Template:FTX Mobile network: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Irmantas.K (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Irmantas.K (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Mobile data settings== | ==Mobile data settings== | ||
[[File: | [[File:FTX mobile data settings.png|right|500px]] | ||
These settings define the main parameters for {{{model | These settings define the main parameters for {{{model}}}. <br/> | ||
'''Auto APN | '''Auto APN''' | ||
*Device automatically searches for the APN based on the operator of the inserted SIM card. | *Device automatically searches for the APN based on the operator of the inserted SIM card. | ||
'''APN | '''APN''' | ||
*Access point name, a mandatory parameter which is used to connect to the internet (GPRS). Access Point Name is the name of a gateway between a mobile operator and the public internet. It can be obtained from your SIM card provider. | *Access point name, a mandatory parameter which is used to connect to the internet (GPRS). Access Point Name is the name of a gateway between a mobile operator and the public internet. It can be obtained from your SIM card provider. | ||
'''APN Username | '''APN Username''' | ||
*Access point name username (optional – depending on operator). | *Access point name username (optional – depending on operator). | ||
'''APN Password | '''APN Password''' | ||
*Access point name password (optional – depending on operator). <br> | *Access point name password (optional – depending on operator). <br> | ||
'''PDP Context Type''' | '''PDP Context Type''' | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
|} | |} | ||
'''GPRS Authentication | '''GPRS Authentication''' | ||
* Some operators use a specific type of authentication for GPRS sessions – Normal (PAP) or Secured (CHAP). If any of these is used, APN should be entered as "chap:<APN>" or "pap:<APN>" respectively. E.g. if the operator is using APN "internet" with CHAP authentication, it should be entered as "chap: internet". Information about APN and authentication type should be provided by your GSM operator. <br /> | * Some operators use a specific type of authentication for GPRS sessions – Normal (PAP) or Secured (CHAP). If any of these is used, APN should be entered as "chap:<APN>" or "pap:<APN>" respectively. E.g. if the operator is using APN "internet" with CHAP authentication, it should be entered as "chap: internet". Information about APN and authentication type should be provided by your GSM operator. <br /> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
==Server settings== | ==Server settings== | ||
[[File: | [[File:FTX server settings.png|right|500px]] | ||
'''Domain | ===Primary server settings=== | ||
'''Domain''' | |||
*Server or Domain address, either IP address or Domain can be written. | *Server or Domain address, either IP address or Domain can be written. | ||
'''Port | '''Port''' | ||
*Server Port. | *Server Port. | ||
'''Data protocol''' | '''Data protocol''' | ||
*TCP (Transmission control protocol) or UDP (User datagram protocol). Changing this parameter will alter how the device communicates. From the device side, TCP and UDP work almost the same, the only difference is that UDP doesn't need additional confirmation from the server side, that the data packet was received. TCP has that and uses more network data for the confirmation. The desired data transfer protocol can be selected through the configurator. For more information on the protocol differences of Teltonika devices, refer here [https://wiki.teltonika-gps.com/view/Teltonika_Data_Sending_Protocols] | *TCP (Transmission control protocol) or UDP (User datagram protocol). Changing this parameter will alter how the device communicates. From the device side, TCP and UDP work almost the same, the only difference is that UDP doesn't need additional confirmation from the server side, that the data packet was received. TCP has that and uses more network data for the confirmation. The desired data transfer protocol can be selected through the configurator. For more information on the protocol differences of Teltonika devices, refer here [https://wiki.teltonika-gps.com/view/Teltonika_Data_Sending_Protocols] | ||
<br> | ===Secondary server settings=== | ||
<br> | |||
<br> | '''Mode''' | ||
<br> | *Backup - the device will send data to a secondary server only if the primary server is not reachable. | ||
<br> | *Duplicate - the device will send data to both servers. | ||
<br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br> | |||
