FMB640 First Start: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|+ | |+ | ||
! style="background: white; color: # | ! style="width:10%; border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #0054A6; background: white; color: #0054A6; text-align: left;"| PIN NUMBER | ||
! style="width:40%; border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #0054A6; background: white; color: #0054A6; text-align: left;"| PIN NAME | |||
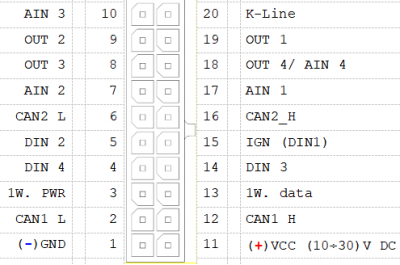
| style=" | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: center; background: white;" rowspan="21" | [[Image:Fmb_640_2x12_pinout.png|400px|center]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="text-align: left; background: | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: center; background: white;"| 1 | ||
| style="text-align: left; background: | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: center; background: white;"| ( - ) Ground pin. (10…30) V DC* | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="text-align: left; background: | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: center; background: white;"| 2 | ||
| style="text-align: left; background: | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: center; background: white;"| SAE J1939 CAN interface Low channel 1 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="text-align: left; background: | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: center; background: white;"| 3 | ||
| style="text-align: left; background: | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: center; background: white;"| Power supply pin for Dallas 1-Wire® devices | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="text-align: left; background: | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: center; background: white;"| 4 | ||
| style="text-align: left; background: | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: center; background: white;"| Digital input. Channel 4 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="text-align: left; background: | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: center; background: white;"| 5 | ||
| style="text-align: left; background: | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: center; background: white;"| Digital input. Channel 2 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="text-align: left; background: | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: center; background: white;"| 6 | ||
| style="text-align: left; background: | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: center; background: white;"| SAE J1939 CAN interface Low channel 2 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="text-align: left; background: | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: center; background: white;"| 7 | ||
| style="text-align: left; background: | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: center; background: white;"| Analog input, channel 2. Input range: 0 - 30V/ 0 - 10V DC | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="text-align: left; background: | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: center; background: white;"| 8 | ||
| style="text-align: left; background: | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: center; background: white;"| Digital output. Channel 3. Open collector output | ||
|-FFA500 | |-FFA500 | ||
| style="text-align: left; background: | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: center; background: white;"| 9 | ||
| style="text-align: left; background: | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: center; background: white;"| Digital output. Channel 2. Open collector output | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="text-align: left; background: | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: center; background: white;"| 10 | ||
| style="text-align: left; background: | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: center; background: white;"| Analog input, channel 3. Input range: 0 - 30V/ 0 - 10V DC | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="text-align: left; background: | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: center; background: white;"| 11 | ||
| style="text-align: left; background: | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: center; background: white;"| Power supply pin | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="text-align: left; background: | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: center; background: white;"| 12 | ||
| style="text-align: left; background: | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: center; background: white;"| SAE J1939 CAN interface High channel 1 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="text-align: left; background: | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: center; background: white;"| 13 | ||
| style="text-align: left; background: | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: center; background: white;"| Data channel for Dallas 1-Wire® devices | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="text-align: left; background: | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: center; background: white;"| 14 | ||
| style="text-align: left; background: | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: center; background: white;"| Digital input, channel 3 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="text-align: left; background: | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: center; background: white;"| 15 | ||
| style="text-align: left; background: | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: center; background: white;"| Digital input, channel 1 (RESERVED FOR IGNITION LINE) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="text-align: left; background: | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: center; background: white;"| 16 | ||
| style="text-align: left; background: | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: center; background: white;"| SAE J1939 CAN interface High channel 2 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="text-align: left; background: | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: center; background: white;"| 17 | ||
| style="text-align: left; background: | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: center; background: white;"| Analog input, channel 1. Input range: 0 - 30V/ 0 - 10V DC | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="text-align: left; background: | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: center; background: white;"| 18 | ||
| style="text-align: left; background: | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: center; background: white;"| Digital output. Channel 4. Open collector output OR Analog input, channel 4. Input range: 0 - 30V/ 0 - 10V DC | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="text-align: left; background: | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: center; background: white;"| 19 | ||
| style="text-align: left; background: | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: center; background: white;"| Digital output. Channel 1. Open collector output | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="text-align: left; background: | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: center; background: white;"| 20 | ||
| style="text-align: left; background: | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: center; background: white;"| K-LINE interface for online Tachograph Vehicle Data transfer | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 15:15, 21 December 2018
Main Page > EOL Products > FMB640 > FMB640 First StartLeading LTE/GNSS/BLE Terminal for advanced applications

How to insert SIM card and connect the battery
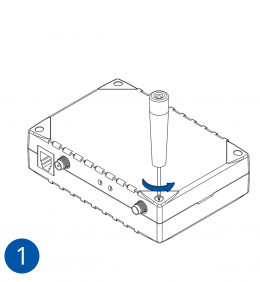
- Unscrew 4 screws counterclockwise that are located on the bottom of the device.
