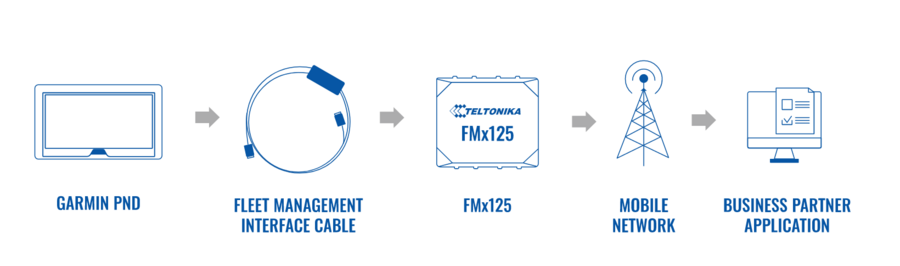
Difference between revisions of "Template:FMX125 RS-232 and RS-485"
(Created page with " ==RS-485 interface== RS-485 supports only half-duplex communication, which means data is transferred only one way at a time.<br />When activated RS-485 driver chip draws con...") |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
==RS-485 interface== | ==RS-485 interface== | ||
| − | RS-485 supports only half-duplex communication, which means data is transferred only one way at a time.<br />When activated RS-485 driver chip draws constant 30mA current | + | RS-485 supports only half-duplex communication, which means data is transferred only one way at a time.<br />When activated RS-485 driver chip draws constant 30mA current when entering Sleep or Deep sleep RS-485 will be powered off.<br />{{{model|}}} RS-485 connection diagram is shown below. |
===RS-485 modes=== | ===RS-485 modes=== | ||
| + | ------------------ | ||
| + | ====RS-485 transmit (FMB log) mode==== | ||
| + | ------------------ | ||
| + | RS-485 prints the FMB device log and does not respond to commands.<br /> | ||
| − | + | ====RS-485 transmit (GNSS NMEA) mode==== | |
| − | + | ------------------ | |
| − | RS-485 prints | + | RS-485 prints GNSS NMEA log and does not respond to commands.<br /> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Image:RS485 MODES.gif]] | [[Image:RS485 MODES.gif]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | ====RS-485 receive (LLS) mode==== | |
| + | ------------------ | ||
| + | This mode supports up to five [[{{{model|FMB125}}}_RS-232_and_RS-485#LLS_Sensor|LLS fuel level sensors]] each of which has a receiver ID.<br/> | ||
| − | + | ====RS-485 TCP (ASCII/Binary) modes==== | |
| + | ------------------ | ||
| + | In TCP ASCII/Binary mode a link with an external device using text messages can be established. In TCP ASCII/Binary mode all data received from the external device through RS-485 is sent directly to the server (if the link is currently active). Data is encapsulated in codec 12 format. | ||
| − | + | =====RS-485 TCP Binary settings===== | |
| − | + | ------------------ | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | ====RS-485 TCP Binary settings==== | ||
| − | |||
[[File:RS-485 TCP BINARY.gif]] | [[File:RS-485 TCP BINARY.gif]] | ||
| − | TCP Binary has a setting Prefix. It is possible to set Prefix 1, Prefix 2 or Prefix 3. These prefixes can be used | + | TCP Binary has a setting Prefix. It is possible to set Prefix 1, Prefix 2, or Prefix 3. These prefixes can be used separately or in unison. |
| − | To configure this setting a value from 0 to 255 in decimal has to be entered. | + | To configure this setting a value from 0 to 255 in decimal has to be entered. The device will convert this value to HEX and compare the 1st, 2nd, or 3rd byte from incoming data. If the values do not match, the device will not accept incoming data. |
Example:<br> | Example:<br> | ||
| Line 41: | Line 39: | ||
<ul><li>FMB device will then check the 3rd byte of incoming data and compare to the set Prefix 3.</li></ul></li> | <ul><li>FMB device will then check the 3rd byte of incoming data and compare to the set Prefix 3.</li></ul></li> | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
| − | When values match, data will be accepted and saved to Buffer (using TCP Binary Buffered mode) or sent to server (using TCP Binary mode).<br> | + | When values match, data will be accepted and saved to Buffer (using TCP Binary Buffered mode) or sent to the server (using TCP Binary mode).<br> |
Incoming packet through RS232/RS485 using TCP Binary/TCP Binary Buffered mode - <font color="red">50</font> <font color="green">0</font> <font color="blue">65</font> 66 69 78 20 57 6f 72 6b 69 6e 67 | Incoming packet through RS232/RS485 using TCP Binary/TCP Binary Buffered mode - <font color="red">50</font> <font color="green">0</font> <font color="blue">65</font> 66 69 78 20 57 6f 72 6b 69 6e 67 | ||
| Line 50: | Line 48: | ||
<ul><li>FMB device will then check the 2nd byte <font color="green">0</font> of incoming data and compare to the set Prefix 2.</li></ul></li> | <ul><li>FMB device will then check the 2nd byte <font color="green">0</font> of incoming data and compare to the set Prefix 2.</li></ul></li> | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
| − | Since Prefix 2 does not match incoming 2nd byte, data will not be accepted. | + | Since Prefix 2 does not match the incoming 2nd byte, data will not be accepted. |
| − | ====RS-485 CMD ID ==== | + | =====RS-485 CMD ID ===== |
| + | ------------------ | ||
This parameter is used when {{{model|}}} is sending RS232/RS485 packet to a server, it overrides command type value in Codec12/Codec13 with user defined CMD ID value (1 - 14). {{{model|}}} behavior when it receives different CMD ID (Type) values in GPRS packet from server: | This parameter is used when {{{model|}}} is sending RS232/RS485 packet to a server, it overrides command type value in Codec12/Codec13 with user defined CMD ID value (1 - 14). {{{model|}}} behavior when it receives different CMD ID (Type) values in GPRS packet from server: | ||
| Line 78: | Line 77: | ||
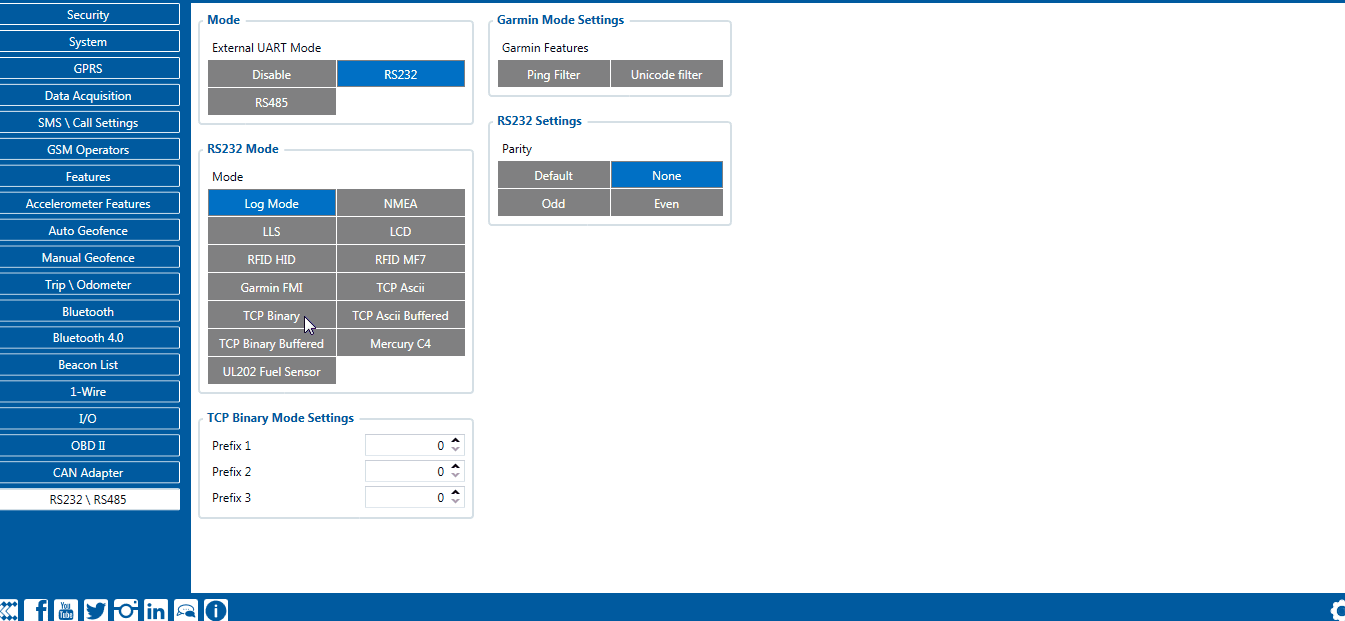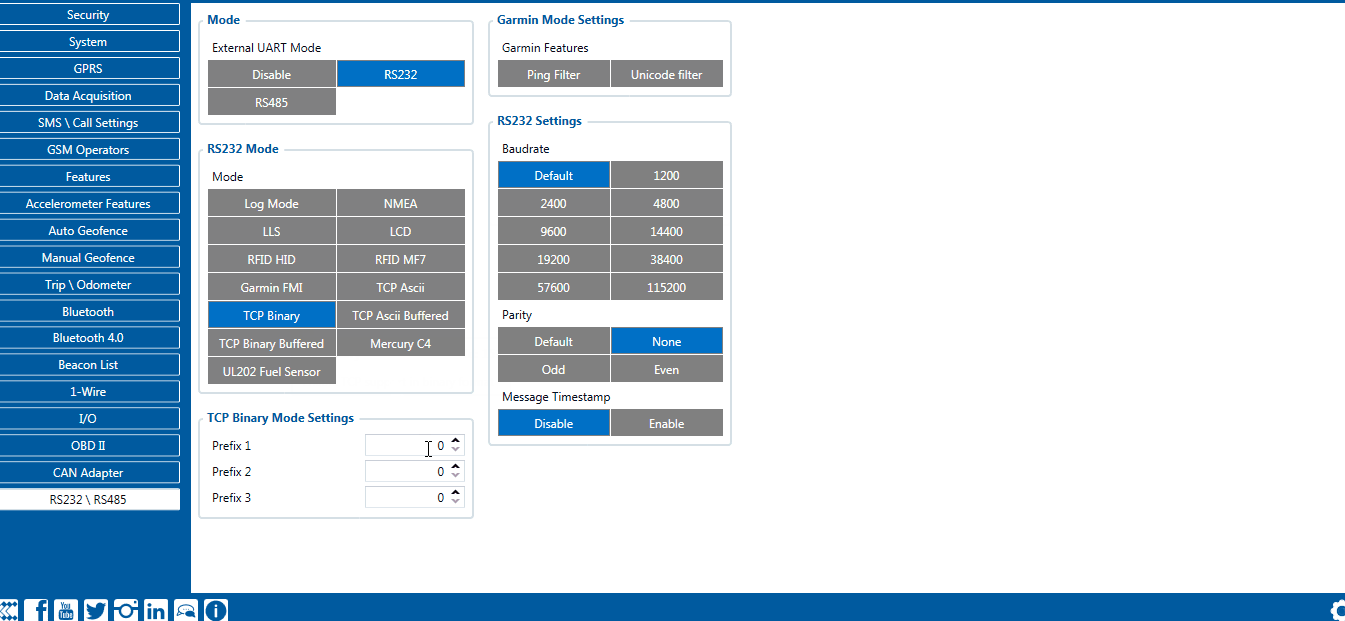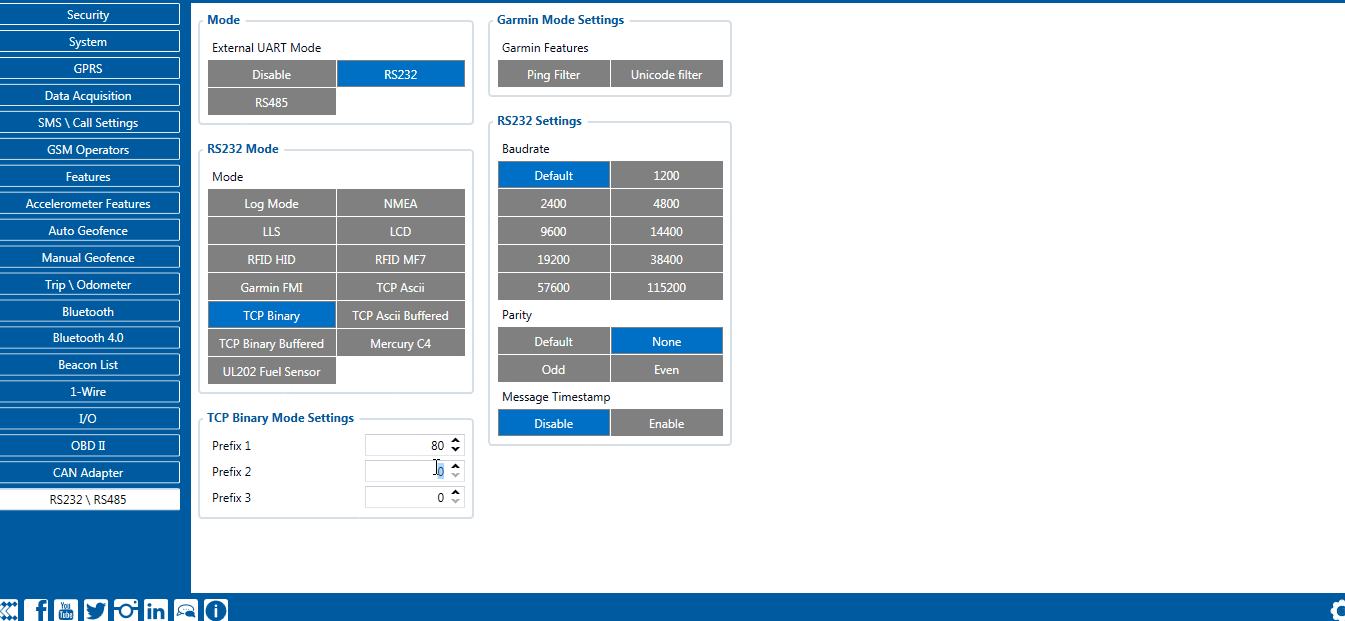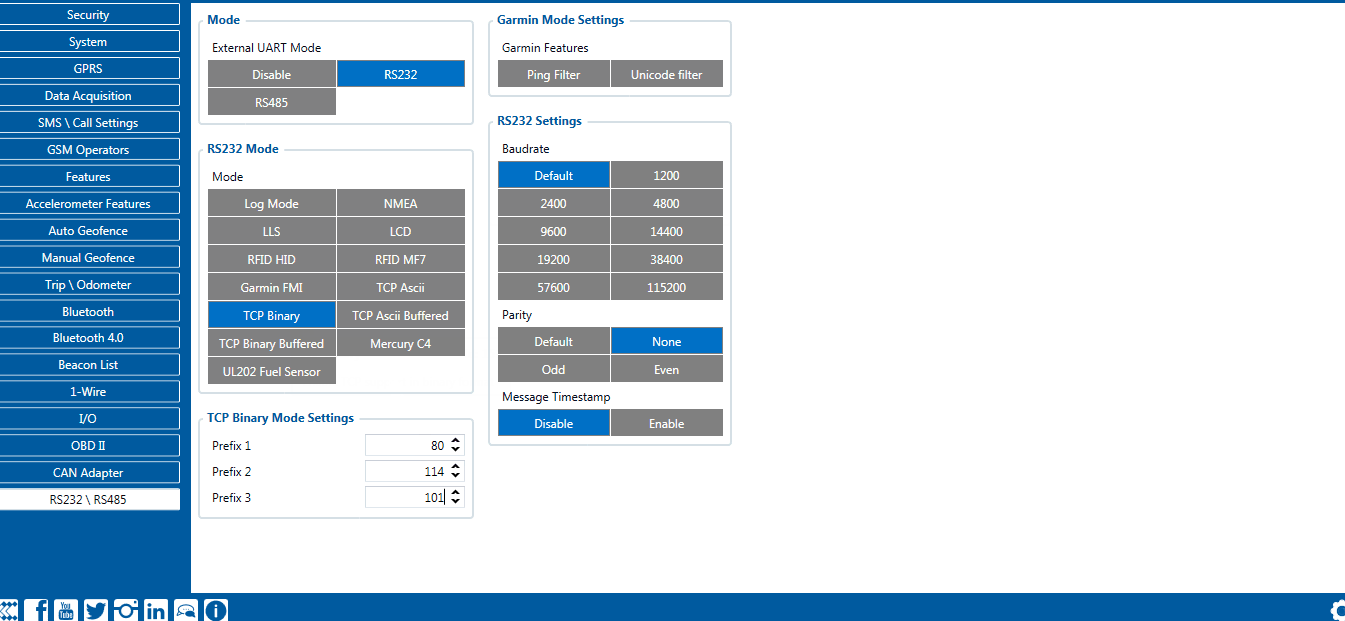
==RS-232 Interface== | ==RS-232 Interface== | ||
| − | RS-232 supports full-duplex communication which means the data can be both sent and received at the same time as they use separate transmission lines. Most of the modes are the same as for [[{{{model|}}}_RS-232_and_RS-485#RS-485_modes|RS-485]]. | + | RS-232 supports full-duplex communication which means the data can be both sent and received at the same time as they use separate transmission lines. Most of the modes are the same as for [[{{{model|FMB125}}}_RS-232_and_RS-485#RS-485_modes|RS-485]]. When entering Sleep or Deep sleep RS-232 will be powered off. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ===RS-232 modes=== | |
| + | ------------------ | ||
| + | Log mode, NMEA, LLS, TCP ASCII, and TCP Binary modes are identical to those of [[{{{model|FMB125}}}_RS-232_and_RS-485#RS-485_modes|RS-485]]. In RS-232 LLS mode only one LLS fuel level sensor can be connected. Additionally TCP ASCII Buffered and TCP Binary Buffered modes are available. | ||
| + | ====RS-232 LCD mode==== | ||
| + | ------------------ | ||
In this mode, the user is able to communicate with the server through the terminal. A link between the FMB device and the server has to be established for this mode to function properly. | In this mode, the user is able to communicate with the server through the terminal. A link between the FMB device and the server has to be established for this mode to function properly. | ||
