Template:FMB System settings: Difference between revisions
Atabasnikov (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
Atabasnikov (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
* ''Sleep Settings'', where user can choose sleep mode; | * ''Sleep Settings'', where user can choose sleep mode; | ||
* ''Ignition Source'', where user can choose between power voltage, digital input 1, accelerometer and engine RPM as ignition sources. More than one ignition source can be selected at the same moment. User can select movement start and movement stop delay time - those parameters are used when accelerometer is selected as ignition source. Ignition status is used in power management and the following functionalities: eco driving, excessive idling, fuel consumption, over speeding, towing and trip functionalities. | * ''Ignition Source'', where user can choose between power voltage, digital input 1, accelerometer and engine RPM as ignition sources. More than one ignition source can be selected at the same moment. User can select movement start and movement stop delay time - those parameters are used when accelerometer is selected as ignition source. Ignition status is used in power management and the following functionalities: eco driving, excessive idling, fuel consumption, over speeding, towing and trip functionalities. | ||
* Object Motion Detection Settings, where user can configure 4 ways how {{{model|FMB1YX}}} detects movement, and change its working mode (for working modes, read section [[{{{ | * Object Motion Detection Settings, where user can configure 4 ways how {{{model|FMB1YX}}} detects movement, and change its working mode (for working modes, read section [[{{Template:FMB Data acquisition settings|{{{model}}}}}|Data acquisition settings]]). Other functionalities that depend from movement source: power manager, fuel consumption and trip. | ||
* ''Static Navigation Settings'', where user can turn static navigation on or off. Additionally, user can choose what source is used (movement or ignition) to activate/deactivate static navigation. | * ''Static Navigation Settings'', where user can turn static navigation on or off. Additionally, user can choose what source is used (movement or ignition) to activate/deactivate static navigation. | ||
* Records Settings, where user can enable or disable records when GPS is not available (no time synchronization). | * Records Settings, where user can enable or disable records when GPS is not available (no time synchronization). | ||
Revision as of 07:54, 26 April 2018
System settings have 9 configurable parameters:
- Sleep Settings, where user can choose sleep mode;
- Ignition Source, where user can choose between power voltage, digital input 1, accelerometer and engine RPM as ignition sources. More than one ignition source can be selected at the same moment. User can select movement start and movement stop delay time - those parameters are used when accelerometer is selected as ignition source. Ignition status is used in power management and the following functionalities: eco driving, excessive idling, fuel consumption, over speeding, towing and trip functionalities.
- Object Motion Detection Settings, where user can configure 4 ways how FMB1YX detects movement, and change its working mode (for working modes, read section [[
Data Acquisition
Data Acquisition modes are an essential part of FMB1YX device, they are also highly configurable.
Through configuration user defines how records will be saved and sent. There are three different modes: Home, Roaming, and Unknown. All these modes with configured data acquisition and report frequencies depend on the current GSM Operator defined in the Operator list (see section Template:FMB GSM Operators settings) and are switched when GSM operator changes (e.g. vehicle passes through a country border).
If current GSM operator is defined as Home Operator, the device will work in Home Data Acquisition mode, if the current operator is defined as Roaming Operator, the device will work in Roaming Data Acquisition mode, and if the current operator code is not written in the Roaming Operator list, the device will work in Unknown mode.
This functionality allows having different AVL records to acquire and send parameter values when the object is moving or standing still. Vehicle moving or stop state is defined by the Stop Detection Source parameter. There are 4 ways for FMB1YX to switch between Vehicle on Stop and Vehicle Moving modes, please refer to the first table in Template:FMB System settings.