- Remove the cover.
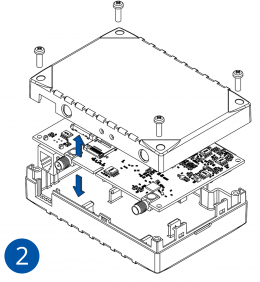
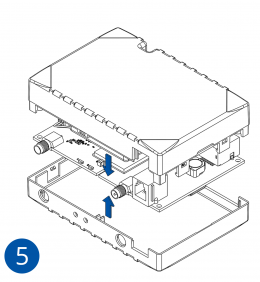
- Insert SIM card as shown with PIN request disabled or read Security info how to enter it later in Teltonika Configurator. Make sure that SIM card cut-off corner is pointing outwards. SIM slot 1 is closer to PCB, SIM slot 2 is the upper one.
- Connect battery as shown to device.
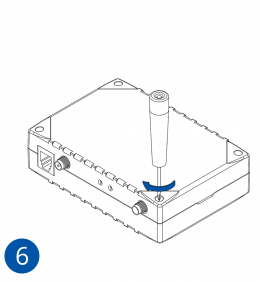
- After configuration, see “PC Connection (Windows)”, attach device cover back.
- Screw in all screws. Device is ready to be mounted.

SIM card insertion/removal must be performed when device is powered off – external voltage and internal battery disconnected. Otherwise SIM card might be damaged or device will not detect it.

FMX6 devices use Standard size SIM cards for SIM1 and SIM2. Currently most of the SIM cards provided by operators can be disassembled into 3 parts - Standard/Micro/Nano. Depending on the SIM card construction - during device usage in harsh conditions, SIM assembly might come apart which causes instability when connecting to operator.
To avoid such risk:
1) If possible - ask operator for Standard SIM card with solid construction (not pre-cut to 3 parts)
2) Do not use SIM cards that were previously disassembled (SIM was taken apart previously)
3) If you plan to use only one SIM card - insert it into SIM1 slot (lower slot) - this ensures greater pressure on SIM contacts as the contact bed is pushed by PCB.
When 2 SIM cards are used simultaneously risk is mitigated as well - when SIM1 is inserted, a greater pressure is applied for SIM2, so SIM parts are harder to come lose
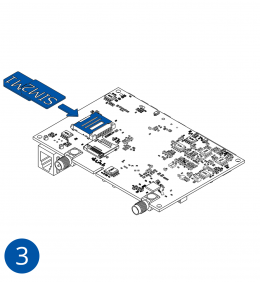
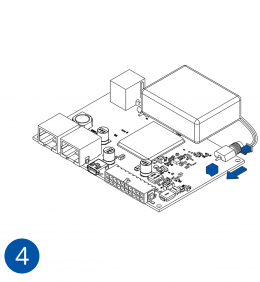
How to insert microSD card into FMB640

- Push microSD card lock case.
- Open microSD card locker.
- Correctly insert microSD card into slot.
- Close microSD card locker.
- Push microSD card lock case to locked position.
2x12 socket pinout
PC Connection (Windows)
- Power-up FMB640 with DC voltage 10-30 V power supply using supplied power cable. LED’s should start blinking, see “FMB640 LED status”.
- Connect device to computer using Micro-USB cable or Bluetooth® connection:
- Using Micro-USB cable
- You will need to install USB drivers, see "How to install USB drivers (Windows)"
- Using Bluetooth®
- FMB640 Bluetooth® is enabled by default. Turn on Bluetooth® on your PC, then select Add Bluetooth® or other device > Bluetooth®. Choose your device named – “FMB640_last_7_imei_digits”, without LE in the end. Enter default password 5555, press Connect and then select Done.
