TachoSync Integrations: Difference between revisions
Reworked some places, expanded on folder and file naming structure. [GTPGTM-10958] |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
TachoSync provides integration mechanisms for automated data transfer to external systems. These integrations support both file-based delivery (e.g., SFTP) and | TachoSync provides integration mechanisms for automated data transfer to external systems. These integrations support both file-based delivery (e.g., SFTP) and request-response (e.g., API), enabling flexible and secure connectivity with fleet management platforms, IT systems, and other third-party services. | ||
This page | This page gives information about the available TachoSync integrations: | ||
* [https://api.tacho.teltonika.lt/api-docs/v1#description/overview REST API] - see this link for TachoSync API documentation portal | * '''[https://api.tacho.teltonika.lt/api-docs/v1#description/overview REST API] - see this link for TachoSync API documentation portal.''' | ||
* [[TachoSync Integrations#SFTP|SFTP]] | * [[TachoSync Integrations#SFTP|SFTP]] | ||
Additional integration methods | Additional integration methods are in development. | ||
==Integrations Menu== | ==Integrations Menu== | ||
[[File:TachoSync Integrations menu.png|frame|center|alt=TachoSync Integrations menu|TachoSync Integrations menu]] | [[File:TachoSync Integrations menu.png|frame|center|alt=TachoSync Integrations menu|TachoSync Integrations menu]] | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
* '''Status''' - displays the status of the integration. See below for explanations. | * '''Status''' - displays the status of the integration. See below for explanations. | ||
* '''Enable''' – toggles the integration on/off. | * '''Enable''' – toggles the integration on/off. | ||
* '''Last event''' – | * '''Last event''' – last time a file was successfully synced. | ||
* '''Edit button''' - allows editing the integration. | * '''Edit button''' - allows editing the integration. | ||
* '''Retry button''' - allows to manually retry the connection. Button is available for Failed and Interrupted statuses. Upon pressing, a connection test is executed: | * '''Retry button''' - allows to manually retry the connection. Button is available for Failed and Interrupted statuses. Upon pressing, a connection test is executed: | ||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
** No failed file transfers. | ** No failed file transfers. | ||
** New (and historical, if enabled) files are queued and uploaded. | ** New (and historical, if enabled) files are queued and uploaded. | ||
• Disabled - integration is disabled by the user: | |||
** No files are queued or uploaded. | ** No files are queued or uploaded. | ||
** No retries can occur. | ** No retries can occur. | ||
• Interrupted – integration works only partially: | |||
** At least one file transferred successfully AND at least one file failed. | ** At least one file transferred successfully AND at least one file failed. | ||
** New files are processed. | ** New files are processed. | ||
** Failed files remain as "Failed" until a successful retry. | ** Failed files remain as "Failed" until a successful retry. | ||
** '''The user can try to fix the connection and manually retry the connection'''. | ** '''The user can try to fix the connection and manually retry the connection'''. | ||
• Failed – integration has failed: | |||
** One or more file transfers have failed AND no file transfer has been successful: | ** One or more file transfers have failed AND no file transfer has been successful: | ||
*** New files are processed. | *** New files are processed. | ||
| Line 61: | Line 61: | ||
*** Integration is skipped when files are queued, no uploads are attempted. | *** Integration is skipped when files are queued, no uploads are attempted. | ||
** '''The user can try to fix the connection and manually retry the connection'''. | ** '''The user can try to fix the connection and manually retry the connection'''. | ||
===SFTP Server Settings=== | ===SFTP Server Settings=== | ||