FMB1YX has 6 different modes. Operational logic is shown in the figure below.
| If home operator is written to roaming operator list, it will still be detected as home operator. |
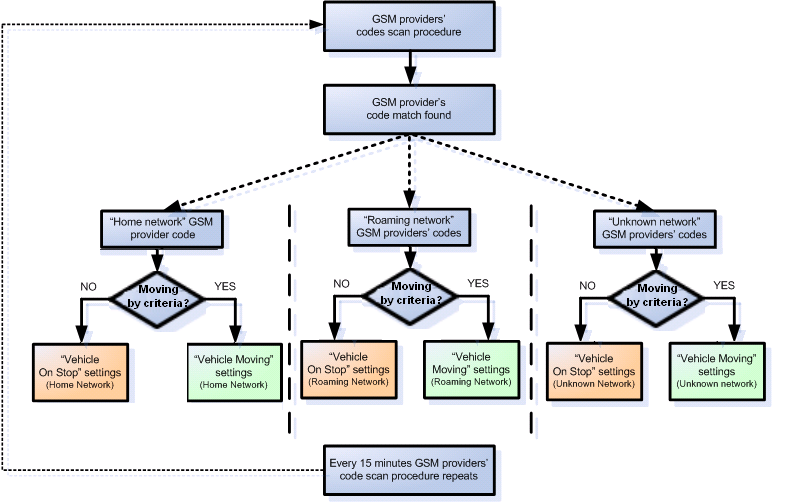
The operator search is performed every 15 minutes. Depending on the current GSM operator Home, Roaming or Unknown mode can be changed faster than every 15 minutes. This process is separate from the operator search. Movement criteria are checked every second.
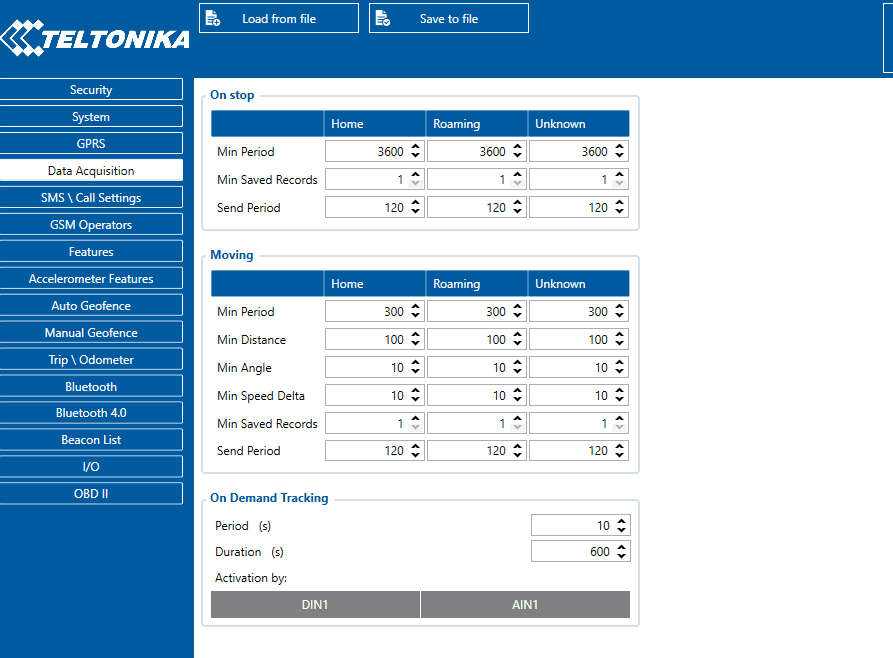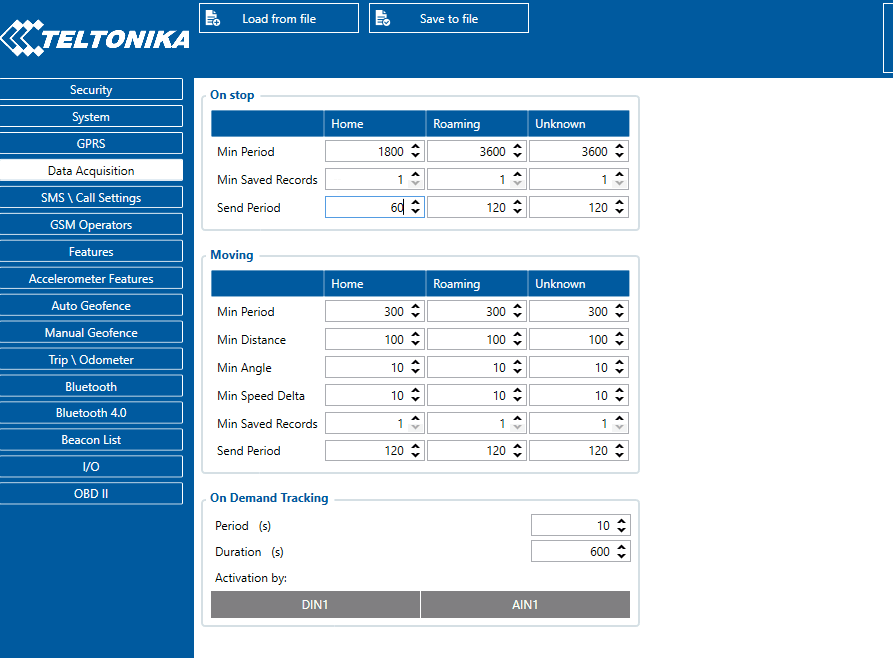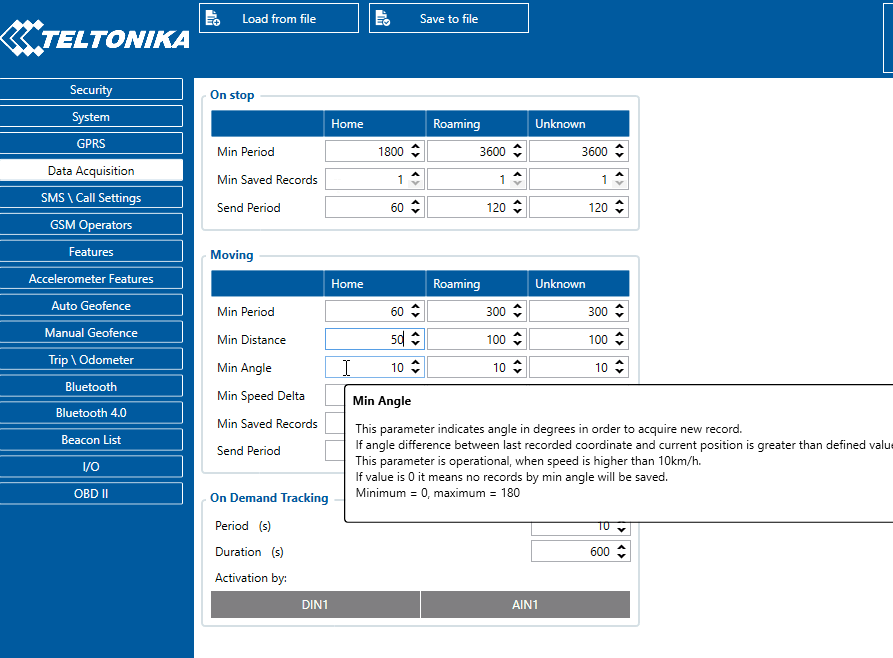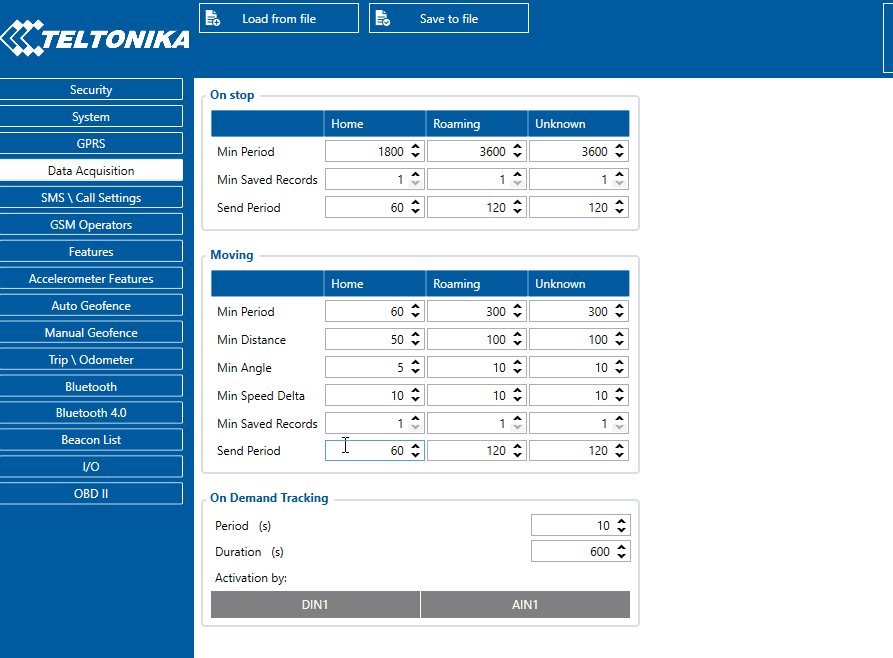
Record Saving settings
Min Saved Records defines the minimum number of coordinates and I/O data that should be transferred within a single connection to the server. If FMB1YX does not have enough coordinates to send to the server, it will check again after a time interval defined in Send Period field.
Send period controls the frequency of data being sent to the server over GPRS. The module makes attempts to send collected data to the server every defined period of time. If it does not have enough records (depends on the parameter Min. Saved Records described above), it tries again after the defined time interval.
| Keep in mind that FMB1YX operates in GMT:0 time zone, without daylight saving. |
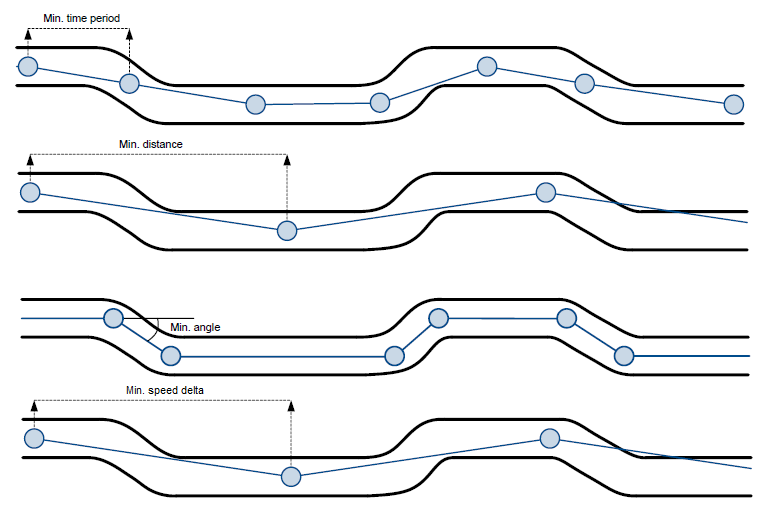
FMB1YX is able to collect records using four methods at the same time: time, distance, angle, and speed-based data acquisition:
- Time based data acquisition (Min Period) – records are acquired every time when a defined interval of time passes. Entering zero disables data acquisition based on time.
- Distance-based data acquisition (Min Distance) – records are acquired when the distance between the previous coordinate and current position is greater than a defined parameter value. Entering zero disables data acquisition based on distance.
- Angle based data acquisition (Min Angle) – records are acquired when the angle difference between the last recorded coordinate and current position is greater than a defined value. Entering zero disables data acquisition based on the angle.
- Speed based data acquisition (Min Speed Delta) – records are acquired when the speed difference between the last recorded coordinate and current position is greater than a defined value. Entering zero disables data acquisition based on speed.
On Demand Tracking
This functionality was made global (for all FMB devices) from 03.25.06.Rev.00. Tracking on Demand can be activated using commands. After device receives SMS/GPRS command " on_demand_trackingX" where X is a number from 0 to 2.
Possible X values are:
- X = 0 – Stops Tracking on Demand functionality.
- X = 1 – Starts Tracking on Demand functionality.
- X = 2 – Generates one high priority record and initiates data sending to the server.
After that, the device starts to generate high priority records and initiate data sending to the server. This
feature is configurable via SMS/GPRS commands only.
