Difference between revisions of "Test Dual Cam wiki"
| Line 146: | Line 146: | ||
* [[Teltonika Dualcam REACH|Teltonika DualCam REACH]] | * [[Teltonika Dualcam REACH|Teltonika DualCam REACH]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Camera ping transmission and TF status checking== | ==Camera ping transmission and TF status checking== | ||
Revision as of 09:50, 14 July 2022
Teltonika DualCam is connected to FMB125,FMC125 and FMB225, FMC225 devices using the RS232 interface.

Video file conversion
Video files and conversion
Videos downloaded from the camera are in the raw h265 format. By default, they could be viewed using the ZMVideoPlayer program in the h265 format. If the videos are needed in a more common format, they can be converted.
Video conversion example and settings
For converting DualCam h265 videos to a more popular mp4 video format, a free open-source converter FFmpeg is used in the example. Although any other converter from h265 would work as well.
To convert DualCam video properly, the converter has to know the frame rate of the video. The frame rate is configured as Config Id: 66003 and could be either 20, 25, or 30 FPS. That same value could be obtained by using the metadata command (see more details at File metadata response (CMD ID 0x000B)).
Recommended parameters using the FFmpeg for the conversion:
ffmpeg -r <fps> -i <input>.h265 -ss 00:00:0.9 -c:a copy -c:v libx264 <output>.mp4
<fps> - configured frame rate of the video;
<input> - file name of the video file from the camera;
<output> - file name of the video that will be converted to mp4.
Firmware Version
We are always improving our device's performance, stability, and reliability.
This document describes DualCAM platform and FMX125 devices' firmware improvements, changes, new features implementations as well as current firmware release version.
Firmware download for FMX125 and DualCam:
Link: Firmware
Password: 3RpOAf96
| FIRMWARE VERSION | RELEASE DATE | CHANGES |
|---|---|---|
| 03.27.13.Rev.362 |
2022-06-17 |
|
| 03.27.07.Rev.365 |
2022-03-17 |
|
| 03.27.07.Rev.361 |
2021-09-17 |
|
| 03.27.07.Rev.360 |
2021-08-30 |
|
| 03.27.03.Rev.104 |
2021-06-18 |
|
| 03.27.00.Rev.100 |
2021-02-19 |
|
| DUALCAM FIRMWARE VERSION | RELEASE DATE | CHANGES |
|---|---|---|
| V2.2.3 |
2022-05-20 |
|
| V2.2.2 |
2022-01-06 |
|
| V1.9.3 |
2021-07-15 |
|
| V1.9.2 |
2021-06-02 |
|
| V1.9.0 |
2021- 02-19 |
|
Certifications & Approvals
Camera ping transmission and TF status checking
Camera pinging was implemented to periodically check if a camera is connected to a device. This is done via “Get TF status” command for both front and rear camera every 20 seconds when ignition is on. The received result from this command is stored in two corresponding AVL elements “Front camera state” and “Rear camera state”. The following do not only store TF status, but also if response from the camera was received or not.
| Parameter name | Parameter AVL ID | Parameter values |
|---|---|---|
| Front camera state: | 498 | 0 - Camera not detected |
| 1 - No card | ||
| Rear camera state: | 497 | |
| 2 - Card mount failed | ||
| 3 - Card mounted | ||
| 4 - Card faulty |
How to read camera data from SD card
The software for reading camera data can be downloaded here
Data reading steps:
- Double-click “VideoPlayer.exe” to open the player
- When the software starts, first select the directory where the TF card files are located. Once located, click "OK". The software starts analyzing the pictures and videos existing in the TF card files.