To communicate from terminal to server - in terminal send command "WT^W your text here" | To communicate from terminal to server - in terminal send command "WT^W your text here" | ||
| − | To communicate with server to terminal - send "#DO DAT=you text here" packet in [https://wiki.teltonika-gps.com/view/Teltonika_Data_Sending_Protocols#Codec_12 Codec12 protocol] | + | To communicate with the server to the terminal - send "#DO DAT=you text here" packet in [https://wiki.teltonika-gps.com/view/Teltonika_Data_Sending_Protocols#Codec_12 Codec12 protocol] |
| − | |||
| − | + | ====RS-232 RFID HID/RFID MF7 mode==== | |
| − | + | ------------------ | |
| − | The difference between RFID HID Mode and RFID MF7 Mode is that in RFID MF7 Mode {{{model|}}} understands RFID messages that are in hexadecimal text format and RFID HID Mode | + | The difference between RFID HID Mode and RFID MF7 Mode is that in RFID MF7 Mode {{{model|}}} understands RFID messages that are in hexadecimal text format and RFID HID Mode interprets messages that are in binary format. The type of RFID message sent to {{{model|}}} depends on the RFID reader. For example, the RFID MF7 mode message looks like "$aa$02$03$04$17$89$00$01" while HID mode message is of the following format: "1213141519". |
The selected mode has to correspond to the RFID reader's mode. | The selected mode has to correspond to the RFID reader's mode. | ||
| Line 102: | Line 99: | ||
Please contact your local sales representative for more information about RFID IDs and devices. | Please contact your local sales representative for more information about RFID IDs and devices. | ||
| − | <br /> | + | ====RS-232 Garmin mode==== |
| + | ------------------ | ||
| + | Garmin provides a Fleet Management Interface Tool Kit, once {{{model|}}} is connected to the navigator it enables the driver to have a "screen" in their vehicle for real-time navigation and messaging and offers job dispatch capabilities to help them be more efficient.<br />{{{model|}}} and Garmin operational diagram is shown on the figure below. | ||
| + | [[Image:FMX125_GARMIN_BLOCK.png|900px|none]] | ||
| − | + | ====RS-232 TCP Binary/TCP ASCII mode==== | |
| + | ------------------ | ||
| + | In TCP ASCII/Binary mode all data received from the external device is sent directly to the server. Data is encapsulated in codec 12 format. TCP Binary Mode has a delay of 30 ms, if no data is received for 30 ms, data is sent to the server. TCP ASCII mode waits for the End of Line (EOL) character (0x0D0A, \r\n) to pack data and send it to the server | ||
| − | + | ====RS-232 TCP Binary Buffered/TCP ASCII Buffered mode==== | |
| − | + | ------------------ | |
| − | + | TCP ASCII Buffered and TCP Binary Buffered modes are used to collect data from RS232 and save it in the buffer if there is no link with the server and data cannot be sent immediately. When the link is established and there is data to transmit, then RS232 data from the buffer is transmitted after all records are sent. Data is sent in codec 13 protocol. | |
| − | + | Note. That in TCP ASCII and TCP Binary modes device sends data from the external device only to the main server. In Buffered modes – to both main and backup/duplicate servers. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | TCP ASCII Buffered and TCP Binary Buffered modes are used to collect data from RS232 and save it in buffer if there is no link with server and data cannot be sent immediately. When link is established and there is data to transmit, then RS232 data from buffer is transmitted after all records are sent. Data is sent in codec 13 protocol. | ||
| − | Note. That in TCP ASCII and TCP Binary modes device sends data from external device only to main server. In Buffered modes – to both main and backup/duplicate servers. | ||
Message timestamp: | Message timestamp: | ||
| − | + | The message Timestamp parameter is used to determine if it is necessary to include a timestamp in the RS232 TCP packet when sending to the server. If the parameter is enabled, then Codec 13 is used for data sending. Otherwise, Codec 12 is used. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | ====RS-232 TCP Binary settings==== | + | =====RS-232 TCP Binary settings===== |
| + | ------------------ | ||
[[Image:RS-232 TCP BINARY SETTINGS.gif]] | [[Image:RS-232 TCP BINARY SETTINGS.gif]] | ||
| − | TCP Binary has a setting Prefix. It is possible to set Prefix 1, Prefix 2 or Prefix 3. These prefixes can be used | + | TCP Binary has a setting Prefix. It is possible to set Prefix 1, Prefix 2, or Prefix 3. These prefixes can be used separately or in unison. |
| − | To configure this setting a value from 0 to 255 in decimal has to be entered. | + | To configure this setting a value from 0 to 255 in decimal has to be entered. The device will convert this value to HEX and compare the 1st, 2nd, or 3rd byte from incoming data. If the values do not match, the device will not accept incoming data. |
Example:<br> | Example:<br> | ||
| Line 138: | Line 132: | ||
<ul><li>FMB device will then check the 3rd byte of incoming data and compare to the set Prefix 3.</li></ul></li> | <ul><li>FMB device will then check the 3rd byte of incoming data and compare to the set Prefix 3.</li></ul></li> | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
| − | When values match, data will be accepted and saved to Buffer (using TCP Binary Buffered mode) or sent to server (using TCP Binary mode).<br> | + | When values match, data will be accepted and saved to Buffer (using TCP Binary Buffered mode) or sent to the server (using TCP Binary mode).<br> |
Incoming packet through RS232/RS485 using TCP Binary/TCP Binary Buffered mode - <font color="red">50</font> <font color="green">0</font> <font color="blue">65</font> 66 69 78 20 57 6f 72 6b 69 6e 67 | Incoming packet through RS232/RS485 using TCP Binary/TCP Binary Buffered mode - <font color="red">50</font> <font color="green">0</font> <font color="blue">65</font> 66 69 78 20 57 6f 72 6b 69 6e 67 | ||
| Line 147: | Line 141: | ||
<ul><li>FMB device will then check the 2nd byte <font color="green">0</font> of incoming data and compare to the set Prefix 2.</li></ul></li> | <ul><li>FMB device will then check the 2nd byte <font color="green">0</font> of incoming data and compare to the set Prefix 2.</li></ul></li> | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
| − | Since Prefix 2 does not match incoming 2nd byte, data will not be accepted. | + | Since Prefix 2 does not match the incoming 2nd byte, data will not be accepted. |
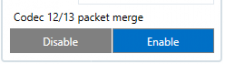
| − | ====Codec 12/13 Packet Merge==== | + | =====Codec 12/13 Packet Merge===== |