==Server communication settings== | ==Server communication settings== | ||
[[File: | [[File:FTX server communication settings.png|right|500px]] | ||
'''Open link timeout (s)''' | '''Open link timeout (s)''' | ||
| Line 49: | Line 50: | ||
'''Keep-alive ping timeout (s)''' | '''Keep-alive ping timeout (s)''' | ||
*The device will ping the server periodically, so the server or operator will not close the link. The keep-alive ping timeout value should always be lower than the open link timeout. | *The device will ping the server periodically, so the server or operator will not close the link. The keep-alive ping timeout value should always be lower than the open link timeout. | ||
'''Permanent link''' | |||
*The permanent link feature is designed to establish and maintain a continuous connection with the main server, enabling access to and management of the device through GPRS commands. After the device starts, it attempts to connect to the main server as soon as possible. If the device fails to establish a connection or if the connection is lost, it will continuously retry to connect to the main server. This retry process will continue indefinitely unless the permanent link feature is disabled. When Permanent link feature is enabled, device ignores Open Link Timeout. | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
==Network settings== | ==Network settings== | ||
[[File:Network settings.png|right|500px]] | [[File:Network settings.png|right|500px]] | ||
Configure the operational mode of the network interface to define how the device connects to and interacts with the network, and adjust other related network settings. | |||
'''Network mode''' | '''Network mode''' | ||
* | *Auto - Let modem decide | ||
<br> | *2G mode only | ||
<br> | *4G mode only | ||
<br> | <br><br><br><br><br><br> | ||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
==FOTA WEB settings== | ==FOTA WEB settings== | ||
[[File:FTX fota web settings.png|right|500px]] | |||
Enable or disable connection to [[FOTA WEB|FOTA WEB]]. When functionality is enabled, the device will communicate with FOTA WEB cloud-based application depending on the configuration settings. | Enable or disable connection to [[FOTA WEB|FOTA WEB]]. When functionality is enabled, the device will communicate with FOTA WEB cloud-based application depending on the configuration settings. | ||
''' | '''Server domain''' | ||
* | *Address which points to FOTA WEB. | ||
*It is a secure TLS/TCP server which is used for safe data exchange. Connection to this server will happen only after Ping server confirms it. | |||
'''Port''' | '''Port''' | ||
*FOTA Web port for connection to FOTA WEB. | *FOTA Web port for connection to FOTA WEB. | ||
''' | '''Ping domain''' | ||
*FOTA Web | *Address which points to FOTA WEB ping server. | ||
<br> | *It is a light UDP service, only used to check if connection to main server is needed. Device always pings this server first. | ||
<br> | |||
<br> | '''Ping port''' | ||
<br> | *FOTA Web ping server port. | ||
<br> | <br><br><br><br><br> | ||
Revision as of 14:28, 4 March 2025
Mobile data settings
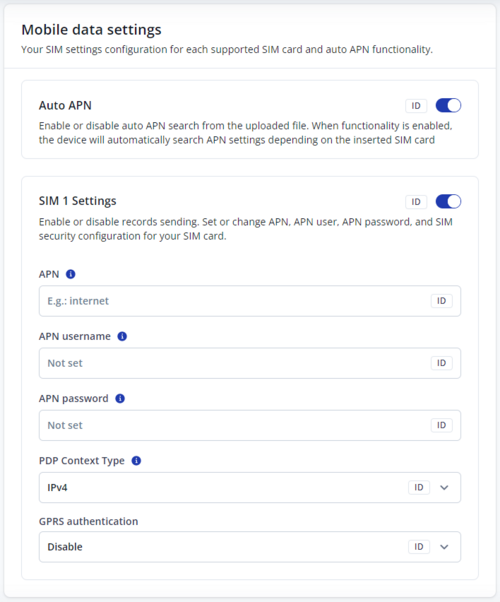
These settings define the main parameters for {{{model}}}.
Auto APN
- Device automatically searches for the APN based on the operator of the inserted SIM card.
APN
- Access point name, a mandatory parameter which is used to connect to the internet (GPRS). Access Point Name is the name of a gateway between a mobile operator and the public internet. It can be obtained from your SIM card provider.
APN Username
- Access point name username (optional – depending on operator).
APN Password
- Access point name password (optional – depending on operator).
PDP Context Type
- PDP context type that is activated by operator for entered APN. It can be either IPv4, IPv6 or IPv4v6.
 |
Make sure that selected context type is enabled for chosen APN by operator. Otherwise, the device will not be able to connect to the network. |
GPRS Authentication
- Some operators use a specific type of authentication for GPRS sessions – Normal (PAP) or Secured (CHAP). If any of these is used, APN should be entered as "chap:<APN>" or "pap:<APN>" respectively. E.g. if the operator is using APN "internet" with CHAP authentication, it should be entered as "chap: internet". Information about APN and authentication type should be provided by your GSM operator.
Server settings
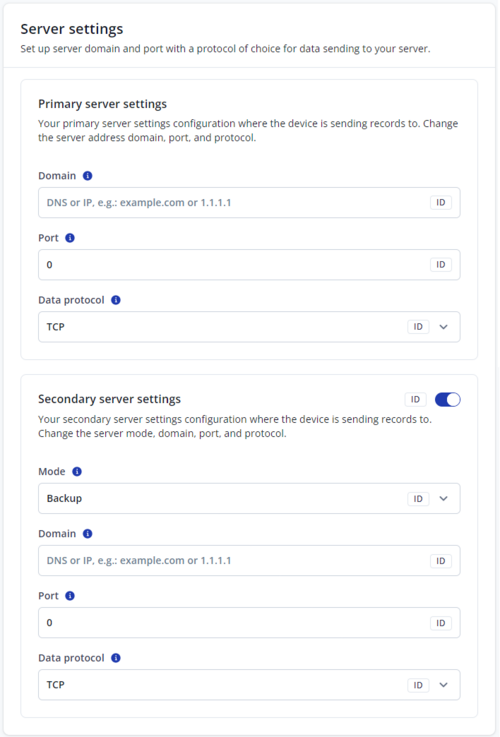
Primary server settings
Domain
- Server or Domain address, either IP address or Domain can be written.