[[File:TachoSync Integrations settings.png|thumb|right|alt=TachoSync Integrations settings|TachoSync SFTP integration settings]] | [[File:TachoSync Integrations settings.png|thumb|right|alt=TachoSync Integrations settings|TachoSync SFTP integration settings]] | ||
| Line 103: | Line 102: | ||
**** /1234567890/ ''← driver folder (set the naming convention in „General Settings“)'' | **** /1234567890/ ''← driver folder (set the naming convention in „General Settings“)'' | ||
***** 2025-01-12.DDD | ***** 2025-01-12.DDD | ||
===File Upload Behavior=== | |||
TachoSync uploads files to your SFTP server as soon as they become available in TachoSync (after being downloaded from device): | |||
* Files are sent to the SFTP server automatically and continuously, there is no fixed schedule. | |||
* If you enable “Include historical files,” TachoSync also adds your previously downloaded files to the queue and syncs them in batches based on current system load. Older files are selected and queued – this uses the same upload and retry logic as regular uploads. | |||
If file upload fails, TachoSync attempts to re-upload. The retry pattern is "exponential backoff" – 5 times in around 6 minutes. If all 5 retry attempts fail, the file is marked as "Failed". | |||
To troubleshoot, see [[TachoSync Integrations#SFTP Integration Troubleshooting|SFTP Integration Troubleshooting]]. | |||
===SFTP Integration Troubleshooting=== | |||
If the SFTP integration does not work as expected, verify the following: | |||
* The [[TachoSync Integrations#Prerequisites|prerequisites]] are met. | |||
* Your internet connection is stable (there are no repeating time-outs or interruptions). | |||
* The user has write permissions for the configured directory. | |||
* The provided path exists on the server. | |||
If issues persist, collect the “Last event” details from the Integrations page and contact Support. | |||
[[Category:TachoSync]] | |||
==Integrations Menu== | |||
[[File:TachoSync Integrations menu.png|frame|center|alt=TachoSync Integrations menu|TachoSync Integrations menu]] | |||
In the TachoSync UI, the Integrations menu shows the configured integrations. | |||
'''To add an integration, click “Add integration” in the top right corner of the window, enter the required details, and click “Save”.''' | |||
The table presents the following data: | |||
* '''Name''' – name (label) given to the integration. | |||
* '''Method''' – integration method. | |||
* '''Company''' - company within TachoSync associated with this integration. | |||
* '''Status''' - displays the status of the integration. See below for explanations. | |||
* '''Enable''' – toggles the integration on/off. | |||
* '''Last event''' – last time a file was successfully synced. | |||
* '''Edit button''' - allows editing the integration. | |||
* '''Retry button''' - allows to manually retry the connection. Button is available for Failed and Interrupted statuses. Upon pressing, a connection test is executed: | |||
** If the test fails, error details are returned. | |||
** If the connection is successful, integration becomes “Active” and failed operations are retried. | |||
==SFTP== | |||
'''''NOTE!''' <u>TachoSync supports only '''SFTP (SSH File Transfer Protocol)'''!</u> Reusing old WEB TACHO FTP settings (such as FTP credentials and ports, e.g. port 21) will not work. FTP and SFTP are not compatible.'' | |||
SFTP (Secure/SSH File Transfer Protocol) is a network protocol that provides secure file access, transfer, and management over a reliable data stream. SFTP is a replacement of File Transfer Protocol (FTP) due to superior security. | |||
SFTP integration allows receiving files from TachoSync directly to your SFTP server. This option is ideal for organizations that want to automate the intake of data from TachoSync into an existing backend system. | |||
Main features: | |||
* You can create as many SFTP connections as needed. | |||
* File transfer to your SFTP server starts as soon as the file is received from device to TachoSync. | |||
* The option to download historical files that were created before the integration was enabled. | |||
