FMB640 System settings: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
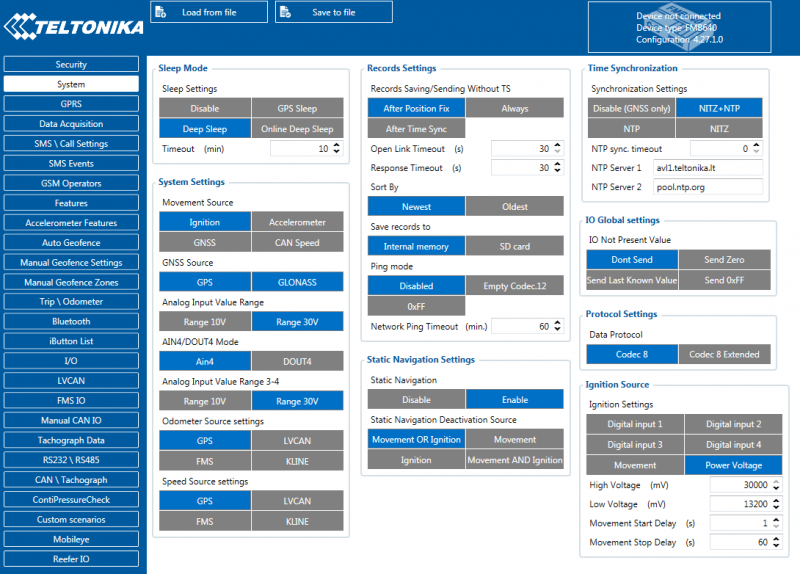
System settings have following configurable parameters: | System settings have following configurable parameters: | ||
* | System settings have 14 configurable parameters: | ||
* | *Sleep settings, where user can choose sleep mode; | ||
*GNSS Source, where user can pick any or all satellite systems to use. More selections might improve tracking quality | |||
*Analog Input value range, where user can choose analog input range 10 V or 30 V (10 V range for now works same as 30 V range). | |||
*AIN4/DOUT4 Mode, user can select on of 2 options to define which way 18th pin (from Figure 5) will work. | |||
*J1708 settings used to enable/disable following vehicle bus standard used for communication. | |||
*Odometer Source settings, where user can select one of the options for odometer counting. There are 5 possible options: GNSS, LVCAN, ALLCAN, FMS and KLINE. | |||
*Speed source settings are used to declare what technology will be used for vehicle speed measurement | |||
*Records Settings, where user can enable or disable records when GPS is not available (no time synchronization). There are additional parameters for records saving: memory selection and sorting option to define where records will be saved and in what order they will be sent. | |||
*Open Link Timeout is used to set timeout of link between FMB640 and AVL application termination. If FMB640 has already sent all records it waits for new records before closing link (except Deep Sleep mode, more information in Deep Sleep mode chapter). If new records are generated in the period of this timeout, and minimum count of timer to send is reached, they are sent to AVL application. This option is useful when GSM operator charge money for link activation. | |||
*Server Response Timeout is used to set time period waiting for response from server side. | |||
*Ping mode, where user can enable and select how frequent device will send packets to inform server about active data link. It works when device did not send any records to server in defined time period. | |||
•Static navigation settings, where user can turn static navigation on or off. Additional, user can chose from what source (movement or ignition) static navigation can be deactivated/activated; | |||
Static Navigation Mode is a filter, which filters out track jumps when the object is stationary. If Static navigation filter is disabled, it will apply no changes on GPS data. If Static navigation filter is enabled, it will filter changes in GPS position if no movement (configured movement source) or ignition (configured ignition source) is detected (depends on what static navigation settings is selected: movement, ignition or both sources). It allows filtering GPS jumps when object is parked (is not moving) and GPS position is still traced. | |||
*Ignition source, where user can choose between power voltage, digital input 1, digital input 2, digital input 3, digital input 4 and accelerometer as ignition sources. More than one ignition source can be selected at the same moment. User can select movement start and movement stop delay time (in seconds): those parameters are used when ignition source is accelerometer. | |||
*Time synchronization settings, where user can choose from what source (or sources) FMB640 time will be synchronized. User has choice to use only one synchronization source by GNSS. When selected synchronization from NTP, time will be synchronized from NTP server and from GNSS. When selected synchronization from NITZ, time will be synchronized from GSM operator and GNSS. When selected synchronization from NITZ+NTP, time will be synchronized from all three sources (if it is necessary). Every time GNSS fix will be acquired time will be synchronized (if needed). User can select from what NTP server (possible to configure two servers) time will be synchronized, as well as delay after which time synchronization from non-GNSS source will begin. | |||
* Object motion detection settings, where user can configure {{{txt_num|4}}} ways how {{{model|FMB640}}} detects movement and change its working mode (for more information refer to section [[FMB640 Data acquisition settings|Data acquisition settings]]). Other functionalities that depend on movement source are: power manager, fuel consumption and trip; | * Object motion detection settings, where user can configure {{{txt_num|4}}} ways how {{{model|FMB640}}} detects movement and change its working mode (for more information refer to section [[FMB640 Data acquisition settings|Data acquisition settings]]). Other functionalities that depend on movement source are: power manager, fuel consumption and trip; | ||
* ''Static Navigation Settings'', where user can turn static navigation on or off. Additionally, user can choose which source (movement or ignition) is used to activate/deactivate static navigation; | * ''Static Navigation Settings'', where user can turn static navigation on or off. Additionally, user can choose which source (movement or ignition) is used to activate/deactivate static navigation; | ||
Revision as of 08:35, 28 May 2018
Main Page > EOL Products > FMB640 > FMB640 Configuration > FMB640 System settingsSystem settings have following configurable parameters: System settings have 14 configurable parameters:
- Sleep settings, where user can choose sleep mode;
- GNSS Source, where user can pick any or all satellite systems to use. More selections might improve tracking quality
- Analog Input value range, where user can choose analog input range 10 V or 30 V (10 V range for now works same as 30 V range).
- AIN4/DOUT4 Mode, user can select on of 2 options to define which way 18th pin (from Figure 5) will work.
- J1708 settings used to enable/disable following vehicle bus standard used for communication.
- Odometer Source settings, where user can select one of the options for odometer counting. There are 5 possible options: GNSS, LVCAN, ALLCAN, FMS and KLINE.
- Speed source settings are used to declare what technology will be used for vehicle speed measurement
- Records Settings, where user can enable or disable records when GPS is not available (no time synchronization). There are additional parameters for records saving: memory selection and sorting option to define where records will be saved and in what order they will be sent.
- Open Link Timeout is used to set timeout of link between FMB640 and AVL application termination. If FMB640 has already sent all records it waits for new records before closing link (except Deep Sleep mode, more information in Deep Sleep mode chapter). If new records are generated in the period of this timeout, and minimum count of timer to send is reached, they are sent to AVL application. This option is useful when GSM operator charge money for link activation.
- Server Response Timeout is used to set time period waiting for response from server side.
- Ping mode, where user can enable and select how frequent device will send packets to inform server about active data link. It works when device did not send any records to server in defined time period.
•Static navigation settings, where user can turn static navigation on or off. Additional, user can chose from what source (movement or ignition) static navigation can be deactivated/activated; Static Navigation Mode is a filter, which filters out track jumps when the object is stationary. If Static navigation filter is disabled, it will apply no changes on GPS data. If Static navigation filter is enabled, it will filter changes in GPS position if no movement (configured movement source) or ignition (configured ignition source) is detected (depends on what static navigation settings is selected: movement, ignition or both sources). It allows filtering GPS jumps when object is parked (is not moving) and GPS position is still traced.