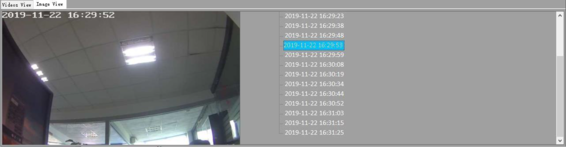
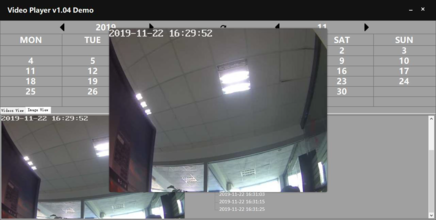
- Software will automatically detect the video and picture in the TF card files, which will last for a few seconds and then enter the software, as shown.,
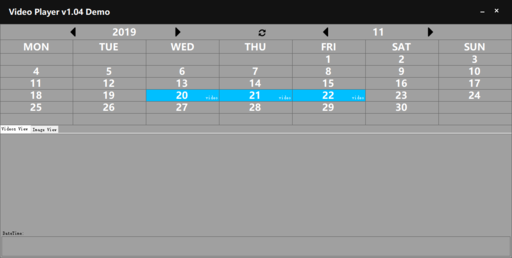
The upper part of the software is a calendar. You can choose to view whether there is a
video in the current month according to the year and month. The number of the year/month can be entered by keyboard after selecting it, and then press the “Enter” key to jump to the entered year/month. You can press ![]() to view the previous year/month and
to view the previous year/month and ![]() to view the next year/month. The date of the recorded video in the current month will be marked in blue. The lower part of the software is the preview interface, divided into two parts: "Video View" and "Image View".
to view the next year/month. The date of the recorded video in the current month will be marked in blue. The lower part of the software is the preview interface, divided into two parts: "Video View" and "Image View".
Video View
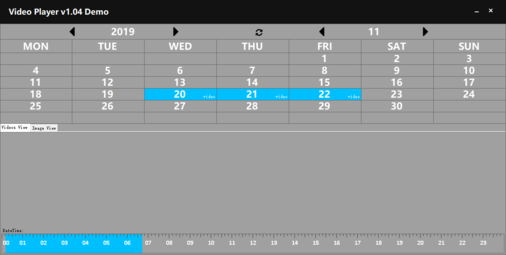
Video view shows the video information. Left click on the date of the video in the calendar, then the following "Video View" section will show which time period there is a video, as shown. For video recording, the time period during which the video is recorded will be marked in blue.
Click on the blue part of the timeline to get the time you clicked, and the video thumbnail of the current time will be displayed in the middle of the screen. The timeline length is 24 hours and it is difficult to locate the exact number of seconds. Hold down the timeline with the left mouse button and then swipe to the right to zoom in on the timeline. For example, we need to carefully view the video at 05:00-07:00. Then, the left mouse button is pressed at the 05:00 position and slide to the right to the position of 07:00, so that this part of time can be enlarged to the entire timeline.
Note: If you need to restore, then left-click and hold the time axis to slide left.
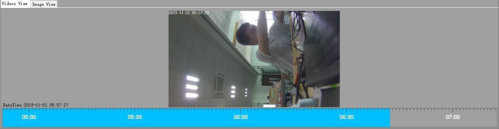
Video Playback
Left click on the timeline will view the video thumbnail of the clicked time point, and double click the left mouse button to start playing the video from the current time. By default, the video will be played for two minutes from the selected time. If you click to find the location you want to play, you don't need to move the mouse, double click again will pop up the play form.
| Video playback interface contains | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Stop button | Speed up
play button | ||
| Pause button | Screenshot
button | ||
| Slow down
play button |
Full screen
button | ||
Note: Closing the current playback interface does not exit the player software.
Image view
"Image View" displays the image information (the camera saves the image in the TF card after the person takes the initiative to take the photo, here you can see the photo taken by the camera). We first click on "Image View" to switch the software to the image page.
After switching to the picture interface, you can view when the photo is taken according to the directory. As shown below, after expanding the index, we can see how many pictures in total were taken.
After the expansion, click the time of the image generation to see the preview on the left side. Clicking on the preview image will pop up the image viewing window. The size of the window is the size of the image itself. The scroll wheel zooms in and out of the picture. You can right click on the preview to save the original image to your hard disk.
Export MP4
Click the "Convert" button ![]() to convert the video in the TF card to MP4 and export it.
to convert the video in the TF card to MP4 and export it.
Then first select the folder you want to export to, enter the MP4 start time and end time to be exported, and then click Export, if you need, cancel the export.

Then wait for the export to complete. The time of export is not certain. Depending on the performance of the computer, it takes about 1 to 5 minutes for each 1-hour duration video.
Camera is configured if all of these conditions are met:
- RS232 mode is selected (DualCam)
- Camera was not configured since startup or one of the related parameters were changed (compression, framerate or OSD)
- Camera file transfer is not active
Active camera reconfiguration is accompanied by two consecutive camera shutter clicks.
If camera is disconnected and later reconnected, a device will detect it by periodic camera ping packet. Once camera is detected, the device will reissue the reconfiguration procedure.
Camera file transfer reconnection
If FMU1YX device has bad reception, server is not reachable or wrong server details are configured, then the device tries to open a link to a camera server few consecutive times. If no connection was possible to be established, then the connection is postponed for 30 minutes and tried again (or tried every configured sending interval if periodic image sending is enabled).
DualCam camera file transfer support
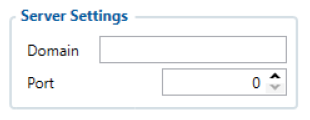
Once camera has at least one file captured, it starts connection to a remote server, which is configured by parameters “Domain” and “Port” found in the “Camera Settings” tab.
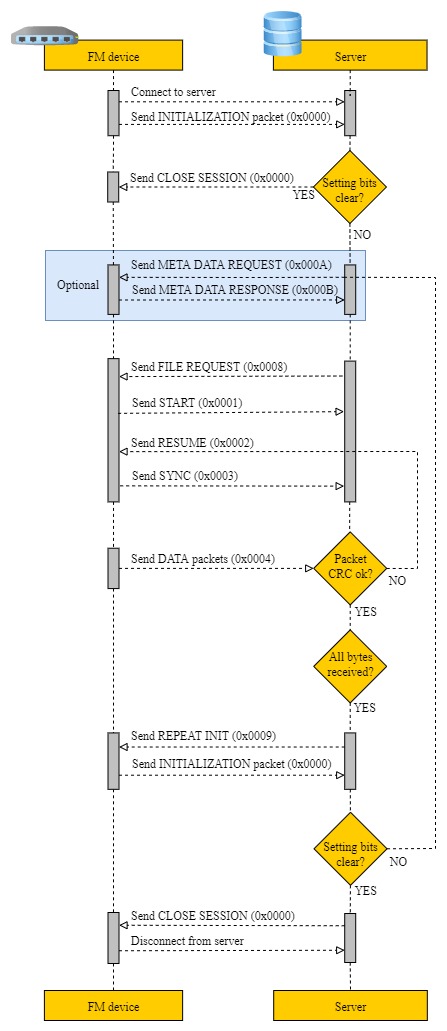
Initialization packet
On connection, a device sends an initialization packet.
| Header(0x0000) | Protocol ID | IMEI | Settings |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 bytes | 2 bytes | 8 bytes | 4 bytes |
Protocol ID – just a reference for the protocol version that is running on a device (for server cross compatibility with older versions). Firmware FMB.Ver.03.27.00.Rev.100 and up have protocol ID 5. Settings flag contains information on what is available for download. Structure is provided below:
| Settings, 4 B | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Byte 3 | Byte 2 | Byte 1 | Byte 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
- Video, rear (%videor)
- Video, front (%videof)
- Photo, rear (%photor)
- Photo, front (%photof)
If identifier sent to a server is not valid, device disconnects.
General command structure
General communication packet structure is as in the table bellow. It consist of CMD_ID (2 bytes), Data length of a command and a payload.
| Command ID | Data length | Data |
|---|---|---|
| 2 bytes | 2 bytes | [data length] bytes |
Communication protocol
Close a session command (CMD ID 0x0000)
In case when a device connects to a server, but the server does not expect it to connect, the server will respond by sending a CLOSE command after which the connection will be terminated. This command is also used when the device connects to a server for a custom file sending and the server finishes to send all custom files to the device.
| Command ID | Data length |
|---|---|
| 0x0000 | 0x0000 |
Start file transfer command (CMD ID 0x0001)
After device received file request command from the server (0x0008) device sends START command with file data (packet count).