'''''NOTE!''' TachoSync does not create or configure the SFTP server. The customer is responsible for ensuring that the server is reachable from the internet and properly secured.'' | |||
===Prerequisites=== | |||
Prepare this before configuring the SFTP integration: | |||
* Set up your SFTP server and know: | |||
** SFTP server host (domain or IP address). | |||
** SFTP server port number. | |||
** Username and password for SFTP authentication. | |||
* Make sure that your SFTP server firewall rules allow inbound SFTP connections from TachoSync ('''IP address 3.126.35.133'''). | |||
* Optional: a dedicated folder path to place the downloaded files. | |||
===SFTP Integration Status Descriptions=== | |||
* '''Active''' – integration is enabled and operates normally: | |||
** No failed file transfers. | |||
** New (and historical, if enabled) files are queued and uploaded. | |||
* '''Disabled''' - integration is disabled by the user: | |||
** No files are queued or uploaded. | |||
** No retries can occur. | |||
* '''Interrupted''' – integration works only partially: | |||
** At least one file transferred successfully AND at least one file failed. | |||
** New files are processed. | |||
** Failed files remain as "Failed" until a successful retry. | |||
** '''The user can try to [[#SFTP Integration Troubleshooting|fix the connection]] and manually retry the connection'''. | |||
* '''Failed''' – integration has failed: | |||
** One or more file transfers have failed AND no file transfer has been successful: | |||
*** New files are processed. | |||
** Alternatively, the integration has failed the connection test. | |||
*** Integration is skipped when files are queued, no uploads are attempted. | |||
** '''The user can try to [[#SFTP Integration Troubleshooting|fix the connection]] and manually retry the connection'''. | |||
===SFTP Server Settings=== | |||
[[File:TachoSync Integrations settings.png|thumb|right|alt=TachoSync Integrations settings|TachoSync SFTP integration settings]] | |||
This section allows configuring the connection to your SFTP server. Settings marked by an asterisk (*) are mandatory. | |||
* '''Host*''': The hostname or IP address of the SFTP server. | |||
* '''Port*''': The port number on the SFTP server (typically 22). | |||
* '''Remote directory path (optional)''': The specific folder on the SFTP server where files will be uploaded. If left blank, files will be placed in the root directory of the configured server user. | |||
* '''Username*''': The username for authenticating with the SFTP server. | |||
* '''Password'''*: The password for the specified username. | |||
===General Settings=== | |||
This section defines how the files and folders are structured and named when sent to the SFTP server. Settings marked by an asterisk (*) are mandatory. | |||
* '''Company'''*: The company within TachoSync, associated with this integration. | |||
* '''SFTP name'''*: A label for this specific SFTP configuration (e.g., "Primary Server" or "Backup Archive"). | |||
* '''File format'''*: The desired format for tachograph files. | |||
** .DDD | |||
** .TGD | |||
** .V1B, .C1B | |||
* '''Vehicles folder naming'''*: The naming convention for the folders that contain vehicle data. | |||
** IMEI (E.g., 123456789012345) | |||
** Vehicle number (E.g., ABC123) | |||
* '''Drivers folder naming'''*: This field is set to "Driver ID", meaning folders for driver data will be named using the driver's unique identification number. | |||
* '''Include files from all sub-companies''': When enabled, in addition to the main company data, data from sub-companies will be gathered and uploaded as well. | |||
* '''Include historical files''': When enabled, TachoSync will attempt to upload files captured before the integration was created. | |||
===File Naming & Server Folder Structure=== | |||
File naming and folder structure is configured in [[TachoSync Integrations#General Settings|General Settings]]. | |||
To ensure valid paths on the SFTP server, TachoSync automatically cleans up folder and file names: | |||
* Removes leading and trailing spaces. | |||
* Replaces empty spaces with "_". | |||
* Removes characters: <code>\ / : * ? " < > | { }</code>. | |||
====Folder Naming Options==== | |||
