FTC921 System
Ignition settings
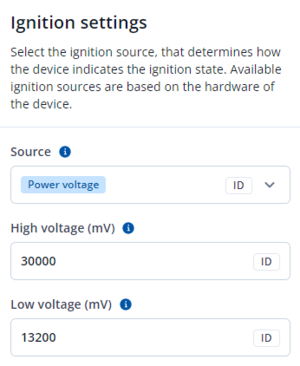
Ignition source will be used to determine ignition of vehicle.
Possible ignition sources:
- DIN 1 (Digital Input 1) - if DIN1 is 1 - ignition is ON; if DIN1 value is 0 - ignition is OFF;
- Power Voltage - if voltage is between High Voltage Level and Low Voltage Level (below Ignition Settings options) - ignition is ON; if voltage is higher than High Voltage Level or lower than Low Voltage Level - ignition is OFF.
- Accelerometer - if movement sensor detects movement - ignition is ON; if movement is not detected - ignition is OFF;
More than one ignition source can be selected at the same moment. When there are 2 or more sources selected, at least one condition has to be met to change Ignition status.
Example: DIN1 and Accelerometer are selected as the Ignition source. When the device detects movement, Ignition status will change to 1, regardless that DIN1 value is 0. Users can select movement start and movement stop delay time - those parameters are used when the accelerometer is selected as an ignition source.
Ignition status is used in power management and the following functionalities: Eco/Green Driving, Excessive Idling, Fuel Consumption, Over Speeding, Towing Detection and Trip.
Movement settings
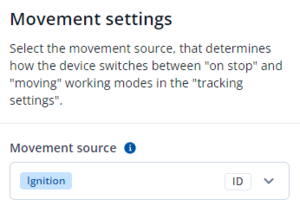
Movement source will be used to determine when a vehicle is on stop or moving.
Possible movement sources:
- Ignition - if ignition (based on ignition source) is ON, Vehicle MOVING mode is used; if the ignition is OFF, Vehicle on STOP mode is used;
- Accelerometer (movement) - if accelerometer detects movement, Vehicle MOVING mode is used; if there is no movement detected, Vehicle on STOP mode is used;
- GNSS - if GPS fix is acquired and speed >= 5 km/h vehicle MOVING mode is used; if GPS speed <5 km/h, Vehicle on STOP mode is used;
GNSS settings
In GNSS Source settings user can configure which GNSS system(s) to use.
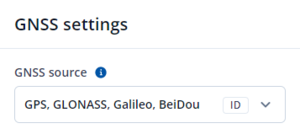
List of configurable GNSS sources:
- GPS
- GPS + GLONASS
- GPS + Galileo
- GPS + BeiDou
- GPS + GLONASS + Galileo + BeiDou
Accelerometer motion detection delays
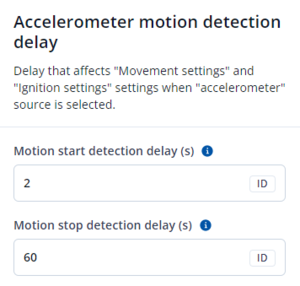
Accelerometer Delay Settings will be use to set timeout of delay when will be detected accelerometer status changes.
Note: these settings impact ignition/movement sources.
The user can set:
- Motion start detection delay - movement start delay in seconds;
- Motion stop detection delay - movement stop delay in seconds;
Sleep settings
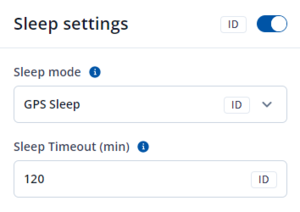
This feature will be used to save power consumption of external battery (power supply). It let the user choose one of four power saving modes which he would prefer: GPS Sleep, Deep Sleep, Online Deep Sleep and Ultra Deep Sleep. Also, after the mentioned options you can find the Timeout (min) parameter which starts counting when the device is in STOP mode. After timeout is reached and all conditions for sleep mode are met, the device goes to sleep mode.
Note: Detail description and conditions about every mode you can find here.
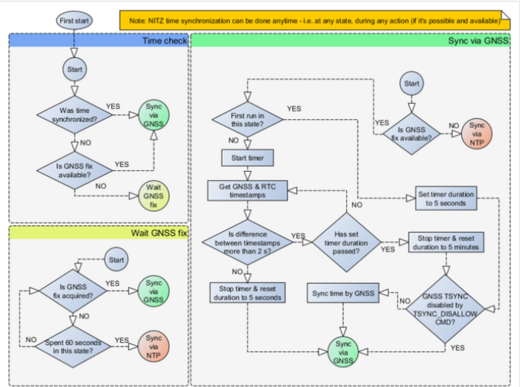
Time synchronization settings
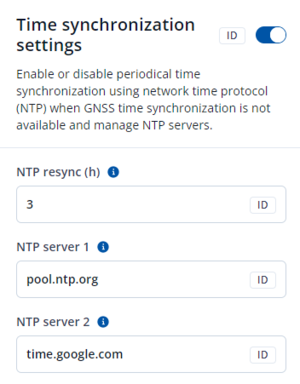
NTP Resync parameter determines how often a device should resynchronize its time. If the set value is not equal to zero, time resynchronization will occur periodically at time intervals to which this parameter is set.
NTP server 1 and NTP Server 2 let the user select which NTP server (s) will be used to re-synchronize time.
Time synchronization works by waiting a minute on startup to acquire fix and consequently synchronizes the time via GNSS.
This state checks the difference between RTC and GNSS times every second. If the difference of at least 3 seconds persists to be for 5 seconds, the firmware triggers a re-synchronization procedure by GNSS.
After that, the time difference is still calculated, but the difference is expected to persist for at least 5 minutes to trigger a GNSS time re-synchronization.
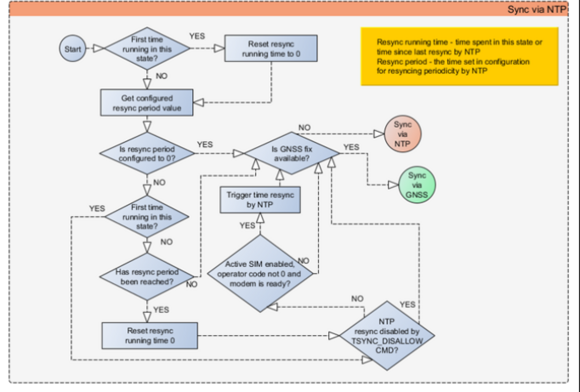
In the case that there is no fix or it is lost during the syncing by GNSS state, the firmware goes to the state of syncing by NTP. Entering the state of NTP syncing, the firmware immediately attempts to synchronize the time by triggering NTP and later on, does this periodically every time the configured NTP re-synchronization time is reached (if the re-synchronization time is set to 0 – no NTP sync is performed at all). Time synchronization by NITZ can occur at any time.