| Command ID | Data length | File Packets (4 bytes) | Blank field (2 bytes) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0x0001 | 0x0006 | 0x12345678 | 0x0000 (always same value) |
File request command (CMD ID 0x0008)
After the device is connected for a file upload, the server initiates file transfer by sending a FILE REQ command.
| Command ID | Data length | File Identifier |
|---|---|---|
| 0x0008 | 2 bytes | See the table below |
The device should answer with a START command described above indicating the size and CRC of the requested file.
| File source, type | Identifier (ASCII chars) |
|---|---|
| Photo from camera, rear | %photor |
| Photo from camera, front | %photof |
| Video from camera, rear | %videor |
| Video from camera, front | %videof |
Resume file transfer command (CMD ID 0x0002)
In a response to the START command a RESUME command must be sent from server.
| Command ID | Data length | Packet offset (4 bytes) |
|---|---|---|
| 0x0002 | 0x0004 | 0x00000001 |
To begin file transfer from the start, offset should be set to 1 (4 bytes value). In case when the file transfer was interrupted, to resume file transfer, offset can be set to the desired value (1 ≤ [offset] ≤ [file packets]).
Synchronize file transfer command (CMD ID 0x0003)
In a response to the RESUME command a SYNC command is sent from device.
| Command ID | Data length | File offset (4 bytes) |
|---|---|---|
| 0x0003 | 0x0004 | 0x00000001 |
By sending the SYNC command it is ensured that the next data command will contain file data starting from the specified offset.
File data transfer command (CMD ID 0x0004)
After sending a SYNC command, a file data transfer is started by sending DATA commands.
| Command ID | Data length | File data (up to 1024 bytes) | Data CRC (2 bytes) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0x0004 | 0x0402 | ... | ... |
A File data is split into 1024 byte parts, each part wrapped into a DATA command and is sent.
Note: if a command with a bad CRC is received, RESUME command should be sent with the last valid file offset, after receiving a RESUME command, the server will stop sending DATA commands and continue communication from “Resume file transfer” step.
CRC polynomial expression: 0x8408
The initial value, when calculating CRC, is the previously received packet (CMD ID 0x0004) CRC value.
File transfer status command (CMD ID 0x0005)
After a file transfer is completed and no more files are required from the device, a server should send a COMPLETED command to the device (this command does not work after executing repeat init command0 x0009 – in this case, the server should send a CLOSE SESSION 0x0000 command mentioned before).
| Command ID | Data length | Status (4 bytes) |
|---|---|---|
| 0x0005 | 0x0004 | 0x00000000 |
In case of the server using invalid arguments, commands or not following the file request flow, the device will send this command with a Status field set to one of the few possible error codes. A list of possible ones is provided below.
| Status value (hexadecimal) | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 0x00000000 | File transfer process completed | Sent from server |
| 0x00000002 | Failed to close GPRS | Sent from device |
| 0x00000003 | Failed to close socket | Sent from device |
| 0x00000005 | Invalid response from server to init packet | Sent from device |
| 0x00000011 | This error code forces the device to disconnect from server | Sent from device. Possible causes:
|
After a COMPLETED command device should disconnect from the server.
Initialization packet repeat command (CMD ID 0x0009)
When sent, the initialization packet is repeated. This is used, when all of the files are downloaded and an additional check is carried out for any additional files, that may have been captured during the download operation.
Query file metadata request (CMD ID 0x000A)
This command is used for retrieving extra information about a selected file. A file identifier is used to determine which file’s information will be received. File identifiers are identical and used in the same way as in the File Request Command (0x0008).
| Command ID (2 bytes) | Data length (2 bytes) | File Identifier (7 bytes) |
|---|---|---|
| 0x000A | 0x0007 | 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFF |
Can be sent after the initialization packet or after the file transfer is complete. It is not a mandatory command and doesn’t have to be used. The response for this command is 0x000B (more details below).
Note: 0x000A command was added since 03.27.04.Rev.104 firmware version and would not work with older versions.
File metadata response (CMD ID 0x000B)
0x000B is a response command to the request command 0x000A.