Port
- Server Port.
Data protocol
- TCP (Transmission control protocol) or UDP (User datagram protocol). Changing this parameter will alter how the device communicates. From the device side, TCP and UDP work almost the same, the only difference is that UDP doesn't need additional confirmation from the server side, that the data packet was received. TCP has that and uses more network data for the confirmation. The desired data transfer protocol can be selected through the configurator. For more information on the protocol differences of Teltonika devices, refer here [1]
Secondary server settings
Mode
- Backup - the device will send data to a secondary server only if the primary server is not reachable.
- Duplicate - the device will send data to both servers.
Server communication settings
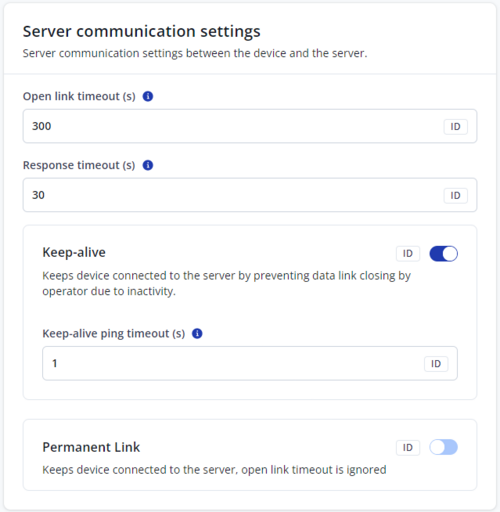
Open link timeout (s)
- The parameter is used to define a timeout between the fleet management device and the server. If the device has sent all records, the device holds the link for the duration of the configured timeout. The “Open link timeout” timer will refresh after the device sends a new record. If there is a need to keep a constant link with a server, increasing the value of the parameter is needed.
Response timeout (s)
- It is used to set a period waiting for the response from the server side. If there is no response from the server during the timeout, the device will close the link and according to device configuration resend the same packet.
Keep-alive ping timeout (s)
- The device will ping the server periodically, so the server or operator will not close the link. The keep-alive ping timeout value should always be lower than the open link timeout.
Permanent link
- The permanent link feature is designed to establish and maintain a continuous connection with the main server, enabling access to and management of the device through GPRS commands. After the device starts, it attempts to connect to the main server as soon as possible. If the device fails to establish a connection or if the connection is lost, it will continuously retry to connect to the main server. This retry process will continue indefinitely unless the permanent link feature is disabled. When Permanent link feature is enabled, device ignores Open Link Timeout.
Network settings
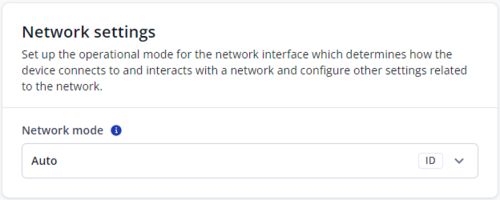
Configure the operational mode of the network interface to define how the device connects to and interacts with the network, and adjust other related network settings.
Network mode
- Auto - Let modem decide
- 2G mode only
- 4G mode only
FOTA WEB settings
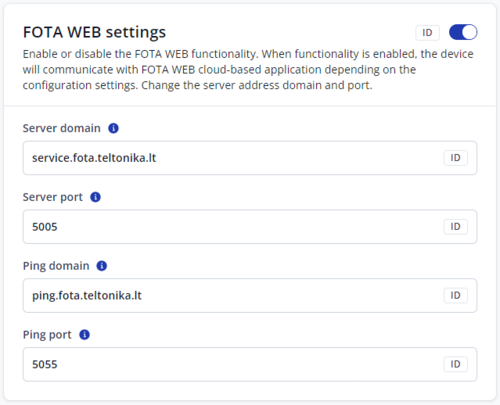
Enable or disable connection to FOTA WEB. When functionality is enabled, the device will communicate with FOTA WEB cloud-based application depending on the configuration settings.
Server domain
- Address which points to FOTA WEB.
- It is a secure TLS/TCP server which is used for safe data exchange. Connection to this server will happen only after Ping server confirms it.
Port
- FOTA Web port for connection to FOTA WEB.
Ping domain
- Address which points to FOTA WEB ping server.
- It is a light UDP service, only used to check if connection to main server is needed. Device always pings this server first.
Ping port
- FOTA Web ping server port.
