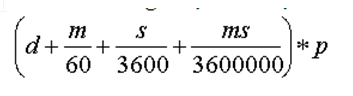Codec: Difference between revisions
| Line 159: | Line 159: | ||
| |... || | | |... || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="background: black; color: white;"| | | style="background: black; color: white;"|N2’th IO ID || 1 byte | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="background: black; color: white;"| | | style="background: black; color: white;"|N2’th IO Value || 2 bytes | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="background: black; color: white;"| | | style="background: black; color: white;"|N4 of Four Bytes || 1 byte | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="background: black; color: white;"| | | style="background: black; color: white;"|1’st IO ID || 1 byte | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="background: black; color: white;"| | | style="background: black; color: white;"|1’st IO Value || 4 byte | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | |... || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="background: black; color: white;"| | | style="background: black; color: white;"|N4’th IO ID || 1 byte | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="background: black; color: white;"| | | style="background: black; color: white;"|N4’th IO Value || 4 bytes | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="background: black; color: white;"| | | style="background: black; color: white;"|N8 of Eight Bytes || 1 byte | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="background: black; color: white;"| | | style="background: black; color: white;"|1’st IO ID || 1 byte | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="background: black; color: white;"| | | style="background: black; color: white;"|1’st IO Value || 8 bytes | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | |... || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="background: black; color: white;"| | | style="background: black; color: white;"|N8’th IO ID || 1 byte | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="background: black; color: white;"| | | style="background: black; color: white;"|N8’th IO Value || 8 bytes | ||
|} | |} | ||
Event IO ID – if data is acquired on event – this field defines which IO property has changed and generated an event. If data cause is not event – the value is 0. | Event IO ID – if data is acquired on event – this field defines which IO property has changed and generated an event. If data cause is not event – the value is 0. | ||
Revision as of 14:36, 30 October 2018
Introduction
A codec is a device or computer program for encoding or decoding a digital data stream or signal. Codec is a portmanteau of coder-decoder. A codec encodes a data stream or a signal for transmission and storage, possibly in encrypted form, and the decoder function reverses the encoding for playback or editing.
Codec ID table
| Codec 8 | Codec 8 extended | Codec 12 | Codec 13 | Codec 16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0x08 | 0x8E | 0x0C | 0x0D | 0x10 |
Codec 8
- AVL data packet
Because the smallest information amount that can be written is one bit, there can be some bits left unused when result is byte array. Any unused bits should be left blank.
Below table represents AVL data packet structure.
| 4 zeros | Data field length | Codec ID | Number of Data 1 | AVL Data | Number of Data 2 | CRC-16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 bytes | 4 bytes | 1 byte | 1 byte | 30-147 bytes | 1 byte | 4 bytes |
Number of data – number of encoded data (number of records). Codec ID is constant 08.
Data field length is the length of bytes [codec id, number of data 2]. Number of data 1 should always be equal to number of data 2 byte. CRC-16 is 4 bytes, but first two are zeroes and last two are CRC-16 calculated for [codec id, number of data 2] Minimum AVL packet size is 45 bytes (all IO elements disabled). Maximum AVL packet size for one record is 783 bytes.
- AVL data
| Timestamp | Priority | GPS Element | IO element |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8 bytes | 1 byte | 15 bytes | 6-123 |
Timestamp – difference, in milliseconds, between the current time and midnight, January 1, 1970 UTC
- Priority
| 0 | Low |
| 1 | High |
| 2 | Panic |
- GPS Element
| Longtitude | Latitude | Alitude | Angle | Stellites | Speed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 bytes | 4 bytes | 2 bytes | 2 bytes | 1 bytes | 2 bytes |
X Longitude
Y Latitude1
Altitude In meters above sea level1
Angle In degrees, 0 is north, increasing clock-wise 1
Satellites Number of visible satellites1
Speed Speed in km/h. 0x0000 if GPS data is invalid1
Longitude and latitude are integer values built from degrees, minutes, seconds and milliseconds by formula
d - Degrees
m - Minutes
s - Seconds
ms - Milliseconds
p - Precision (10000000)
If longitude is in west or latitude in south, multiply result by –1. To determine if the coordinate is negative, convert it to binary format and check the very first bit. If it is 0, coordinate is positive, if it is 1, coordinate is negative.
Example:
Received value: 20 9c ca 80 Converted to BIN: 00100000 10011100 11001010 10000000 first bit is 0, which means coordinate is positive Convered to DEC: 547146368 For more information see two‘s compliment arithmetics.
- IO Element
| Event IO ID | 1 byte |
| N of Total IO | 1 byte |
| N1 of One Byte IO | 1 byte |
| 1’st IO ID | 1 byte |
| 1’st IO Value | 1 byte |
| ... | |
| N1’th IO ID | 1 byte |
| N1’th IO Value | 1 byte |
| N2 of Two Bytes | 1 byte |
| 1’st IO ID | 1 byte |
| 1’st IO Value | 2 bytes |
| ... | |
| N2’th IO ID | 1 byte |
| N2’th IO Value | 2 bytes |
| N4 of Four Bytes | 1 byte |
| 1’st IO ID | 1 byte |
| 1’st IO Value | 4 byte |
| ... | |
| N4’th IO ID | 1 byte |
| N4’th IO Value | 4 bytes |
| N8 of Eight Bytes | 1 byte |
| 1’st IO ID | 1 byte |
| 1’st IO Value | 8 bytes |
| ... | |
| N8’th IO ID | 1 byte |
| N8’th IO Value | 8 bytes |
Event IO ID – if data is acquired on event – this field defines which IO property has changed and generated an event. If data cause is not event – the value is 0.
N total number of properties coming with record (N=N1+N2+N4+N8)
N1 number of properties, which length is 1 byte
N2 number of properties, which length is 2 bytes
N4 number of properties, which length is 4 bytes
N8 number of properties, which length is 8 bytes
Example
Received data: