Manual CAN Commands
To use Manual CAN commands functionality user should select Manual CAN Commands tab in Configurator. Afterwards, user will be able to configure CAN parameters in Manual CAN commands settings tab.
Manual CAN Commands
The main benefit of using Manual CAN command functionality is that the user is able to send data via CAN BUS without requiring additional CAN protocol development from the device's firmware side if vehicle should take an action with equipment connected via CAN line. To send command via CAN line with this functionality, the user must have:
- FMC650/FMM650/FMB641 device
| 03.00.13.Rev.05 or newer firmware (for FMC650/FMM650) | 03.01.00.Rev.00 or newer firmware for (FMB641/FMC650/FMM650) |
- Transport or equipment with CAN interface which works via J1939 protocol
- Transport or equipment CAN communication protocol (with information about frames, parameters, ID‘s, Baudrate)
Manual CAN Command I/O settings
User can configure up to 10 Manual CAN I/O commands by setting CAN Type, Data mask, CAN ID, Request Period, Request Data Length parameters. Each CAN I/O has its own parameters and can be configured independently.
Functionality will work only when Ignition will be ON
Baudrates are configurable in CAN \ Tachograph settings for connected CAN line which could be CAN1 or CAN2
- Manual CAN Type parameter - defines which CAN ID type will be received and requested (Standard - 11bit, Extended - 29bit).
- CAN ID/PGN - depends on CAN Type parameter and defines which CAN ID will be received by device
- Data Mask - defines which data mask will be applied to received CAN data. CAN Data mask parameter is 8byte hex value. Displayed data value will be Received Data Value AND Data Mask. In other words - Data Mask parameter defines which data will be taken from the specific frame.
- Request data length - defines data length of requested ID.
- Send type – Could be selected with three different choices:
- Once – it defines request will be sent once if Run On Startup is enabled
- Periodic – it defines the request via CAN will be sent by set period in ms, for configured send count.
- Response – it defines to which MANUAL CAN value will be sent.
- Run On Startup – Enable/disable defines if on Ignition startup will be needed to send a command.
Configuration of Manual CAN commands
Example
In the Tachograph/CAN section the user has to select suitable baudrate. Manual CAN baudrate should be visible in the CAN protocol. If it is not known, the user can try to choose different baudrates to indicate which one works.
Protocol example:
1. Select CAN Type. Normally every CAN protocol documentation should mentioned which CAN type to use. If not, select Extended.
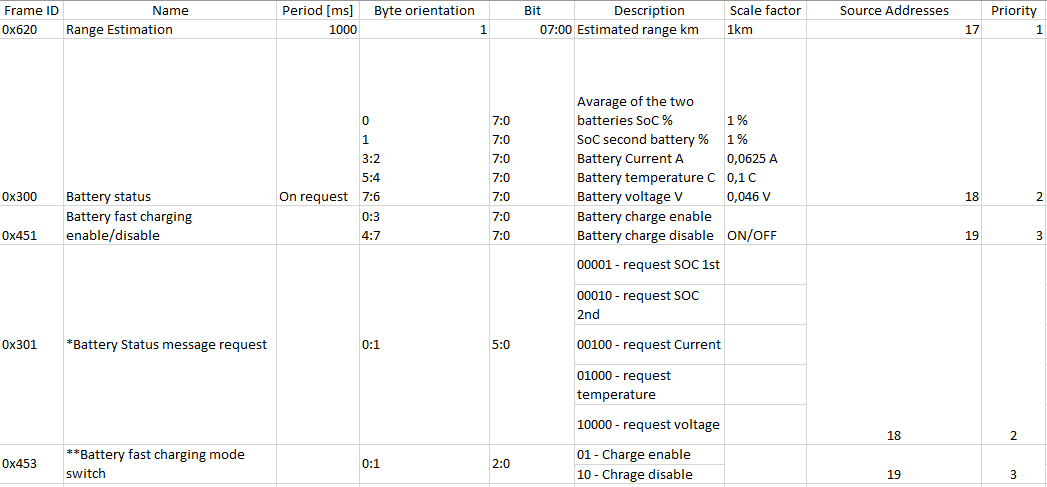
2. Fill in the correct Data mask in Manual CAN command 0 setting. This field determines which IO elements of the frame the user will send via CAN line. As an example, the part of the CAN protocol was taken. First, the user has to locate the data frame, he/she wants to send, for this situation, data frame „Battery fast charge enable/disable “ was taken into account. It holds two states enable or disable. If we would like to send data of frame, in the configurator the user has to configure 0000000000000000 – to disable or 0000000000000001 to enable.
3. For Manual CAN command 0 settings CAN ID it must be written with sources adresses Frame ID and priority – 19045303
4. Request data lenght configured as 8 bytes
5. Send type Once
6. To receive data if the command were permitted correctly in Manual CAN0 we will configure CAN Type Extended.
7. Data mask will have from LSB side selected first two bytes
8. CAN ID will be FF0452FF as we are only interested to receive information about the command status execution.