| + | ------------------ | ||
This additional option configures the device to merge RS-232 records into a single packet instead of sending many separate packets. This functionality only affects TCP Binary Buffered or TCP Ascii Buffered RS232 modes. When enabled, the device will merge saved RS-232 records together into a single data packet until it is able to send it to the server.<br /> | This additional option configures the device to merge RS-232 records into a single packet instead of sending many separate packets. This functionality only affects TCP Binary Buffered or TCP Ascii Buffered RS232 modes. When enabled, the device will merge saved RS-232 records together into a single data packet until it is able to send it to the server.<br /> | ||
This optimizes RS-232 data sending by not having to send each RS-232 record separately. | This optimizes RS-232 data sending by not having to send each RS-232 record separately. | ||
| Line 155: | Line 150: | ||
[[Image:packet_merge.png|225px|none]] | [[Image:packet_merge.png|225px|none]] | ||
| − | ====RS-232 CMD ID==== | + | =====RS-232 CMD ID===== |
| + | ------------------ | ||
This parameter is used when {{{model|}}} is sending RS232/RS485 packet to a server, it overrides command type value in Codec12/Codec13 with user defined CMD ID value (1 - 14). {{{model|}}} behavior when it receives different CMD ID (Type) values in GPRS packet from server: | This parameter is used when {{{model|}}} is sending RS232/RS485 packet to a server, it overrides command type value in Codec12/Codec13 with user defined CMD ID value (1 - 14). {{{model|}}} behavior when it receives different CMD ID (Type) values in GPRS packet from server: | ||
| Line 179: | Line 175: | ||
|} | |} | ||
[[File:RS-232-CMD1.gif|alt=]] | [[File:RS-232-CMD1.gif|alt=]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==LLS Sensor== | ||
| + | LLS sensor series liquid level sensors are solid-state capacitive devices with no moving parts. The sensors use capacitive technology to produce accurate liquid level measurements of standard factory-grade DIESEL OIL and PURE GASOLINE (BENZINE) carbon fuels. The LLS sensor liquid level sensors are strictly prohibited to use in any liquids which are not factory-grade carbon fuels or contain: BIOFUEL, METHANOL, ETHANOL, UREA, and similar aggressive components in pure form or as additives for factory-grade carbon fuels for use in INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES. Operating media – Diesel fuel (oil), pure gasoline (benzene). <br> | ||
| + | In order to use the LLS fuel counter, the newest firmware version is needed which can be obtained from Teltonika or a representative. Firmware is updated over GPRS or using a cable update method. <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Specifications=== | ||
| + | -------------------- | ||
| + | <table class="nd-othertables_2" style="width:40%;"> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <th rowspan="1" style="width:70%; vertical-align: middle; text-align: center;">Parameter</th> | ||
| + | <th rowspan="1" style="width:30%; vertical-align: middle; text-align: center;">Value</th> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <th style="border-bottom: 1px solid #E8E8E8; vertical-align: middle; text-align: left; color:black">Supply voltage</th> | ||
| + | <td style="vertical-align: middle; text-align: left; ">+10..+50 V</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <th style="border-bottom: 1px solid #E8E8E8; vertical-align: middle; text-align: left; color:black">Current consumption, mA (for 12/24 V)</th> | ||
| + | <td style="vertical-align: middle; text-align: left; ">25 mA / 50 mA</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <th style="border-bottom: 1px solid #E8E8E8; vertical-align: middle; text-align: left; color:black">Working temperature</th> | ||
| + | <td style="vertical-align: middle; text-align: left; ">-40..+85 ºC</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <th style="border-bottom: 1px solid #E8E8E8; vertical-align: middle; text-align: left; color:black">Working mode</th> | ||
| + | <td style="vertical-align: middle; text-align: left; ">Continuous</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <th style="border-bottom: 1px solid #E8E8E8; vertical-align: middle; text-align: left; color:black">Weight</th> | ||
| + | <td style="vertical-align: middle; text-align: left; ">< 2.0 kg</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <th style="border-bottom: 1px solid #E8E8E8; vertical-align: middle; text-align: left; color:black">Working pressure</th> | ||
| + | <td style="vertical-align: middle; text-align: left; ">Atmospheric</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | </table> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Wiring And Configuration=== | ||
| + | ------------------------------ | ||
| + | First of all, the LLS fuel sensor must be connected to the [[{{{model|FMB125}}}]] device. Please find examples below: | ||
| + | <table class="nd-othertables_2" style="width:100%;"> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td style="vertical-align: middle; text-align: left; ">'''Using RS232 socket'''</td> | ||
| + | <td style="vertical-align: middle; text-align: left; ">'''Using RS485 socket'''</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td style="vertical-align: middle; text-align: left; ">[[Image:FMX125_LLS_RS232-wiring scheme.png|580px]]</td> | ||
| + | <td style="vertical-align: middle; text-align: left; ">[[Image:FMX125_LLS_RS485-wiring scheme.png|580px]]</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | </table> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Then [[{{{model|FMB125}}}]] must be configured. Both fuel level and fuel temperature has to be set up by the configurator’s I/O menu: <br> | ||
| + | [[image:FMB640_RS232_LLSmenu.png]] | ||
| + | |||
==Garmin protocols== | ==Garmin protocols== | ||
| − | The following is a list of protocols supported and the corresponding list of features/benefits. {{{model|}}} can fully support Fleet Management Interface (FMI) versions up to 2.1. Other or higher versions may be supported, but Teltonika is not responsible for the changes made by Garmin, which may affect the function of {{{model|}}} and Garmin products. For more information about Garmin products and FMI versions, please refer to https://www.garmin.com/en-US/fleet-ready-navigators/. Notice that some Garmin products use different connection cables than others. | + | The following is a list of protocols supported and the corresponding list of features/benefits. {{{model|FMB125}}} can fully support Fleet Management Interface (FMI) versions up to 2.1. Other or higher versions may be supported, but Teltonika is not responsible for the changes made by Garmin, which may affect the function of {{{model|FMB125}}} and Garmin products. For more information about Garmin products and FMI versions, please refer to https://www.garmin.com/en-US/fleet-ready-navigators/. Notice that some Garmin products use different connection cables than others. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | ====Standard protocols==== | ||