From version 03.25.11.Rev.00 tracking on demand can be triggered by multiple IO Events. To enable functionality at least one activation source must be selected and an appropriate IO Event (in I/O tab) should be enabled (Low/High/Panic priority, the operand must NOT be “Monitoring”). When IO Event is generated and if the event is enabled in activation sources, tracking on demand will be started. THE new IO event will not interrupt or restart tracking on-demand until the Duration period has expired. If tracking on demand is already running, SMS/GPRS command will restart tracking on demand. If tracking the on-demand period is lower than the normal record acquisition period, only high priority records will be created. If tracking the on-demand period is larger than the normal record acquisition period, low priority records will be created according to data acquisition configuration and high priority records will be created after configured tracking on-demand period. Some new Tracking on Demand parameters are introduced in devices.
There are three available options for the activation source of tracking on demand - DIN/AIN or both (devices that support multiple DINs/AINs allow choosing which DINs/AINs to use). Note that, these inputs will work as buttons, rather than switches, and are used to trigger the functionality, the duration of tracking on demand will not be extended if the activation source status is high for a period of time.|Data acquisition settings]]). Other functionalities that depend from movement source: power manager, fuel consumption and trip.
- Static Navigation Settings, where user can turn static navigation on or off. Additionally, user can choose what source is used (movement or ignition) to activate/deactivate static navigation.
- Records Settings, where user can enable or disable records when GPS is not available (no time synchronization).
- GNSS Source settings, where user can choose the necessary satellite system.
- LED Indication, where user can turn on or off the indication LEDs.
- Battery Charge Mode, where user can choose when battery will be charged: On Need (battery will be charged anytime when it needs to be charged) and After Ignition ON (battery will be charged only when ignition is on).
- Analog Input Value Range, where user can choose analog input range of 10 V or 30 V (currently 10 V is in fact a 30 V range).
- Time Synchronization settings, where user can choose which source(s) to use for FMB1YX time synchronization. User has a choice to use only one synchronization source (Disable (GPS only)), allow synchronization from both the GNSS and NTP server (NTP), select synchronization through GNSS and GSM operator (NITZ) or from all three sources (when NITZ+NTP is selected). User can select which NTP server (it is possible to configure up to two servers) and what time period to use to resynchronize time.
| Movement source | Vehicle on Stop mode | Vehicle Moving mode |
|---|---|---|
| Ignition (recommmended) | If ignition (ignition source) is logic low | If ignition (ignition source) is logic high |
| Movement (movement sensor) | Internal movement sensor does not detect movement. | Internal movement sensor detects movement. |
| GPS | GPS fix is available and vehicle speed is lower than 5 km/h. | GPS fix is available and vehicle speed is higher than 5 km/h. |
| While GPS fix is unavailable, Object Motion Detection Settings are working like in Msensor mode. | ||
| CAN speed | If speed from BT OBDII dongle is equal 0 km/h. | If speed from BT OBDII dongle is higher that 0 km/h. |
Static Navigation mode is a filter, which filters out track jumps when the object is stationary. If static navigation filter is disabled, it will apply no changes to GPS data. If static navigation filter is enabled, it will filter changes in GPS position if no movement (configured movement source) or ignition (configured ignition source) is detected (depends on what static navigation settings is selected: movement, ignition or both sources). It allows filtering GPS jumps when object is parked (not moving) and GPS position is still traced.
In GNSS source Settings user can configure which GNSS system(s) to use.
User has a choice to use only one system of GPS, Glonass, Galileo or Beidou. Also it is possible to choose two or three systems together. One exception is that you cannot combine Beidou and Glonass systems together.
| Selected source(s) | ID |
|---|---|
| BeiDou only | 01 |
| GLONASS only | 02 |
| Galileo only | 04 |
| Galileo + Beidou | 05 |
| Galileo + Glonass | 06 |
| GPS only | 08 |
| GPS + BeiDou | 09 |
| GPS + GLONASS | 10 |
| GPS + Galileo | 12 |
| GPS + Galileo + BeiDou | 13 |
| GPS + Galileo + GLONASS | 14 |
Examples of NON-configurable GNSS sources:
- GLONASS + BeiDou;
- Galileo + GLONASS + BeiDou;
- GPS + GLONASS + BeiDou;
- GPS + Galileo + GLONASS + BeiDou.