- Ignition source, where user can choose between power voltage, digital input 1, digital input 2, digital input 3, digital input 4 and accelerometer as ignition sources. More than one ignition source can be selected at the same moment. User can select movement start and movement stop delay time (in seconds): those parameters are used when ignition source is accelerometer.
- Time synchronization settings, where user can choose from what source (or sources) FMB640 time will be synchronized. User has choice to use only one synchronization source by GNSS. When selected synchronization from NTP, time will be synchronized from NTP server and from GNSS. When selected synchronization from NITZ, time will be synchronized from GSM operator and GNSS. When selected synchronization from NITZ+NTP, time will be synchronized from all three sources (if it is necessary). Every time GNSS fix will be acquired time will be synchronized (if needed). User can select from what NTP server (possible to configure two servers) time will be synchronized, as well as delay after which time synchronization from non-GNSS source will begin.
- Object motion detection settings, where user can configure 4 ways how FMB640 detects movement and change its working mode (for more information refer to section Data acquisition settings). Other functionalities that depend on movement source are: power manager, fuel consumption and trip;
- Static Navigation Settings, where user can turn static navigation on or off. Additionally, user can choose which source (movement or ignition) is used to activate/deactivate static navigation;
- Records settings (no time synchronization), where user can enable or disable records when GPS is not available;
- GNSS Source settings, where user can choose the necessary satellite system(s);
- LED Indication, where user can turn on or off the indication LEDs;
- Analog Input Value Range, where user can choose analog input range of 10 V or 30 V;}}}
- Time Synchronization settings, where user can choose which source(s) to use for FMB640 time synchronization. User has a choice to: use only one synchronization source (Disable (GPS only)), allow synchronization from both the GNSS and NTP server (NTP), select synchronization through GNSS and GSM operator (NITZ) or from all three sources (when NITZ+NTP is selected). User can select which NTP server (it is possible to configure up to two servers) and what time period to use to resynchronize time.
| Movement source | Vehicle on Stop mode | Vehicle Moving mode |
|---|---|---|
| Ignition (recommended) | If ignition (ignition source) is logic low. | If ignition (ignition source) is logic high. |
| Movement (movement sensor) | Internal movement sensor does not detect movement. | Internal movement sensor detects movement. |
| GPS | GPS fix is available and vehicle speed is lower than 5 km/h. | GPS fix is available and vehicle speed is higher than 5 km/h. |
| While GPS fix is unavailable, Object Motion Detection Settings are working like in Msensor mode. | ||
| CAN speed | If speed from BT OBDII dongle is equal to 0 km/h. | If speed from BT OBDII dongle from BT OBDII dongle is higher than 0 km/h. |
Static Navigation mode is a filter, which filters out track jumps when the object is stationary. If static navigation filter is disabled, it will apply no changes to GPS data. If static navigation filter is enabled, it will filter changes in GPS position if no movement (as defined by configured movement source) or ignition (as defined by configured ignition source) is detected. It allows filtering GPS jumps when the object is parked (not moving) and GPS position is still traced.
In GNSS Source settings user can configure which GNSS system(s) to use.
User has a choice to use only one system between GPS, GLONASS, Galileo or Beidou and it is possible to choose two or three systems together. One exception is that you cannot combine BeiDou and GLONASS systems together. Examples of non-configurable GNSS source combinations are:
- GLONASS + BeiDou;
- Galileo + GLONASS + BeiDou;
- GPS + GLONASS + BeiDou;
- GPS + Galileo + GLONASS + BeiDou.
| Selected source(s) | ID |
|---|---|
| BeiDou only | 01 |
| GLONASS only | 02 |
| Galileo only | 04 |
| Galileo + Beidou | 05 |
| Galileo + Glonass | 06 |
| GPS only | 08 |
| GPS + BeiDou | 09 |
| GPS + GLONASS | 10 |
| GPS + Galileo | 12 |
| GPS + Galileo + BeiDou | 13 |
| GPS + Galileo + GLONASS | 14 |