| + | ------------------ | ||
Text Message Protocol: | Text Message Protocol: | ||
| Line 191: | Line 243: | ||
*Garmin can also provide a yes/no box below the text of the message to enable a quicker response; | *Garmin can also provide a yes/no box below the text of the message to enable a quicker response; | ||
*Messages can be up to 199 characters long; | *Messages can be up to 199 characters long; | ||
| − | *Messages can also be generated from device and sent to dispatcher/office; | + | *Messages can also be generated from the device and sent to dispatcher/office; |
| − | *Messages received will be notified to driver through a pop-up alert on Garmin screen; | + | *Messages received will be notified to the driver through a pop-up alert on the Garmin screen; |
*Garmin provides a "virtual keyboard" for text communication. | *Garmin provides a "virtual keyboard" for text communication. | ||
| Line 198: | Line 250: | ||
* Garmin can display a list of Stops/Jobs reported to the device in a separate category called "My Stops"; | * Garmin can display a list of Stops/Jobs reported to the device in a separate category called "My Stops"; | ||
| − | *Driver has ability to navigate directly to Stop from the list; | + | *Driver has the ability to navigate directly to Stop from the list; |
* Garmin can provide status of a current Stop in progress; | * Garmin can provide status of a current Stop in progress; | ||
*Garmin can indicate whether the driver has stopped at the location; | *Garmin can indicate whether the driver has stopped at the location; | ||
*Garmin can inform how far the driver has progressed through the list of Stops; | *Garmin can inform how far the driver has progressed through the list of Stops; | ||
| − | *Garmin can provide confirmation that the driver has received a particular Stop, familiarized himself/herself with its details or removed it from the list; | + | *Garmin can provide confirmation that the driver has received a particular Stop, familiarized himself/herself with its details, or removed it from the list; |
*Can provide confirmation that a Stop has been reached. | *Can provide confirmation that a Stop has been reached. | ||
| Line 218: | Line 270: | ||
* Dispatcher/office has the ability to wipe clean the data on Garmin PND; | * Dispatcher/office has the ability to wipe clean the data on Garmin PND; | ||
| − | *It allows to clean messages in inbox and remove stops. | + | *It allows to clean messages in the inbox and remove stops. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | ====Enhanced protocols==== | ||
| + | ------------------ | ||
Canned Responses/Messages: | Canned Responses/Messages: | ||
*Fleet managers can communicate by sending up to 200 "canned" responses from the server to be stored directly on Garmin devices; | *Fleet managers can communicate by sending up to 200 "canned" responses from the server to be stored directly on Garmin devices; | ||
| − | *Up to 50 of these canned responses can be utilized for any given | + | *Up to 50 of these canned responses can be utilized for any given scenario; |
*Drivers can store up to 120 canned messages, eliminating the need to type while driving. | *Drivers can store up to 120 canned messages, eliminating the need to type while driving. | ||
| Line 231: | Line 283: | ||
*Up-to-the-minute communications that allow drivers to automatically send status updates; | *Up-to-the-minute communications that allow drivers to automatically send status updates; | ||
| − | *Driver's units can store up to 16 status indicators such as start/stop shift, on/off break etc. | + | *Driver's units can store up to 16 status indicators such as start/stop shift, on/off break, etc. |
| − | ===Supported features on TAVL client application=== | + | ====Supported features on TAVL client application==== |
| − | TAVL client application lets | + | ------------------ |
| + | TAVL client application lets users use the following features of Garmin FMI: | ||
*Text messaging; | *Text messaging; | ||
| Line 240: | Line 293: | ||
*ETA request. | *ETA request. | ||
| − | ===Text messaging === | + | ====Text messaging==== |
| − | + | ------------------ | |
| − | + | The text messaging feature lets the user communicate with the driver (the user that operates the Garmin device) by sending text messages via GPRS. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | === | + | ====Destination message==== |
| − | + | ------------------ | |
| + | Destination message is used to inform the driver of a new destination. When the Garmin device receives a destination message from the server it displays it as a Stop to the driver and also gives the driver the ability to start navigating to the Stop location. A new destination in the TAVL client is represented as a Geozone so a new Geozone (as destination) has to be created first. | ||
| − | + | ====ETA request message==== | |
| + | ------------------ | ||
| + | ''Estimated Time of Arrival'' request message is used when the user wants to know an expected arrival time to the currently active destination and the distance (in meters) from the current object location to the destination. | ||
Latest revision as of 14:45, 12 October 2021
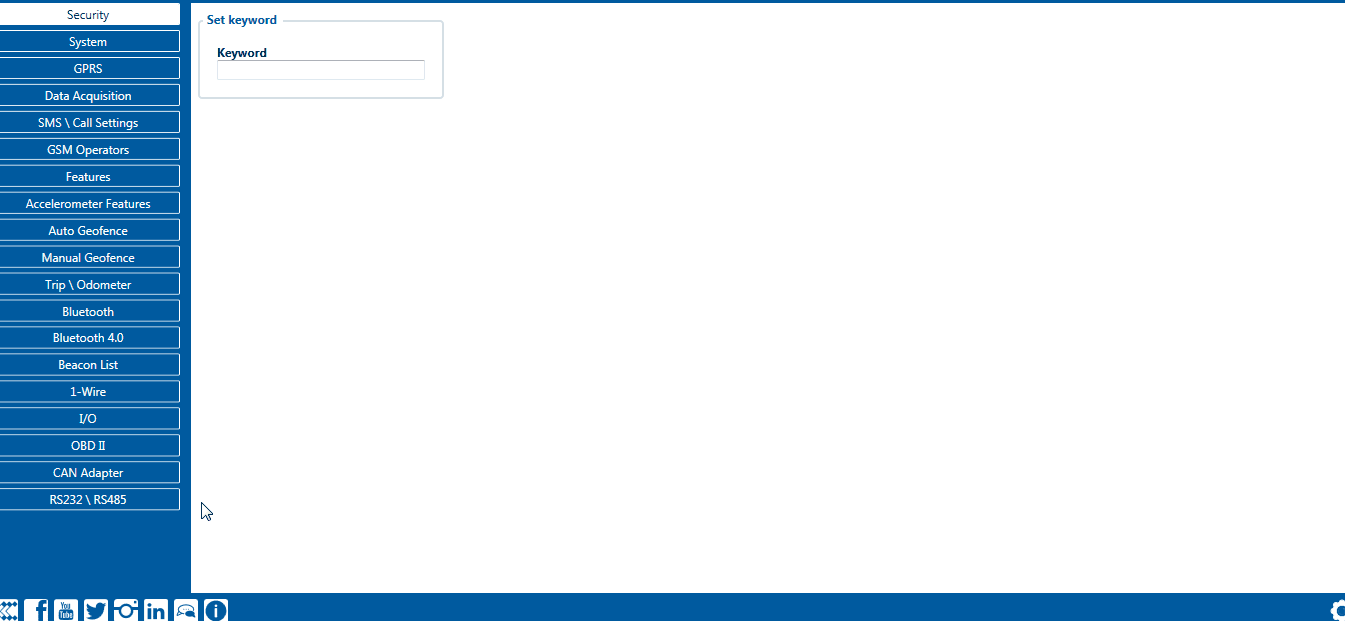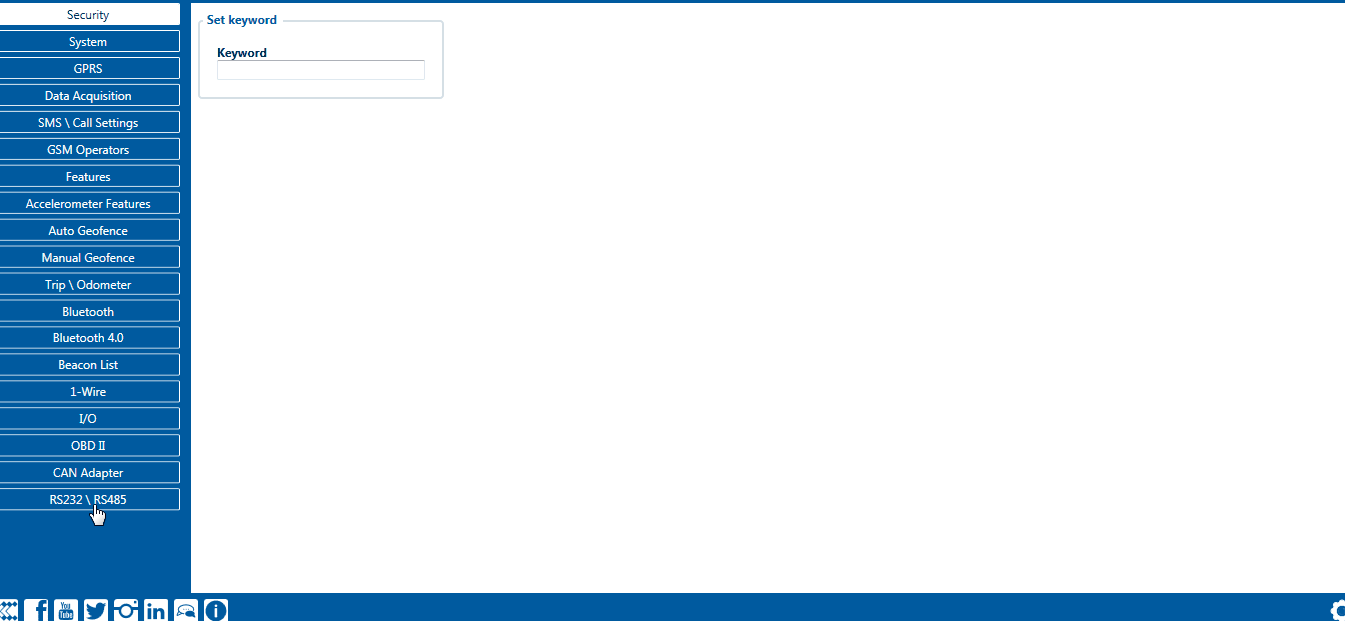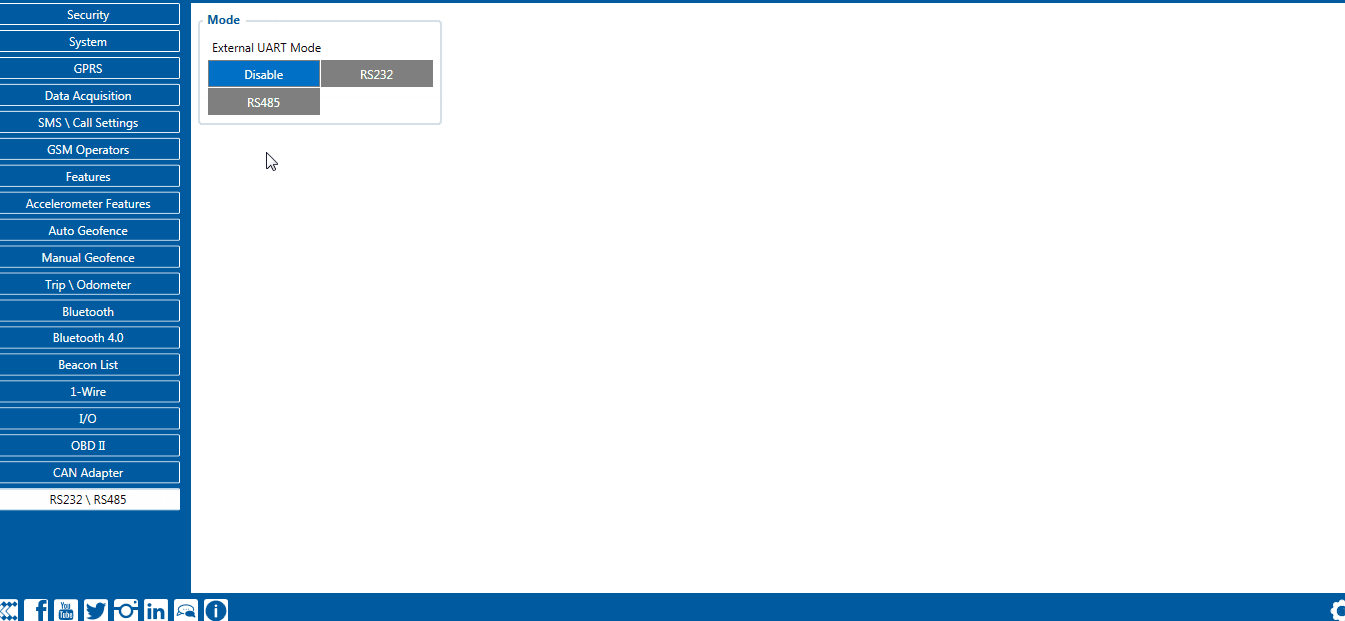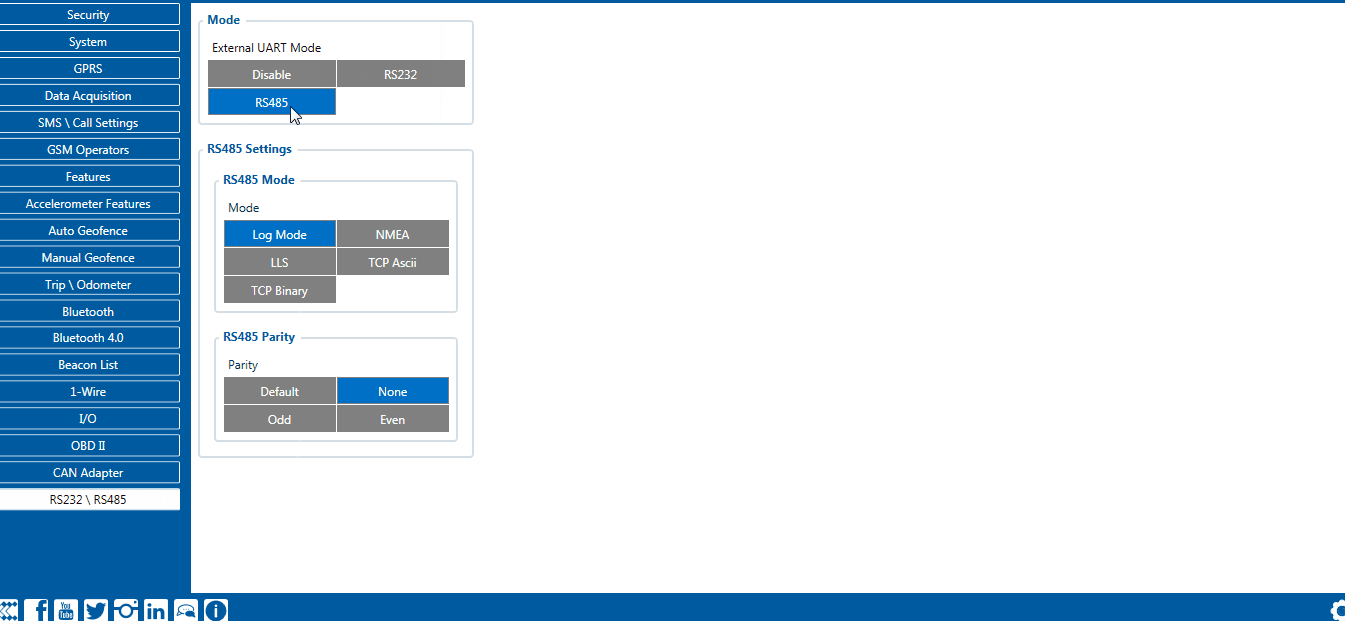
RS-485 interface
RS-485 supports only half-duplex communication, which means data is transferred only one way at a time.
When activated RS-485 driver chip draws constant 30mA current when entering Sleep or Deep sleep RS-485 will be powered off.
RS-485 connection diagram is shown below.
RS-485 modes
RS-485 transmit (FMB log) mode
RS-485 prints the FMB device log and does not respond to commands.
RS-485 transmit (GNSS NMEA) mode
RS-485 prints GNSS NMEA log and does not respond to commands.
RS-485 receive (LLS) mode
This mode supports up to five LLS fuel level sensors each of which has a receiver ID.
RS-485 TCP (ASCII/Binary) modes
In TCP ASCII/Binary mode a link with an external device using text messages can be established. In TCP ASCII/Binary mode all data received from the external device through RS-485 is sent directly to the server (if the link is currently active). Data is encapsulated in codec 12 format.
