo.
Battery Charge Mode
Here user can change battery charger settings, where charging is allowed. Battery will be charged: On Need (battery will be charged anytime when it needs to be charged) and After Ignition ON (battery will be charged only when ignition is on).
Three charging modes is available:
- On neeed: charger enabled if external voltage is higher than 5.05 voltage and Battery Voltage is below 3.90V. Charging is disabled if device enters any sleep mode.
- After Ignition On: charger enabled after ignition is turned on, except if the battery is fully charged or 10-minute timeout has not passed since the device was turned on for faster FIX receiving.
- Always: charger is always enabled, except if the battery is fully charged or 10-minute timeout has not passed since the device was turned on for faster FIX receiving.
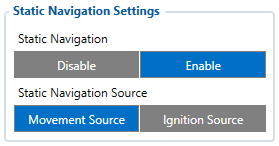
Static Navigation mode is a filter, which filters out track jumps when the object is stationary. If static navigation filter is disabled, it will apply no changes to GPS data. If static navigation filter is enabled, it will filter changes in GPS position if no movement (as defined by configured movement source) or ignition (as defined by configured ignition source) is detected. It allows filtering GPS jumps when the object is parked (not moving) and GPS position is still traced.
Additionally, user can choose which source (movement or ignition) is used to activate/deactivate static navigation.
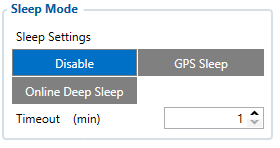
Sleep Mode
| User can choose sleep mode. More about sleep modes can be found here. |
 |
Accelerometer Delay Settings
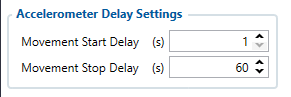
Here the user can set the movement start/stop delays.
For example, if the Movement Start Delay is set to 1s and Movement Stop Delay to 60s, the movement will be detected after 1s of moving and defined as stopped after 60s when device stopped moving.
| Parameter ID | Name | Min Value | Max Value | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 19001 | Movement Start Delay | 1 | 60 | 5 |
| 19002 | Movement Stop Delay | 5 | 300 | 60 |
Time Synchronization