- Using Micro-USB cable
- You are now ready to use the device on your computer.
How to install USB drivers (Windows)
- Please download COM port drivers from here.
- Extract and run TeltonikaCOMDriver.exe.
- Click Next in driver installation window.
- In the following window click Install button.
- Setup will continue installing the driver and eventually the confirmation window will appear. Click Finish to complete the setup.
Configuration (Windows)
At first FMB640 device will have default factory settings set. These settings should be changed according to the user's needs.
Main configuration can be performed via Teltonika Configurator software. Get the latest FMB640 Configurator version from here. Configurator operates on Microsoft Windows OS and uses prerequisite MS .NET Framework. Make sure you have the correct version installed.
| MS .NET requirements | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Operating system | MS .NET Framework version | Version | Link |
|
MS .NET Framework 8.0 | 64 bit | .NET Framework |
Downloaded Configurator will be in compressed archive. Extract it and launch Configurator.exe. After launch software language can be changed by clicking ![]() in the right bottom corner:
in the right bottom corner:
Configuration process begins by pressing on connected device:
After connection to Configurator Status window will be displayed:
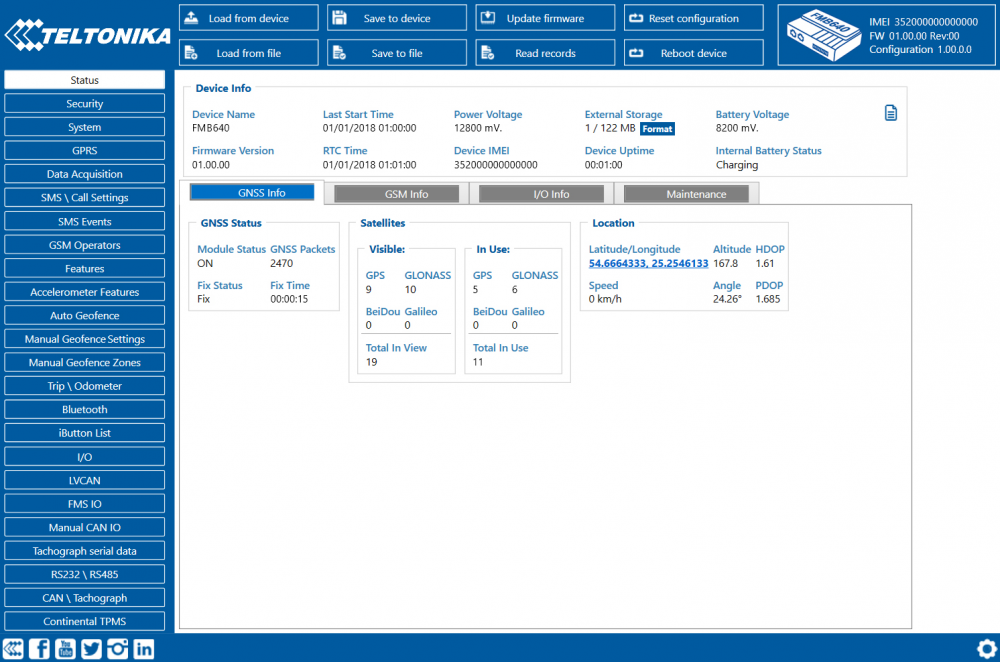
Various Status window tabs display information about GNSS, GSM, I/O, Maintenance and etc. FMB640 has one user editable profile, which can be loaded and saved to the device. After any modification of configuration the changes need to be saved to device using Save to device button. Main buttons offer following functionality:
 Load from device – loads configuration from device.
Load from device – loads configuration from device. Save to device – saves configuration to device.
Save to device – saves configuration to device. Load from file – loads configuration from file.
Load from file – loads configuration from file. Save to file – saves configuration to file.
Save to file – saves configuration to file. Update firmware – updates firmware on device.
Update firmware – updates firmware on device. Read records – read records from device.
Read records – read records from device. Reboot device – restarts device.
Reboot device – restarts device. Reset configuration – sets device configuration to default.
Reset configuration – sets device configuration to default.
Most important configurator section is GPRS – where all your server and GPRS settings can be configured and Data Acquisition – where data acquiring parameters can be configured. More details about FMB640 configuration using Configurator can be found here.
Quick SMS configuration
Default configuration has optimal parameters present to ensure best performance of track quality and data usage.
Quickly set up your device by sending this SMS command to it:
" setparam 2001:APN;2002:APN_username;2003:APN_password;2004:Domain;2005:Port;2006:0"
GPRS settings:
- 2001 – APN
- 2002 – APN username (if there are no APN username, empty field should be left)
- 2003 – APN password (if there are no APN password, empty field should be left)
Server settings:
- 2004 – Domain
- 2005 – Port
- 2006 – Data sending protocol (0 – TCP, 1 – UDP)
Note: Before SMS text, two space symbols should be inserted.
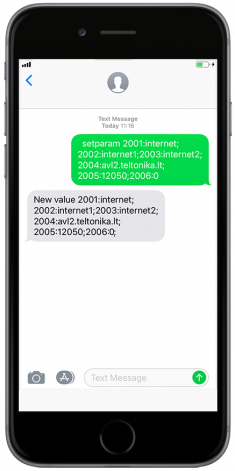
After successful SMS configuration, FMB640 device will synchronize time and update records to configured server. Time intervals and default I/O elements can be changed by using Teltonika Configurator or SMS parameters.
Mounting recommendations
- Connecting wires
- Wires should be connected while the module is not plugged in.
- Wires should be fastened to stable wires or other non-moving parts. Any heat emitting and/or moving objects should be kept away from the wires.
- There should be no exposed wires. If factory isolation was removed while connecting the wires, the isolation material should be applied.
- If the wires are placed in the exterior or in places where they can be damaged or exposed to heat, humidity, dirt, etc., additional isolation should be applied and the wires should not be loose.
- Wires cannot be connected to the board computers or control units.
- Connecting power source
- Be sure that after the car computer goes to sleep mode, power might be still available on the power wires. Depending on the car model, this may happen in 5 to 30 minutes period.
- When the module is connected, measure the voltage again to make sure it did not decrease.
- It is recommended to connect to the main power cable in the fuse box.
- 3 A, 125 V external fuse shall be used.
- Connecting ignition wire
- Be sure to check if it is a real ignition wire i. e. power does not disappear after starting the engine.
- Check if this is not an ACC wire (when key is in the first position, most of the vehicle electronics are available).
- Check if power is still available when you turn off any of vehicles devices.
- Ignition is connected to the ignition relay output. As alternative, any other relay, which has power output when ignition is on, may be chosen.
- Connecting ground wire
- Ground wire is connected to the vehicle frame or metal parts that are fixed to the frame.
- If the wire is fixed with the bolt, the loop must be connected to the end of the wire.
- For better contact scrub paint from the spot where loop is going to be connected.
 |
PAY ATTENTION! Connecting the power supply must be carried out in a very low impedance point of on-board vehicle network. These points in the car are the battery terminals. Therefore, we recommend connecting the power of FMB640 (GND and POWER wires) directly to the battery terminals. Another valid option is to connect the wires to the main POWER cable inside the fuse box (if there is none, then to the power supply where the fuses of vehicle’s computer are), GND wire must be connected in a special point, designed to connect GND vehicle computer. Connecting the GND at an arbitrary point to the mass of the car is unacceptable, as static and dynamic potentials on the line GND will be unpredictable, which can lead to unstable FMB640 operation and even its failure. |
Safety information
This message contains information on how to operate FMB640 safely. By following these requirements and recommendations, you will avoid dangerous situations. You must read these instructions carefully and follow them strictly before operating the device!
- The device uses SELV limited power source. The nominal voltage is +12 V DC. The allowed voltage range is +10..+30 V DC.
- To avoid mechanical damage, it is advised to transport the device in an impact-proof package. Before usage, the device should be placed so that its LED indicators are visible. They show the status of device operation.
- When connecting the 2x6 connector wires to the vehicle, the appropriate jumpers of the vehicle power supply should be disconnected.
- Before unmounting the device from the vehicle, the 2x6 connector must be disconnected.
- The device is designed to be mounted in a zone of limited access, which is inaccessible to the operator. All related devices must meet the requirements of EN 60950-1 standard.
- The device FMB640 is not designed as a navigational device for boats.