* The vehicle folders can be named based on vehicle IMEI or vehicle registration number. | |||
* The driver folders are named based on the driver card number. | |||
====File Naming Schema==== | |||
* Vehicle files <code>M_YYYYMMDD_HHmm_VEHICLEREGNUMBER_VIN.DDD</code> | |||
** M – vehicle (mass memory) data | |||
** YYYYMMDD – download date (UTC) | |||
** HHmm – download time (UTC) | |||
** VEHICLEREGNUMBER – vehicle registration number | |||
** VIN – vehicle identification number | |||
* Driver files | |||
<code>C_YYYYMMDD_HHmm_N_SURNAME_CARDNUMBER.DDD</code> | |||
** C – driver card data | |||
** YYYYMMDD – download date (UTC) | |||
** HHmm – download time (UTC) | |||
** N – first letter of driver’s first name | |||
** SURNAME – driver’s surname | |||
** CARDNUMBER – driver card number | |||
====Folder Logic==== | |||
''Each SFTP integration has a base folder'', configured in the field "Remote directory path". Inside this base folder, the system always creates folders that reflect your company hierarchy, e.g. <code>base_folder/MainCompany/SubCompany/Department/…</code>. | |||
Beyond company structure, '''the “Driver file destination“ setting determines how folders are structured'''''Italic text'': | |||
'''* If you choose to store driver files in a separate driver folder (option “Driver folder”):''' | |||
'''** Two separate folders named “Drivers” and “Vehicles” are created.''' | |||
** In these folders, subfolders are created according to driver card and vehicle IMEI/number, respectively. | |||
** Files are placed accordingly. | |||
'''* If you choose to store driver files in the vehicle folder (option “Vehicle folder”):''' | |||
'''** Separate “Drivers” and “Vehicles” folders are NOT created.''' | |||
'''** Under the company hierarchy, only specific vehicle folders are created''' (named according to vehicle IMEI/number). | |||
** Both driver and vehicle files are placed under these specific vehicle folders. To correctly place driver files under a vehicle folder, the system must determine which vehicle the driver is operating: | |||
*** The system checks vehicle information included in the driver file. | |||
*** If vehicle information is not available in the driver file, the system places that driver file under the last known vehicle folder. | |||
*** If this last known vehicle cannot be determined, the file is not uploaded (upload status set to “Failed”). | |||
====Folder Structure Examples==== | |||
Assuming “Vehicles folder naming” = “Vehicle number” and .DDD file format. | |||
# Driver file destination = Driver folder | |||
* /base_folder | |||
** /MainCompany | |||
*** /SubCompany | |||
**** /Department | |||
***** /Vehicles | |||
****** /ABC123 ''← vehicle folder | |||
******* M_YYYYMMDD_HHmm_ABC123_VIN.DDD ← vehicle file | |||
******* … | |||
***** /Drivers | |||
****** /1234567890/ ''← driver folder | |||
******* C_YYYYMMDD_HHmm_N_SURNAME_1234567890.DD← driver file | |||
******* … | |||
# Driver file destination = Vehicle folder | |||
* /base_folder | |||
** /MainCompany | |||
*** /SubCompany | |||
**** /Department | |||
***** /Vehicles | |||
****** /ABC123 ''← vehicle folder | |||
******* M_YYYYMMDD_HHmm_ABC123_VIN.DDD ← vehicle file | |||
******* C_YYYYMMDD_HHmm_N_SURNAME_1234567890.DD← driver file | |||
******* … | |||
===File Upload Behavior=== | ===File Upload Behavior=== | ||
TachoSync uploads files to your SFTP server as soon as they become available in TachoSync (after being downloaded from device): | TachoSync uploads files to your SFTP server as soon as they become available in TachoSync (after being downloaded from device): | ||
Revision as of 10:51, 6 February 2026
Main Page > Software & Applications > TachoSync > TachoSync IntegrationsTachoSync provides integration mechanisms for automated data transfer to external systems. These integrations support both file-based delivery (e.g., SFTP) and request-response (e.g., API), enabling flexible and secure connectivity with fleet management platforms, IT systems, and other third-party services.
This page gives information about the available TachoSync integrations:
Additional integration methods are in development.
Integrations Menu
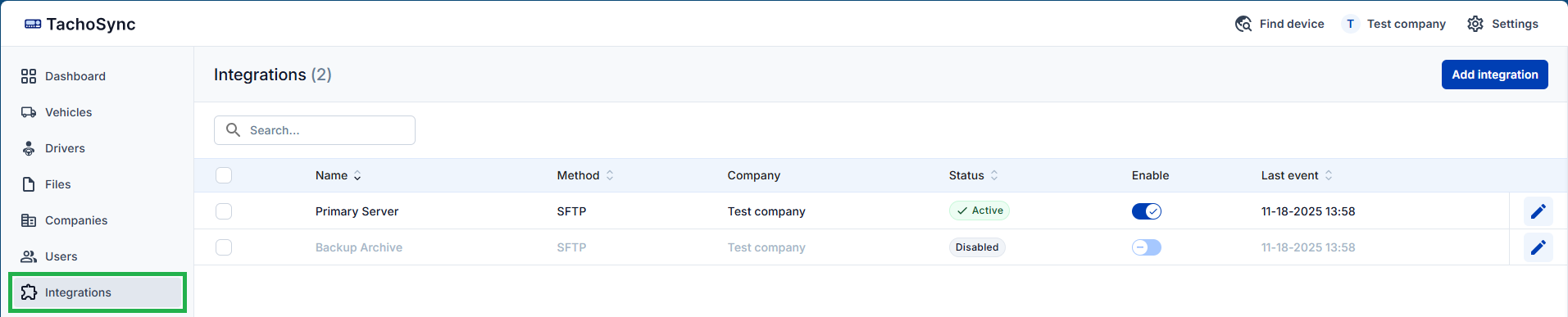
In the TachoSync UI, the Integrations menu shows the configured integrations.
To add an integration, click “Add integration” in the top right corner of the window, enter the required details, and click “Save”.
The table presents the following data:
- Name – name (label) given to the integration.
- Method – integration method.
- Company - company within TachoSync associated with this integration.
- Status - displays the status of the integration. See below for explanations.
- Enable – toggles the integration on/off.
- Last event – last time a file was successfully synced.
- Edit button - allows editing the integration.
- Retry button - allows to manually retry the connection. Button is available for Failed and Interrupted statuses. Upon pressing, a connection test is executed:
- If the test fails, error details are returned.
- If the connection is successful, integration becomes “Active” and failed operations are retried.
SFTP
NOTE! TachoSync supports only SFTP (SSH File Transfer Protocol)! Reusing old WEB TACHO FTP settings (such as FTP credentials and ports, e.g. port 21) will not work. FTP and SFTP are not compatible.
SFTP (Secure/SSH File Transfer Protocol) is a network protocol that provides secure file access, transfer, and management over a reliable data stream. SFTP is a replacement of File Transfer Protocol (FTP) due to superior security.
SFTP integration allows receiving files from TachoSync directly to your SFTP server. This option is ideal for organizations that want to automate the intake of data from TachoSync into an existing backend system.
Main features:
- You can create as many SFTP connections as needed.
- File transfer to your SFTP server starts as soon as the file is received from device to TachoSync.
- The option to download historical files that were created before the integration was enabled.
NOTE! TachoSync does not create or configure the SFTP server. The customer is responsible for ensuring that the server is reachable from the internet and properly secured.
Prerequisites
Prepare this before configuring the SFTP integration:
- Set up your SFTP server and know:
- SFTP server host (domain or IP address).
- SFTP server port number.
- Username and password for SFTP authentication.
- Make sure that your SFTP server firewall rules allow inbound SFTP connections from TachoSync (IP address 3.126.35.133).
- Optional: a dedicated folder path to place the downloaded files.
SFTP Integration Status Descriptions
- Active – integration is enabled and operates normally:
- No failed file transfers.
- New (and historical, if enabled) files are queued and uploaded.
• Disabled - integration is disabled by the user:
- No files are queued or uploaded.
- No retries can occur.
• Interrupted – integration works only partially:
- At least one file transferred successfully AND at least one file failed.
- New files are processed.
- Failed files remain as "Failed" until a successful retry.
- The user can try to fix the connection and manually retry the connection.
• Failed – integration has failed:
- One or more file transfers have failed AND no file transfer has been successful:
- New files are processed.
- Alternatively, the integration has failed the connection test.
- Integration is skipped when files are queued, no uploads are attempted.
- The user can try to fix the connection and manually retry the connection.