Response command returns information about a specified file: file type, timestamp, trigger, and video length. Complete command’s structure:
| Command ID (2 bytes) | Data length (2 bytes) | Command version (1 byte) | File type (1 byte) | Timestamp (8 bytes) | Trigger (1 byte) | Video length (2 bytes) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0x000B | 0x000D | 0xFF | 0xFF | 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFF | 0xFF | 0xFFFF |
Note: 0x000B command was added since 03.27.04.Rev.104 firmware version and would not work with older versions.
Response command meta data:
| Data | Description |
|---|---|
| Command version | Iteration of the command itself to determine to parse of the data |
| File type | Media type for confirming which file’s metadata is received. Byte structure is the same as byte 3 in the initialization packet settings data |
| Timestamp | Timestamp at the time of the trigger. Same used in a corresponding SOS record |
| Trigger | Trigger values. Same values as video sending trigger in SOS record. |
| Video length | Duration of the video in seconds. If the file type is a photo, this value is 0x0000. |
File transfer visual flow
DualCam update procedure
NOTE: This update procedure is for the DualCam which has 1.9.3 firmware version, if you already have DualCam firmware version 2.2.1, 2.2.2 or 2.2.3 skip to step 10.
Firmware download for FMX125 and DualCam:
Link: https://drive.teltonika.lt/d/e5c4b09a60b74fa5b6a0/
Password: 3RpOAf96
DualCam firmware video update
Before the update, FMx125 has to be updated first. The latest camera firmware requires 03.27.13.Rev.362 or newer firmware. After FMx125 update, update of the camera can start:
1 Connect the camera to the FMx125. Power up, wait for the configuration finish (about 30 seconds after power up).
2 Ensure, that power supply at all times has stable 14V and not less that 2.5A output. If update is performed with the camera, that is installed in the vehicle, it is strongly recommended to have the engine running for stable alternator power supply.
3 Make sure that the camera works and responds (for example, try getting an image or try sending “camgetver” and check whether for both front and rear camera firmware versions are returned).
4 Format the SD cards of both cameras using SMS command "camget_sdformat:<cam id>". Cam id is the same as in “camreq”: 1 - Front Camera, 2 - Rear Camera. For example:
camget_sdformat:1
camget_sdformat:2
Our device will return success if the format goes well. The result returned of a successful SD card format: Camera front/rear SD Card format success
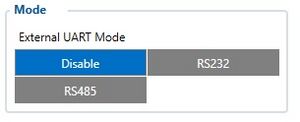
5 After the cards are formatted, power off everything, disconnect the camera from FMx125 and take out the SD cards. If disconnecting FMx125 from the DualCam is not possible, disable external UART mode from the configuration:
6 After taking out SD cards, write the firmware file of V2.2.0 to the root of both (front/rear) SD cards. Do not rename the firmware file, it has to be as it is, "JPEG_IPC_APP".
7 Put the cards back in, power the camera on. Do not reconnect the camera to the FMx125 or configure RS232 mode back yet.
8 Wait 60-90s for 2.2.0 version (for 2.2.3 version wait 120s). You should hear a click from the rear camera after the update succeeds. That click sound indicates restart of the rear camera which happens after successful firmware update.
9 Even if you don't hear the clicking sound, reconnect the camera to the FMx125 (or reconfigure RS232 mode back to DualCam) after few minutes anyway and send SMS “camgetver” command to check the versions.
At this point the command should return “Front/Rear camera camgetver failed.” If it does, it does not mean a problem, because V2.2.0 is a transitional firmware and it does not return version. Therefore, if the camera was returning V1.9.3/1.9.2 or other 1.9.X version, this means it has updated to the V2.2.0 successfully and update procedure can continue.
10 Format SD cards again as it is in step 4 and disconnect from the camera the FMx125. After that go with step 11.
11 Take the cards out and write the firmware files of V2.2.1 V2.2.2 and V2.2.3 to the root of both SD cards. The file name is“ALL221_IPC_BIN”, “ALL222_IPC_BIN” and “ALL223_IPC_BIN”. Again, do not rename it. (You must write 3 files to the SD card)
12 Repeat steps 7, and 8. After that go with step 13.
Note: Only for 2.2.3 version wait 120 second
13 Now, if all went successfully, return to the “camgetver” should return this: Front camera V2.2.3. Rear camera V2.2.3.
If it does, that means the camera is updated to V2.2.3 successfully.