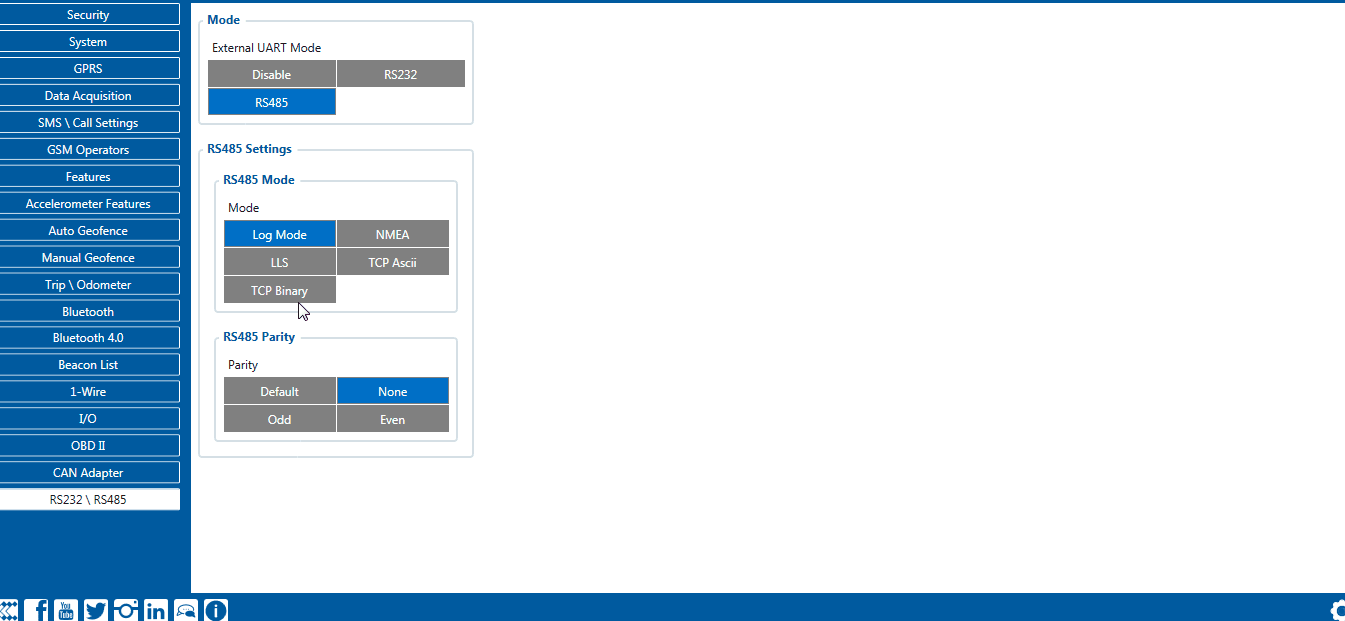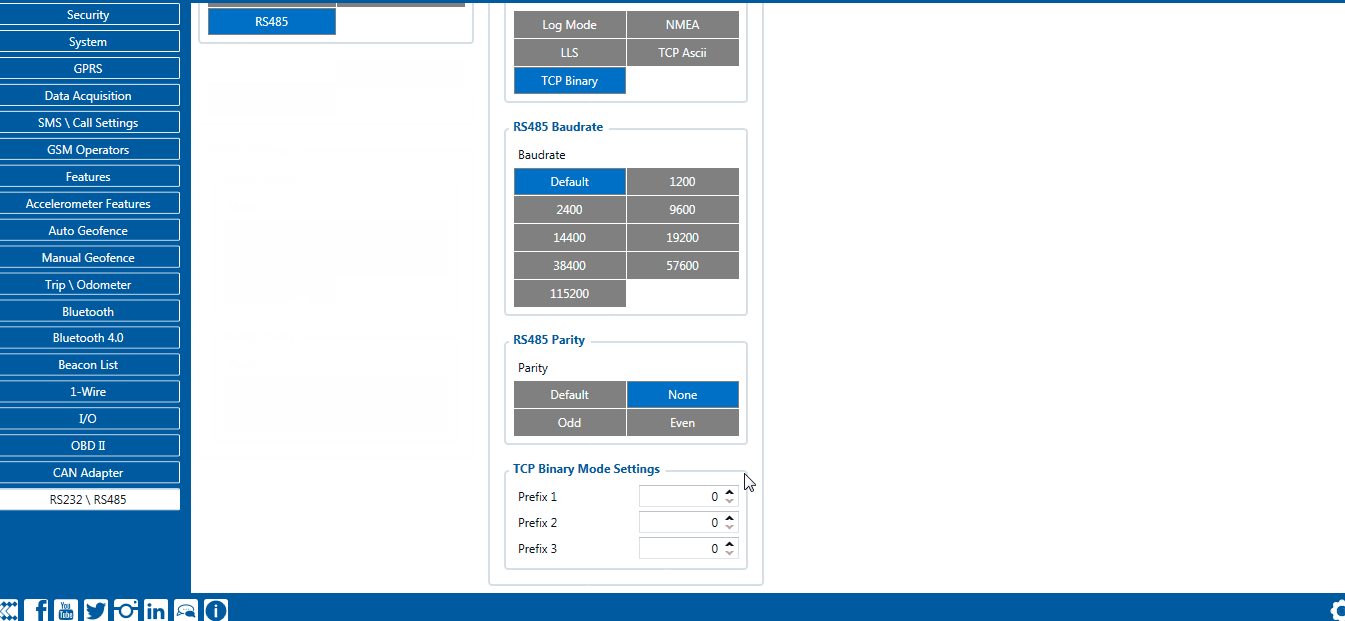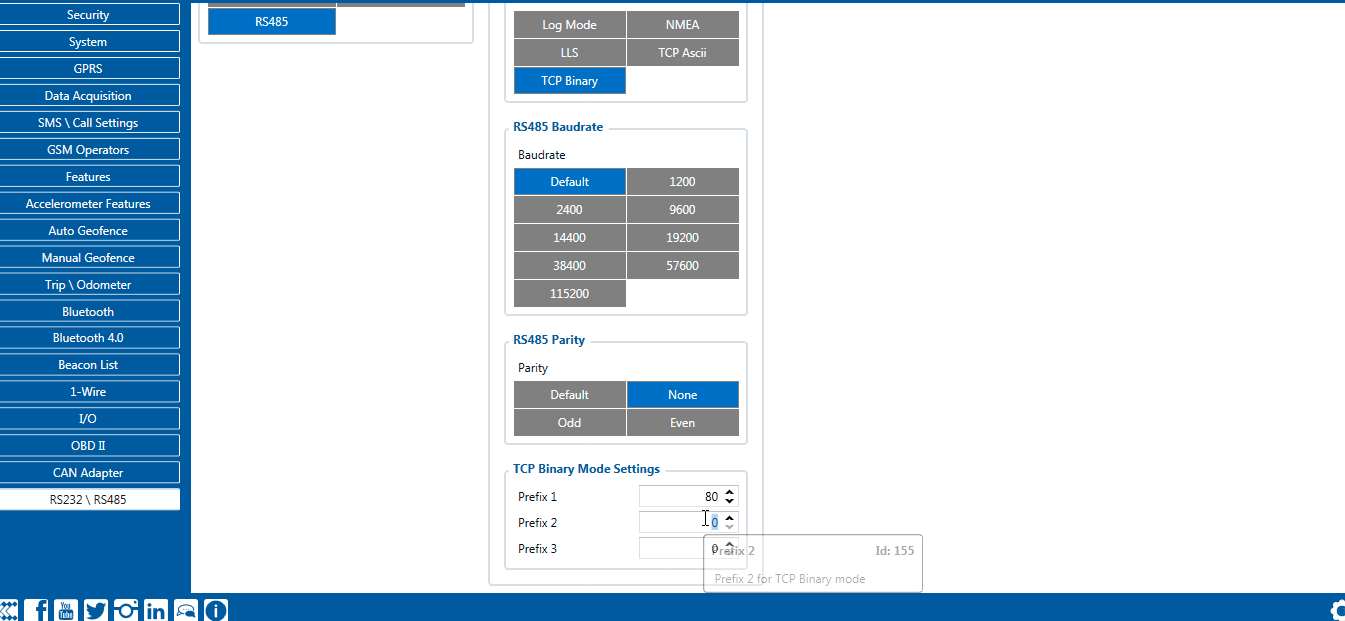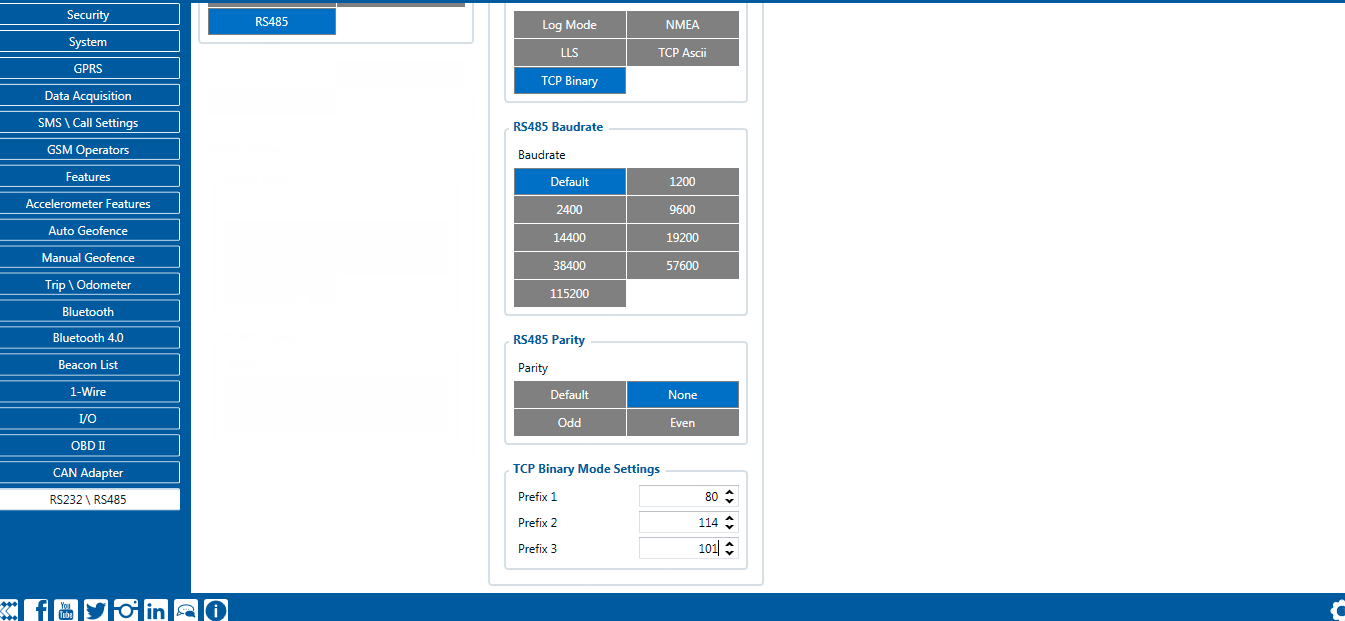
RS-485 TCP Binary settings
TCP Binary has a setting Prefix. It is possible to set Prefix 1, Prefix 2, or Prefix 3. These prefixes can be used separately or in unison. To configure this setting a value from 0 to 255 in decimal has to be entered. The device will convert this value to HEX and compare the 1st, 2nd, or 3rd byte from incoming data. If the values do not match, the device will not accept incoming data.
Example:
Incoming packet through RS232/RS485 using TCP Binary/TCP Binary Buffered mode - 50 72 65 66 69 78 20 57 6f 72 6b 69 6e 67
- If Prefix 1 is set to 80 in decimal, it is equal to 50 in HEX.
- FMB device will then check the 1st byte of incoming data and compare to the set Prefix 1.
- If Prefix 2 is set to 114 in decimal, it is equal to 72 in HEX.
- FMB device will then check the 2nd byte of incoming data and compare to the set Prefix 2.
- If Prefix 3 is set to 101 in decimal, it is equal to 65 in HEX.
- FMB device will then check the 3rd byte of incoming data and compare to the set Prefix 3.
When values match, data will be accepted and saved to Buffer (using TCP Binary Buffered mode) or sent to the server (using TCP Binary mode).
Incoming packet through RS232/RS485 using TCP Binary/TCP Binary Buffered mode - 50 0 65 66 69 78 20 57 6f 72 6b 69 6e 67
- If Prefix 1 is set to 80 in decimal, it is equal to 50 in HEX.
- FMB device will then check the 1st byte of incoming data and compare to the set Prefix 1.
- If Prefix 2 is set to 114 in decimal, it is equal to 72 in HEX.
- FMB device will then check the 2nd byte 0 of incoming data and compare to the set Prefix 2.
Since Prefix 2 does not match the incoming 2nd byte, data will not be accepted.
RS-485 CMD ID
This parameter is used when is sending RS232/RS485 packet to a server, it overrides command type value in Codec12/Codec13 with user defined CMD ID value (1 - 14). behavior when it receives different CMD ID (Type) values in GPRS packet from server:
| CMD ID | Functionality |
|---|---|
| 5 | Parse Codec12/Codec14 packet from the server |
| 7 | Forward packet meant for Garmin system |
| 14 | Forward packet to external device via uart using RS232/RS485 |
| 16 | Forward packet to paired Bluetooth device |
RS-232 Interface
RS-232 supports full-duplex communication which means the data can be both sent and received at the same time as they use separate transmission lines. Most of the modes are the same as for RS-485. When entering Sleep or Deep sleep RS-232 will be powered off.
RS-232 modes
Log mode, NMEA, LLS, TCP ASCII, and TCP Binary modes are identical to those of RS-485. In RS-232 LLS mode only one LLS fuel level sensor can be connected. Additionally TCP ASCII Buffered and TCP Binary Buffered modes are available.
RS-232 LCD mode
In this mode, the user is able to communicate with the server through the terminal. A link between the FMB device and the server has to be established for this mode to function properly.
To communicate from terminal to server - in terminal send command "WT^W your text here"
To communicate with the server to the terminal - send "#DO DAT=you text here" packet in Codec12 protocol
RS-232 RFID HID/RFID MF7 mode
The difference between RFID HID Mode and RFID MF7 Mode is that in RFID MF7 Mode understands RFID messages that are in hexadecimal text format and RFID HID Mode interprets messages that are in binary format. The type of RFID message sent to depends on the RFID reader. For example, the RFID MF7 mode message looks like "$aa$02$03$04$17$89$00$01" while HID mode message is of the following format: "1213141519".
The selected mode has to correspond to the RFID reader's mode.
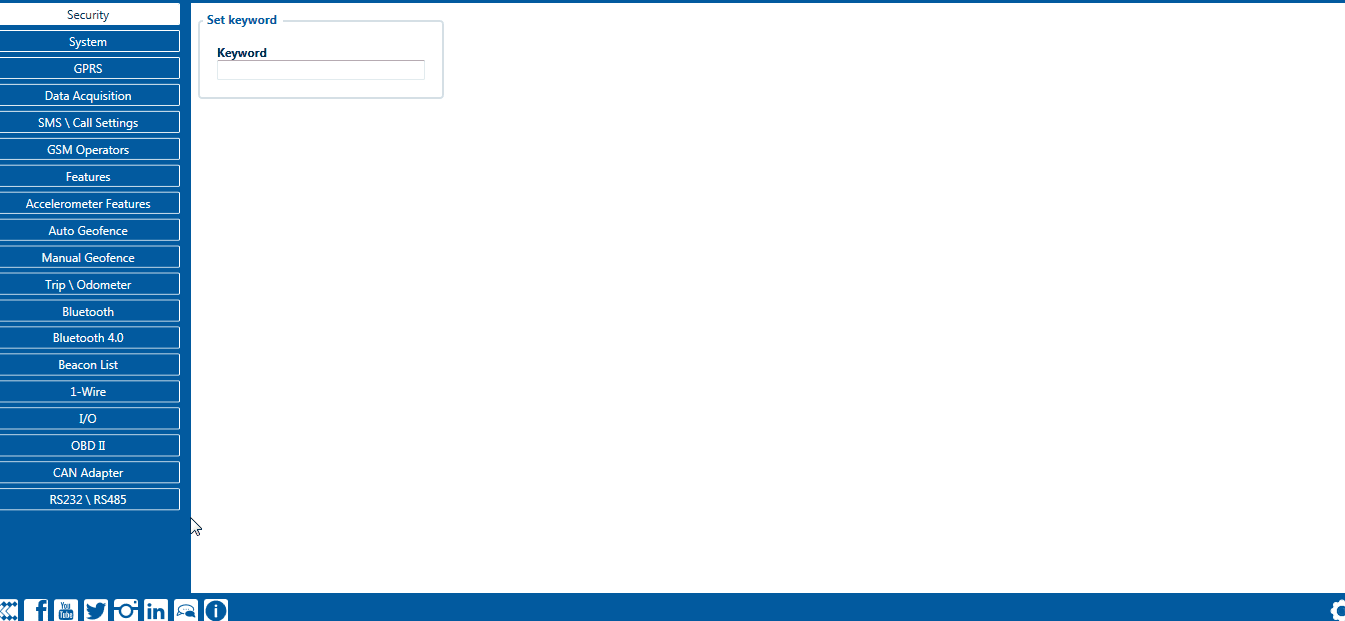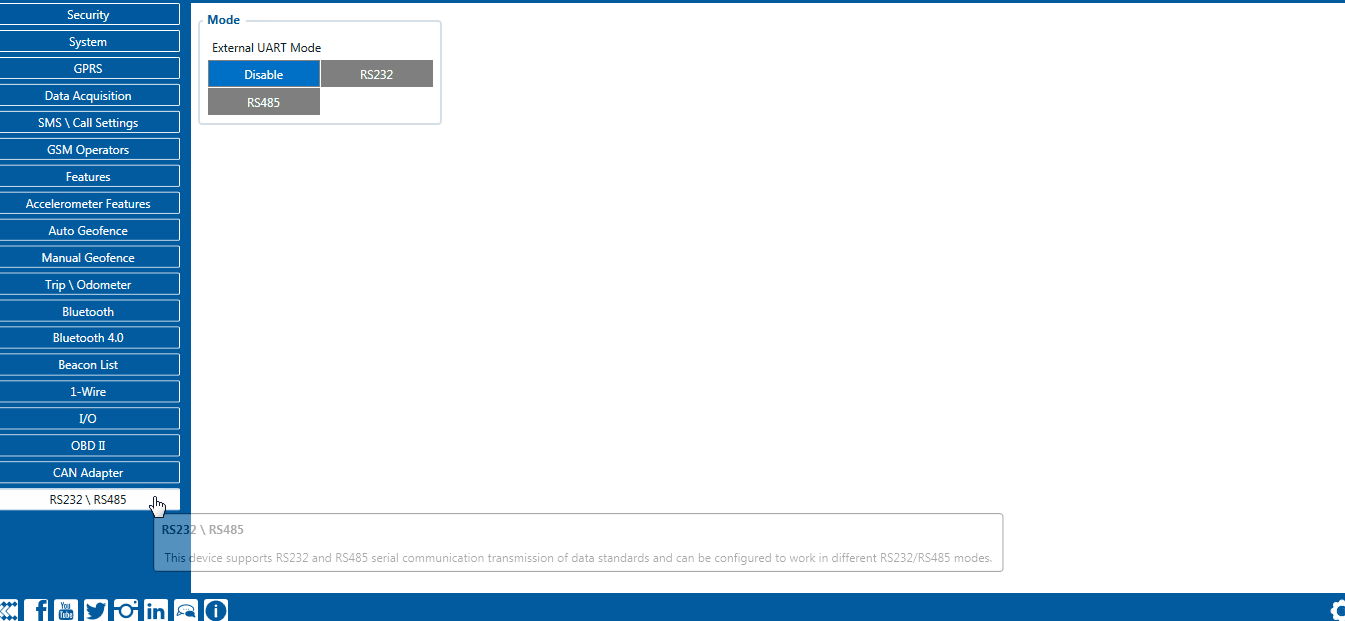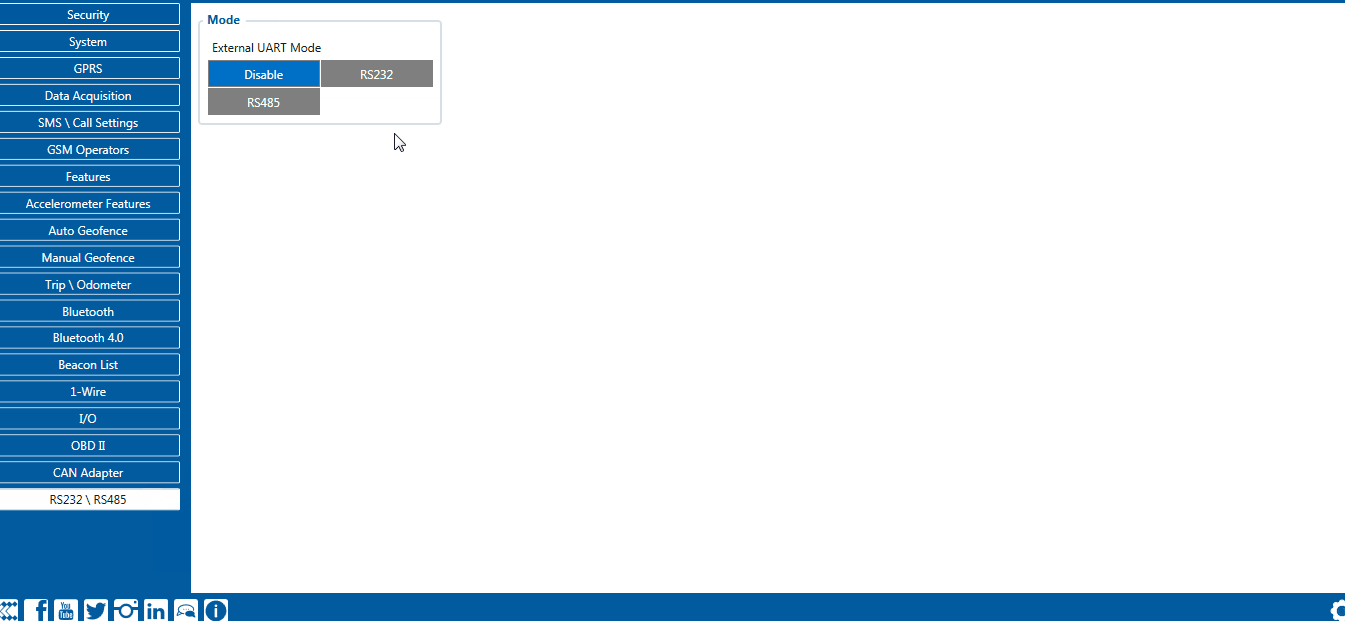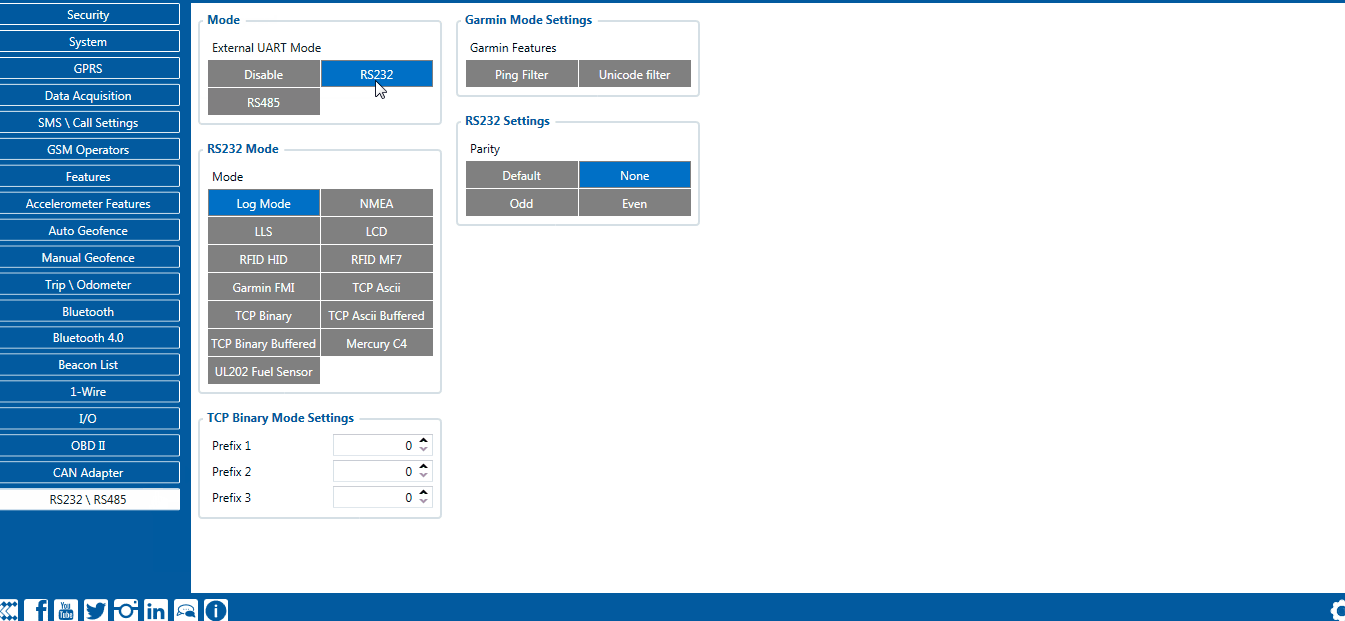 Please contact your local sales representative for more information about RFID IDs and devices.
Please contact your local sales representative for more information about RFID IDs and devices.
RS-232 Garmin mode
Garmin provides a Fleet Management Interface Tool Kit, once is connected to the navigator it enables the driver to have a "screen" in their vehicle for real-time navigation and messaging and offers job dispatch capabilities to help them be more efficient.
and Garmin operational diagram is shown on the figure below.
RS-232 TCP Binary/TCP ASCII mode
In TCP ASCII/Binary mode all data received from the external device is sent directly to the server. Data is encapsulated in codec 12 format. TCP Binary Mode has a delay of 30 ms, if no data is received for 30 ms, data is sent to the server. TCP ASCII mode waits for the End of Line (EOL) character (0x0D0A, \r\n) to pack data and send it to the server
RS-232 TCP Binary Buffered/TCP ASCII Buffered mode
TCP ASCII Buffered and TCP Binary Buffered modes are used to collect data from RS232 and save it in the buffer if there is no link with the server and data cannot be sent immediately. When the link is established and there is data to transmit, then RS232 data from the buffer is transmitted after all records are sent. Data is sent in codec 13 protocol. Note. That in TCP ASCII and TCP Binary modes device sends data from the external device only to the main server. In Buffered modes – to both main and backup/duplicate servers. Message timestamp: The message Timestamp parameter is used to determine if it is necessary to include a timestamp in the RS232 TCP packet when sending to the server. If the parameter is enabled, then Codec 13 is used for data sending. Otherwise, Codec 12 is used.
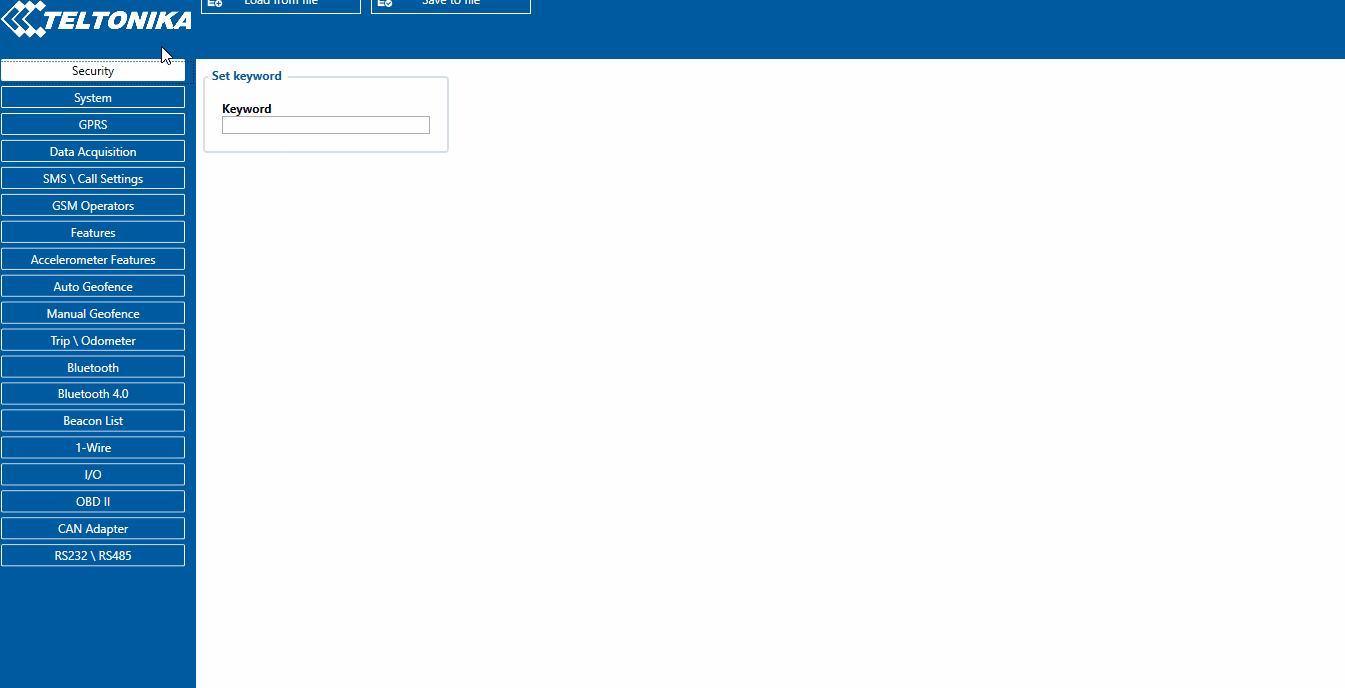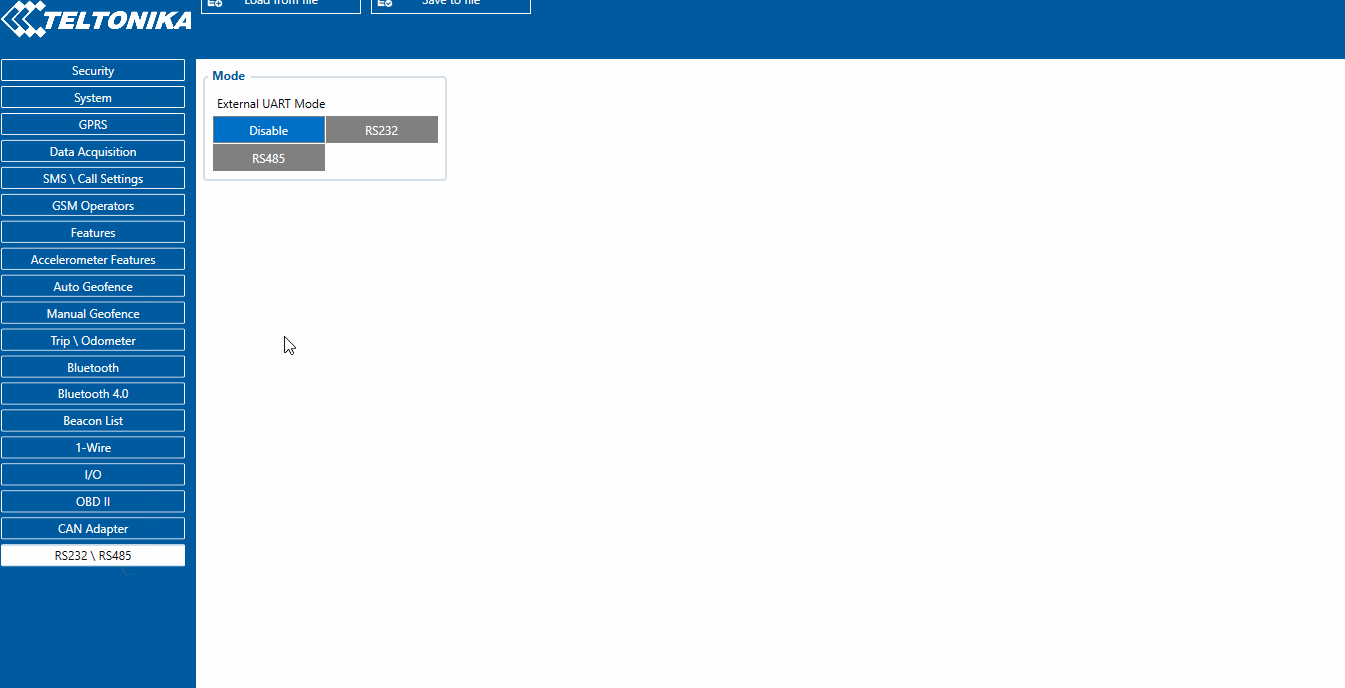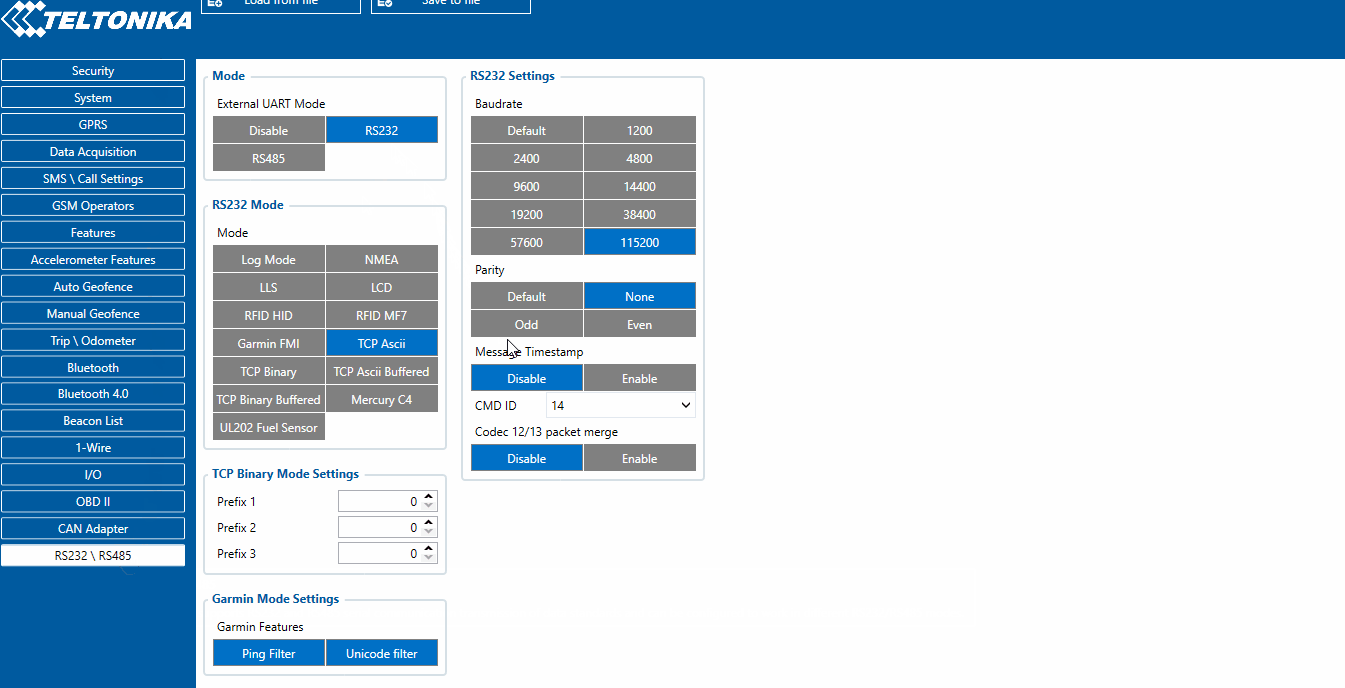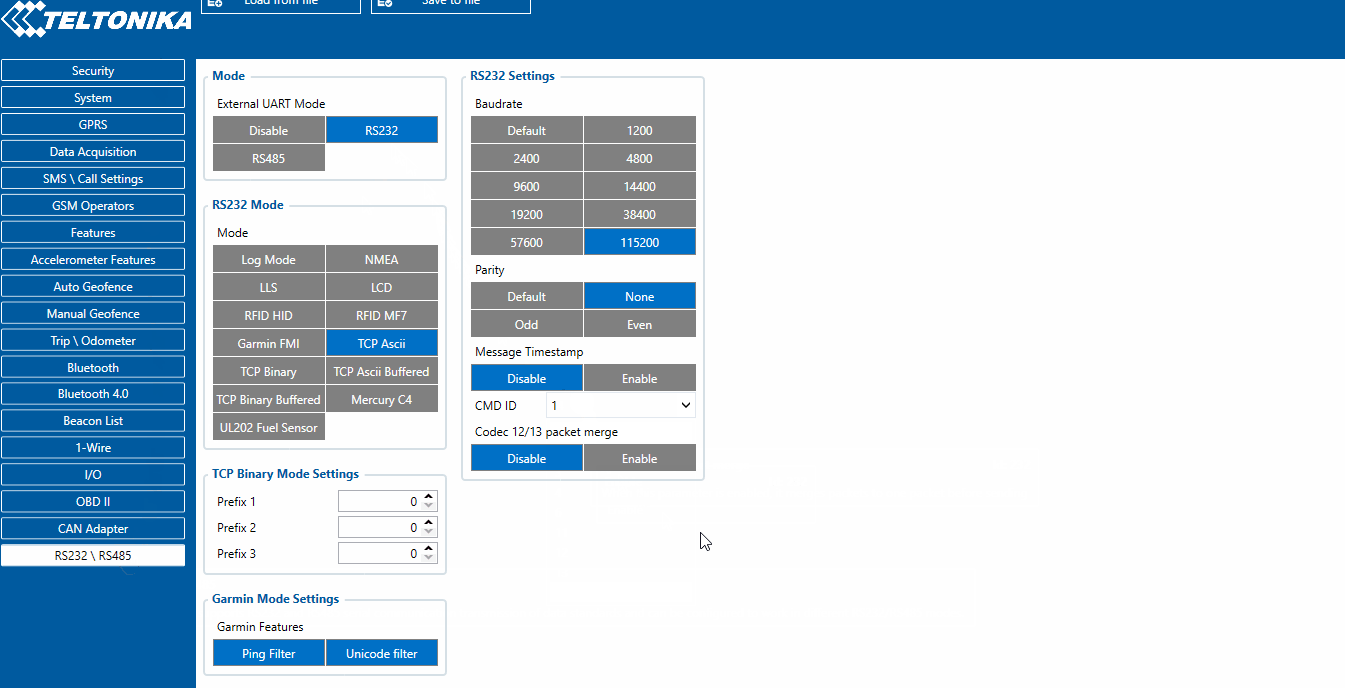
RS-232 TCP Binary settings
TCP Binary has a setting Prefix. It is possible to set Prefix 1, Prefix 2, or Prefix 3. These prefixes can be used separately or in unison. To configure this setting a value from 0 to 255 in decimal has to be entered. The device will convert this value to HEX and compare the 1st, 2nd, or 3rd byte from incoming data. If the values do not match, the device will not accept incoming data.