- One or more file transfers have failed AND no file transfer has been successful:
SFTP Server Settings

This section allows configuring the connection to your SFTP server. Settings marked by an asterisk (*) are mandatory.
- Host*: The hostname or IP address of the SFTP server.
- Port*: The port number on the SFTP server (typically 22).
- Remote directory path (optional): The specific folder on the SFTP server where files will be uploaded. If left blank, files will be placed in the root directory of the configured server user.
- Username*: The username for authenticating with the SFTP server.
- Password*: The password for the specified username.
General Settings
This section defines how the files and folders are structured and named when sent to the SFTP server. Settings marked by an asterisk (*) are mandatory.
- Company*: The company within TachoSync, associated with this integration.
- SFTP name*: A label for this specific SFTP configuration (e.g., "Primary Server" or "Backup Archive").
- File format*: The desired format for tachograph files.
- .DDD
- .TGD
- .V1B, .C1B
- Vehicles folder naming*: The naming convention for the folders that contain vehicle data.
- IMEI (E.g., 123456789012345)
- Vehicle number (E.g., ABC123)
- Drivers folder naming*: This field is set to "Driver ID", meaning folders for driver data will be named using the driver's unique identification number.
- Include files from all sub-companies: When enabled, in addition to the main company data, data from sub-companies will be gathered and uploaded as well.
- Include historical files: When enabled, TachoSync will attempt to upload files captured before the integration was created.
File Naming & Server Folder Structure
File naming and folder structure is configured in General Settings.
The file name that appears in your SFTP server is identical to the file name in TachoSync. Only the file extension may change (depends on the selected file format).
The general structure of folders is base-folder/MainCompany/SubCompany/Department/….
Below is an example of how files may be organized on your SFTP server:
- /base-folder
- /company
- /vehicles
- /ABC123 ← vehicle folder (set the naming convention in „General Settings“)
- 2025-01-12.DDD
- 2025-01-13.DDD
- /ABC123 ← vehicle folder (set the naming convention in „General Settings“)
- /drivers/
- /1234567890/ ← driver folder (set the naming convention in „General Settings“)
- 2025-01-12.DDD
- /1234567890/ ← driver folder (set the naming convention in „General Settings“)
- /vehicles
- /company
File Upload Behavior
TachoSync uploads files to your SFTP server as soon as they become available in TachoSync (after being downloaded from device):
- Files are sent to the SFTP server automatically and continuously, there is no fixed schedule.
- If you enable “Include historical files,” TachoSync also adds your previously downloaded files to the queue and syncs them in batches based on current system load. Older files are selected and queued – this uses the same upload and retry logic as regular uploads.
If file upload fails, TachoSync attempts to re-upload. The retry pattern is "exponential backoff" – 5 times in around 6 minutes. If all 5 retry attempts fail, the file is marked as "Failed".
To troubleshoot, see SFTP Integration Troubleshooting.
SFTP Integration Troubleshooting
If the SFTP integration does not work as expected, verify the following:
- The prerequisites are met.
- Your internet connection is stable (there are no repeating time-outs or interruptions).
- The user has write permissions for the configured directory.
- The provided path exists on the server.
If issues persist, collect the “Last event” details from the Integrations page and contact Support.
Integrations Menu

In the TachoSync UI, the Integrations menu shows the configured integrations.
To add an integration, click “Add integration” in the top right corner of the window, enter the required details, and click “Save”.
The table presents the following data:
- Name – name (label) given to the integration.
- Method – integration method.
- Company - company within TachoSync associated with this integration.
- Status - displays the status of the integration. See below for explanations.
- Enable – toggles the integration on/off.
- Last event – last time a file was successfully synced.
- Edit button - allows editing the integration.
- Retry button - allows to manually retry the connection. Button is available for Failed and Interrupted statuses. Upon pressing, a connection test is executed:
- If the test fails, error details are returned.
- If the connection is successful, integration becomes “Active” and failed operations are retried.
SFTP
NOTE! TachoSync supports only SFTP (SSH File Transfer Protocol)! Reusing old WEB TACHO FTP settings (such as FTP credentials and ports, e.g. port 21) will not work. FTP and SFTP are not compatible.
SFTP (Secure/SSH File Transfer Protocol) is a network protocol that provides secure file access, transfer, and management over a reliable data stream. SFTP is a replacement of File Transfer Protocol (FTP) due to superior security.
SFTP integration allows receiving files from TachoSync directly to your SFTP server. This option is ideal for organizations that want to automate the intake of data from TachoSync into an existing backend system.
Main features:
- You can create as many SFTP connections as needed.
- File transfer to your SFTP server starts as soon as the file is received from device to TachoSync.
- The option to download historical files that were created before the integration was enabled.
NOTE! TachoSync does not create or configure the SFTP server. The customer is responsible for ensuring that the server is reachable from the internet and properly secured.
Prerequisites
Prepare this before configuring the SFTP integration:
- Set up your SFTP server and know:
- SFTP server host (domain or IP address).
- SFTP server port number.
- Username and password for SFTP authentication.
- Make sure that your SFTP server firewall rules allow inbound SFTP connections from TachoSync (IP address 3.126.35.133).
- Optional: a dedicated folder path to place the downloaded files.
SFTP Integration Status Descriptions
- Active – integration is enabled and operates normally:
- No failed file transfers.
- New (and historical, if enabled) files are queued and uploaded.
- Disabled - integration is disabled by the user:
- No files are queued or uploaded.
- No retries can occur.
- Interrupted – integration works only partially:
- At least one file transferred successfully AND at least one file failed.
- New files are processed.
- Failed files remain as "Failed" until a successful retry.
- The user can try to fix the connection and manually retry the connection.
- Failed – integration has failed:
- One or more file transfers have failed AND no file transfer has been successful:
- New files are processed.
- Alternatively, the integration has failed the connection test.
- Integration is skipped when files are queued, no uploads are attempted.
- The user can try to fix the connection and manually retry the connection.
- One or more file transfers have failed AND no file transfer has been successful:
SFTP Server Settings

This section allows configuring the connection to your SFTP server. Settings marked by an asterisk (*) are mandatory.
- Host*: The hostname or IP address of the SFTP server.
- Port*: The port number on the SFTP server (typically 22).
- Remote directory path (optional): The specific folder on the SFTP server where files will be uploaded. If left blank, files will be placed in the root directory of the configured server user.
- Username*: The username for authenticating with the SFTP server.
- Password*: The password for the specified username.
General Settings
This section defines how the files and folders are structured and named when sent to the SFTP server. Settings marked by an asterisk (*) are mandatory.
- Company*: The company within TachoSync, associated with this integration.
- SFTP name*: A label for this specific SFTP configuration (e.g., "Primary Server" or "Backup Archive").
- File format*: The desired format for tachograph files.
- .DDD
- .TGD
- .V1B, .C1B
- Vehicles folder naming*: The naming convention for the folders that contain vehicle data.
- IMEI (E.g., 123456789012345)
- Vehicle number (E.g., ABC123)
- Drivers folder naming*: This field is set to "Driver ID", meaning folders for driver data will be named using the driver's unique identification number.
- Include files from all sub-companies: When enabled, in addition to the main company data, data from sub-companies will be gathered and uploaded as well.
- Include historical files: When enabled, TachoSync will attempt to upload files captured before the integration was created.
File Naming & Server Folder Structure
File naming and folder structure is configured in General Settings.
To ensure valid paths on the SFTP server, TachoSync automatically cleans up folder and file names:
- Removes leading and trailing spaces.
- Replaces empty spaces with "_".
- Removes characters:
\ / : * ? " < > | { }.
Folder Naming Options
- The vehicle folders can be named based on vehicle IMEI or vehicle registration number.
- The driver folders are named based on the driver card number.