14 After the update, it would be advisable to format SD cards again.
Potential issues and solutions
Update is pretty straightforward most of the time. However, sometimes the update does not trigger. In case it doesn’t and the camera does not update, check whether it is really disconnected from FMx125 device. If it is, do not power off the camera at first. Keep it powered on and take out and put back in both SD cards. After this, wait 60-90s again and check the firmware version using “camgetver”.
If it still is not updated, disconnect from FMx125, power the camera off for at least 20 seconds and power it back on. Wait for a few minutes and then re-insert the cards again. Reconnect and check the firmware version using “camgetver”.
Can also note that if just one camera updates, only front or only rear, all mentioned solutions and steps could be done to only camera.
Reminder, that the rear camera is with IR LEDs and light sensor and the front one is without them.
Troubleshoot
DualCam Checks
- Check RS232 configuration, baud rate, etc. Default values should be set for the DualCam.
- See if both cameras are working. Try sending separate picture requests and check the result. “camreq:1:1” for the front camera and “camreq:1;2” for the rear camera. Possible responses to "camreq" command - Camera request command
Check camera IO values in the configurator.
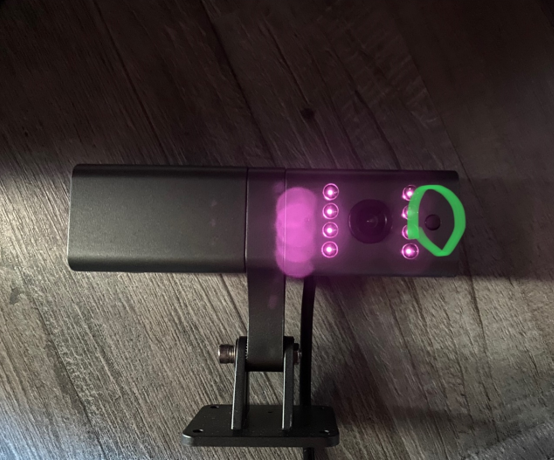
- See if the camera is physically enabled, gets power, and re-check the RS232 connections. You can also test if the camera is physically enabled by covering the light sensor on the rear camera (marked green in the picture below). The rear camera’s IR LEDs should turn on by doing so in a dark environment.
- If the camera seems to be enabled, check the SD card content. See if there are any files and review the footage using TF CardVideoPlayer v1.14. If there is some footage from the time the camera was turned on. The actual time in the camera might differ, therefore check older dates to see if there are any videos.
- If some recent video files were found, it means that the camera is working, but not responding to RS232 commands. Otherwise, the camera is either not working or not responding to commands and does not detect SD card.
Possible solutions
- Camera might have a problem detecting SD card. Format microSD card using FAT32 file system. Try different cards. Try re-inserting the cards while the camera is turned on. Also, keep in mind that the smallest supported card is 16 GB.
- Physical camera restart. Disconnect the camera’s power supply and disconnect from the FMX125 device. Leave the camera for a few minutes like that and power it on but do not connect to the FMX125 for a few minutes. After some time, reconnect the device and check if the camera responds.
- Try firmware update:
- Upload firmware to both SD cards. The firmware file has to be the exact name “JPEG_IPC_APP” name without any extensions.
- Disconnect the camera from the FMX125 device.
- Power the camera off.
- Put the SD cards in.
- Turn the power on but do not connect to the FMX125.
- Wait for 3-5 minutes.
- Turn off the power and reconnect to the FMX125 device.
- Power on the camera with the FMX125 device.
- Check whether Codec8 Extended is enabled. Without Codec8 Extended, parameters of AVL ID 497, 498, 499 WILL not be sent.
If nothing helps and the camera is still not working or working incorrectly, log data using 2;3;9;1 filter and collect the log files.