FMP100 Accelerometer Features settings
Accelerometer Calibration
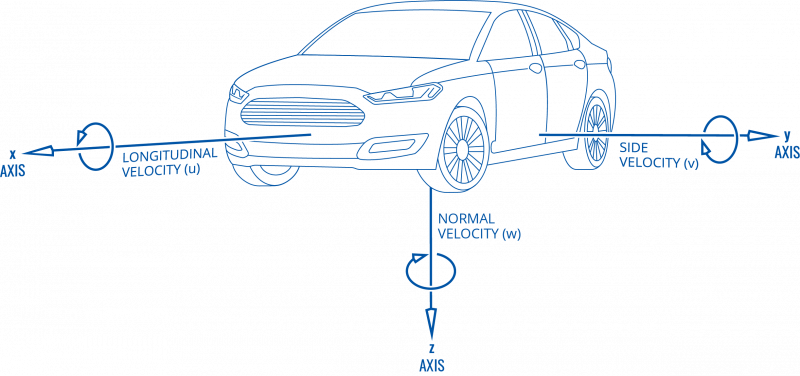
Calibration algorithm is used to recalculate accelerometer axes to represent vehicle‘s axes (see Picture below). Vehicles axes are as follows:
1. X is front.
2. Y is left.
3. Z is down.
Once vehicle‘s axes are calculated, device is considered calibrated.
Note: moving forward along any axis will generate negative values. This means acceleration will generate -X values, accordingly breaking will generate X values. Same goes for other axes.
Configurable parameters can be found at System Settings Accelerometer Auto Calibration
Commands that can be used during calibration:
| Command | Response | Description |
|---|---|---|
| auto_calibrate:set | Yes | Request auto calibration task start |
| auto_calibrate:get | Yes | Request calibration info (time, ground vector, side vector) |
| auto_calibrate:clear | Yes | Request calibration clear from flash and stop calibration task |
| auto_calibrate:status | Yes | Request calibration status and calibration task status |
Auto calibration before firmware version 03.25.07.Rev.00.
Accelerometer auto calibration functionality has one purpose - determine how FMB device
is mounted in a vehicle. After the calibration process eco driving functionality becomes active
and calibration data will be used to determine harsh acceleration, braking and cornering events.
There are two conditions when auto calibration takes place:
- If on device startup no calibration was detected;
- If the device receives an SMS/GPRS message with auto_calibrate:set text.
After functionality has started FMB device periodically checks current appliance GNSS,
ignition and movement source parameters and if the conditions match:
- position fix got;
- GNSS speed is zero;
- ignition is ON;
- first calibration vector was not saved yet;
Then first vector is taken. Saved vector will be considered as ground vector and it will be
used at further calibration calculations.
Note: When FMB device saves first ground vector vehicle must be parked on flat ground.
Crooked vector may have an impact on further calculations.
Afterwards first ground vector was taken, device analyses conditions:
- position fix got;
- GNSS speed is at least 20 km/h;
- ignition is ON;
- second vector was not saved yet;
- vehicle driving in the same direction with 5⁰ tolerance;
- vehicle speed increase by 7km/h within 1 second.
For next vector. Second vector will be taken if all conditions match. Immediately after
second vector is received, it will be multiplied by first (ground) vector, the result of these
vectors is vector multiplication cross product which is the right side of a car. By using
same vector multiplication method, device front, left side will be calculated. At this point
calibration is successfully ended as indication device sends an SMS/GPRS message with
Device is calibrated, to recalibrate send:auto_calibrate:set.
Note: SMS/GPRS message will be sent only if auto calibration functionality was triggered by
SMS/GPRS message.
For user convenience in case auto calibration functionality fails then notification message
will be sent. For exact messages, check algorithm section.
Note: SMS/GPRS message will be sent only if auto calibration functionality was triggered by
SMS/GPRS message.
To get current calibration status auto_calibrate:get SMS/GPRS command must be sent to
the device. If device is calibrated it will respond with Calibration state: calibrated or otherwise
Calibration state: not calibrated. Also this command returns saved Ground and Side vectors.
After every TRIP START event, device starts shadow calibration. This type of calibration is
running in parallel with already saved vectors (this means that vectors does not reset until
shadow calibration have both new vectors). After shadow calibration is done, device updates the
vector values to the new ones. There are two conditions when shadow calibration does not run
at TRIP start event:
- Normal calibration is still running.
- Shadow calibration is still running from previous TRIP event.
To take ground vector these conditions should be met:
- Ignition is ON
- Device got GPS FIX
- Vehicle speed = 0km/h
Device will check these conditions every 1sec until they will pass.
To take side vector these conditions should be met:
- Vehicle speed >= 20km/h
- Device got GPS FIX
- Ignition is ON
- Device angle does not change more than 5 degrees in past 1 sec
- Speed need to increase by 7km/h in 1s period.
Device will check these conditions every 1 sec until they will pass.
Auto calibration rework and improvements from firmware version 03.25.07.Rev.00.
- Exponential moving average (EMI) Filter added.