File Naming Schema
- Vehicle files
M_YYYYMMDD_HHmm_VEHICLEREGNUMBER_VIN.DDD- M – vehicle (mass memory) data
- YYYYMMDD – download date (UTC)
- HHmm – download time (UTC)
- VEHICLEREGNUMBER – vehicle registration number
- VIN – vehicle identification number
- Driver files
C_YYYYMMDD_HHmm_N_SURNAME_CARDNUMBER.DDD
- C – driver card data
- YYYYMMDD – download date (UTC)
- HHmm – download time (UTC)
- N – first letter of driver’s first name
- SURNAME – driver’s surname
- CARDNUMBER – driver card number
Folder Logic
Each SFTP integration has a base folder, configured in the field "Remote directory path". Inside this base folder, the system always creates folders that reflect your company hierarchy, e.g. base_folder/MainCompany/SubCompany/Department/….
Beyond company structure, the “Driver file destination“ setting determines how folders are structuredItalic text: * If you choose to store driver files in a separate driver folder (option “Driver folder”): ** Two separate folders named “Drivers” and “Vehicles” are created.
- In these folders, subfolders are created according to driver card and vehicle IMEI/number, respectively.
- Files are placed accordingly.
* If you choose to store driver files in the vehicle folder (option “Vehicle folder”): ** Separate “Drivers” and “Vehicles” folders are NOT created. ** Under the company hierarchy, only specific vehicle folders are created (named according to vehicle IMEI/number).
- Both driver and vehicle files are placed under these specific vehicle folders. To correctly place driver files under a vehicle folder, the system must determine which vehicle the driver is operating:
- The system checks vehicle information included in the driver file.
- If vehicle information is not available in the driver file, the system places that driver file under the last known vehicle folder.
- If this last known vehicle cannot be determined, the file is not uploaded (upload status set to “Failed”).
- Both driver and vehicle files are placed under these specific vehicle folders. To correctly place driver files under a vehicle folder, the system must determine which vehicle the driver is operating:
Folder Structure Examples
Assuming “Vehicles folder naming” = “Vehicle number” and .DDD file format.
- Driver file destination = Driver folder
- /base_folder
- /MainCompany
- /SubCompany
- /Department
- /Vehicles
- /ABC123 ← vehicle folder
- M_YYYYMMDD_HHmm_ABC123_VIN.DDD ← vehicle file
- …
- /ABC123 ← vehicle folder
- /Drivers
- /1234567890/ ← driver folder
- C_YYYYMMDD_HHmm_N_SURNAME_1234567890.DD← driver file
- …
- /1234567890/ ← driver folder
- /Vehicles
- /Department
- /SubCompany
- /MainCompany
- Driver file destination = Vehicle folder
- /base_folder
- /MainCompany
- /SubCompany
- /Department
- /Vehicles
- /ABC123 ← vehicle folder
- M_YYYYMMDD_HHmm_ABC123_VIN.DDD ← vehicle file
- C_YYYYMMDD_HHmm_N_SURNAME_1234567890.DD← driver file
- …
- /ABC123 ← vehicle folder
- /Vehicles
- /Department
- /SubCompany
- /MainCompany
File Upload Behavior
TachoSync uploads files to your SFTP server as soon as they become available in TachoSync (after being downloaded from device):
- Files are sent to the SFTP server automatically and continuously, there is no fixed schedule.
- If you enable “Include historical files,” TachoSync also adds your previously downloaded files to the queue and syncs them in batches based on current system load. Older files are selected and queued – this uses the same upload and retry logic as regular uploads.
If file upload fails, TachoSync attempts to re-upload. The retry pattern is "exponential backoff" – 5 times in around 6 minutes. If all 5 retry attempts fail, the file is marked as "Failed".
To troubleshoot, see SFTP Integration Troubleshooting.
SFTP Integration Troubleshooting
If the SFTP integration does not work as expected, verify the following:
- The prerequisites are met.
- Your internet connection is stable (there are no repeating time-outs or interruptions).
- The user has write permissions for the configured directory.
- The provided path exists on the server.
If issues persist, collect the “Last event” details from the Integrations page and contact Support.