Example:
Incoming packet through RS232/RS485 using TCP Binary/TCP Binary Buffered mode - 50 72 65 66 69 78 20 57 6f 72 6b 69 6e 67
- If Prefix 1 is set to 80 in decimal, it is equal to 50 in HEX.
- FMB device will then check the 1st byte of incoming data and compare to the set Prefix 1.
- If Prefix 2 is set to 114 in decimal, it is equal to 72 in HEX.
- FMB device will then check the 2nd byte of incoming data and compare to the set Prefix 2.
- If Prefix 3 is set to 101 in decimal, it is equal to 65 in HEX.
- FMB device will then check the 3rd byte of incoming data and compare to the set Prefix 3.
When values match, data will be accepted and saved to Buffer (using TCP Binary Buffered mode) or sent to the server (using TCP Binary mode).
Incoming packet through RS232/RS485 using TCP Binary/TCP Binary Buffered mode - 50 0 65 66 69 78 20 57 6f 72 6b 69 6e 67
- If Prefix 1 is set to 80 in decimal, it is equal to 50 in HEX.
- FMB device will then check the 1st byte of incoming data and compare to the set Prefix 1.
- If Prefix 2 is set to 114 in decimal, it is equal to 72 in HEX.
- FMB device will then check the 2nd byte 0 of incoming data and compare to the set Prefix 2.
Since Prefix 2 does not match the incoming 2nd byte, data will not be accepted.
Codec 12/13 Packet Merge
This additional option configures the device to merge RS-232 records into a single packet instead of sending many separate packets. This functionality only affects TCP Binary Buffered or TCP Ascii Buffered RS232 modes. When enabled, the device will merge saved RS-232 records together into a single data packet until it is able to send it to the server.
This optimizes RS-232 data sending by not having to send each RS-232 record separately.
If the amount of saved RS-232 data exceeds the maximum 4 bytes of data in one Codec 12 packet, the device will start saving incoming RS-232 data into a new record.
RS-232 CMD ID
This parameter is used when is sending RS232/RS485 packet to a server, it overrides command type value in Codec12/Codec13 with user defined CMD ID value (1 - 14). behavior when it receives different CMD ID (Type) values in GPRS packet from server:
| CMD ID | Functionality |
|---|---|
| 5 | Parse Codec12/Codec14 packet from the server |
| 7 | Forward packet meant for Garmin system |
| 14 | Forward packet to external device via uart using RS232/RS485 |
| 16 | Forward packet to paired Bluetooth device |
LLS Sensor
LLS sensor series liquid level sensors are solid-state capacitive devices with no moving parts. The sensors use capacitive technology to produce accurate liquid level measurements of standard factory-grade DIESEL OIL and PURE GASOLINE (BENZINE) carbon fuels. The LLS sensor liquid level sensors are strictly prohibited to use in any liquids which are not factory-grade carbon fuels or contain: BIOFUEL, METHANOL, ETHANOL, UREA, and similar aggressive components in pure form or as additives for factory-grade carbon fuels for use in INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES. Operating media – Diesel fuel (oil), pure gasoline (benzene).
In order to use the LLS fuel counter, the newest firmware version is needed which can be obtained from Teltonika or a representative. Firmware is updated over GPRS or using a cable update method.
Specifications
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Supply voltage | +10..+50 V |
| Current consumption, mA (for 12/24 V) | 25 mA / 50 mA |
| Working temperature | -40..+85 ºC |
| Working mode | Continuous |
| Weight | < 2.0 kg |
| Working pressure | Atmospheric |
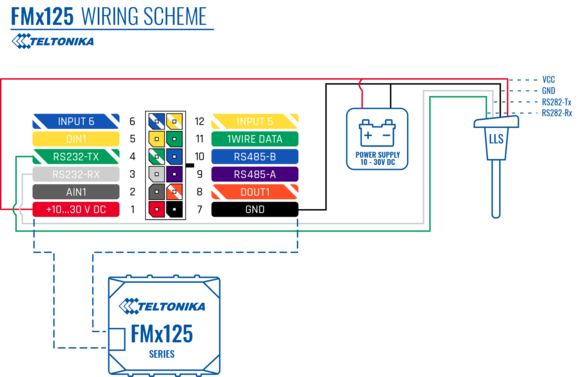
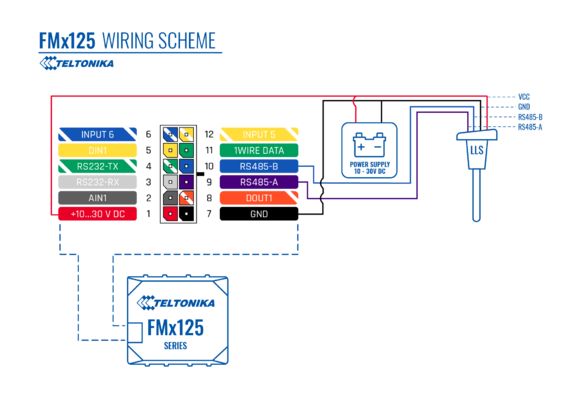
Wiring And Configuration
First of all, the LLS fuel sensor must be connected to the FMB125 device. Please find examples below:
| Using RS232 socket | Using RS485 socket |
 |
 |
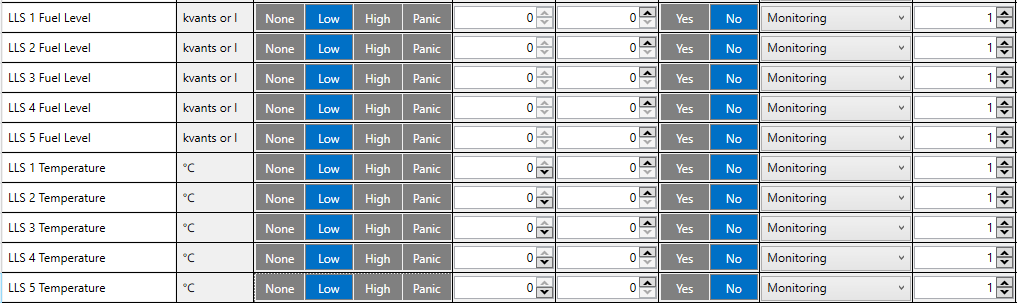
Then FMB125 must be configured. Both fuel level and fuel temperature has to be set up by the configurator’s I/O menu:
Garmin protocols
The following is a list of protocols supported and the corresponding list of features/benefits. FMB125 can fully support Fleet Management Interface (FMI) versions up to 2.1. Other or higher versions may be supported, but Teltonika is not responsible for the changes made by Garmin, which may affect the function of FMB125 and Garmin products. For more information about Garmin products and FMI versions, please refer to https://www.garmin.com/en-US/fleet-ready-navigators/. Notice that some Garmin products use different connection cables than others.
Standard protocols
Text Message Protocol:
- Allows text messages sent to the device to be displayed in "inbox" on navigation unit;
- Garmin can provide a confirmation that message was read;
- Garmin can also provide a yes/no box below the text of the message to enable a quicker response;
- Messages can be up to 199 characters long;
- Messages can also be generated from the device and sent to dispatcher/office;
- Messages received will be notified to the driver through a pop-up alert on the Garmin screen;
- Garmin provides a "virtual keyboard" for text communication.
Stop (Destination) Protocol:
- Garmin can display a list of Stops/Jobs reported to the device in a separate category called "My Stops";
- Driver has the ability to navigate directly to Stop from the list;
- Garmin can provide status of a current Stop in progress;
- Garmin can indicate whether the driver has stopped at the location;
- Garmin can inform how far the driver has progressed through the list of Stops;
- Garmin can provide confirmation that the driver has received a particular Stop, familiarized himself/herself with its details, or removed it from the list;
- Can provide confirmation that a Stop has been reached.
Estimated Time of Arrival Protocol:
- Dispatcher/office can request the ETA of the current Stop/job in progress;
- Garmin can notify about the actual time of arrival as well as the distance remaining to a Stop.
Auto-Arrival at Stop Protocol:
- This feature is used to tell Garmin PND to automatically detect that it has arrived at a Stop and then to prompt the driver if he/she would like to mark the Stop as done and begin navigating to a next Stop on the list;
- Auto-arrival can be determined by how long the unit is stopped close to the destination (in the case driver has to park and walk) or by how close the unit needs to be to the destination before the Auto-arrival feature is activated.
Data Deletion Protocol:
- Dispatcher/office has the ability to wipe clean the data on Garmin PND;
- It allows to clean messages in the inbox and remove stops.
Enhanced protocols
Canned Responses/Messages:
- Fleet managers can communicate by sending up to 200 "canned" responses from the server to be stored directly on Garmin devices;
- Up to 50 of these canned responses can be utilized for any given scenario;
- Drivers can store up to 120 canned messages, eliminating the need to type while driving.
Status Protocol:
- Up-to-the-minute communications that allow drivers to automatically send status updates;
- Driver's units can store up to 16 status indicators such as start/stop shift, on/off break, etc.
Supported features on TAVL client application
TAVL client application lets users use the following features of Garmin FMI:
- Text messaging;
- Destination message;
- ETA request.
Text messaging
The text messaging feature lets the user communicate with the driver (the user that operates the Garmin device) by sending text messages via GPRS.
Destination message
Destination message is used to inform the driver of a new destination. When the Garmin device receives a destination message from the server it displays it as a Stop to the driver and also gives the driver the ability to start navigating to the Stop location. A new destination in the TAVL client is represented as a Geozone so a new Geozone (as destination) has to be created first.
ETA request message
Estimated Time of Arrival request message is used when the user wants to know an expected arrival time to the currently active destination and the distance (in meters) from the current object location to the destination.