Auto-calibration Improvement
Auto calibration task is launched on one of these conditions (assume calibration is enabled in configuration):
1. Every time device turns on, it checks whether it was previously calibrated and has calibration stored in flash. If device has no calibration in flash, auto calibration task is started.
2. Device calibration was previously disabled by configuration and now is enabled.
3. SMS “auto_calibrate:set” is received. Note: SMS response is sent after calibration has been acquired.
This SMS triggers an SMS response to be sent. Response is sent when calibration is acquired. When 1 hour passes without successful calibration, failed SMS response is sent.
4. Calibrated device’s mean axes of set interval differ more than set amount from desired (0,0,1) calibration is considered inaccurate. Calibration is deleted from flash and auto calibration task started.
After auto calibration task has been started, it will go on indefinitely until satisfactory calibration is acquired.
Data Required
Auto calibration need to fill two buffers to calibrate device:
1. All accelerometer data – buffer which collects all data from accelerometer at 10Hz frequency. To fill this buffer set seconds of data samples are needed. When buffer is full, oldest data is dumped and new data is placed into the buffer.
2. Straight accelerometer data – buffer which collect straight accelerations data from accelerometer at 10Hz frequency. To fill this buffer set seconds of data samples (set times Hz samples) are needed. When buffer is full, oldest data is dumped and new data is placed into the buffer. Algorithm rules to acquire these samples:
2.1. GPS fix is present.
2.2. Ignition is on.
2.3. GPS speed is more than 5 km/h.
2.4. GPS heading is equal to last GPS heading (+/-1 degree) at GPS sample rate 1Hz.
2.5. GPS speed more then 5 km/h from last sample (accelerating).
Once both buffers are full, auto calibration is attempted. If calibrated values pass calibration quality threshold, calculated calibration is written to flash as current calibration – device is calibrated.
Note: If GPS fix is lost or ignition is turned off, buffers’ data is dumped and must be gathered from 0 again.
Re-Calibration
When calibration is present, device checks for re-calibration every 60s indefinitely. Re-calibration requires fix and ignition to run also re-calibration is turned off when vehicle is stopped for more than 15s until conditions are satisfied again. When calibrated device’s mean axes of set interval(calibrated accelerometer data) differ more than set amount from desired (0,0,1) (perfect vehicle’s axes) calibration is considered inaccurate, or device’s position has changed and re-calibration is needed. Calibration is cleared from flash and auto calibration task is started.
Note: turning device around calibrated Z axis will not trigger re-calibration, after turning device around Z axis manual re-calibration is advised. After calibration if quality value is less than 0.80, calibration update functionality is run. Calibration update constantly tries calibrating device in background until 0.80 quality is reached. Calibration update functionality does not change calibration if calculated new calibration quality is less than 0.80.
Excessive Idling
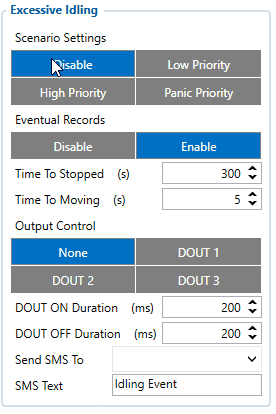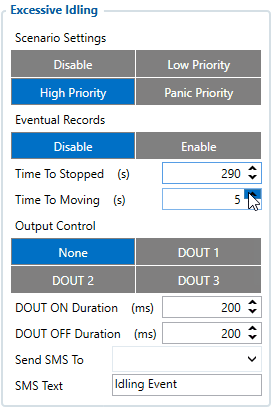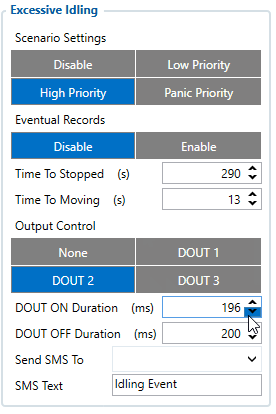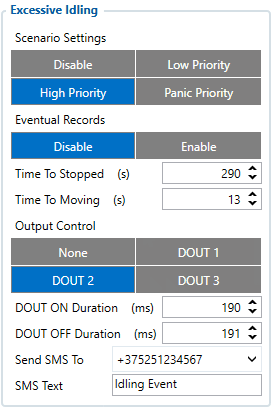
When vehicle stops for a specific amount of time the scenario is activated, a record will be generated and digital output status will be changed to 1 when configured. You can configure the time it takes to turn on this scenario (Time to Stopped). Scenario is activated until the vehicle starts moving (movement is detected only by the accelerometer) and keeps moving for an amount of time that is configured. You can configure the time it takes to turn off this scenario (Time to Moving)
info
Unplug Detection
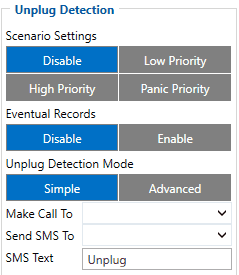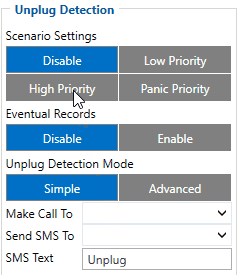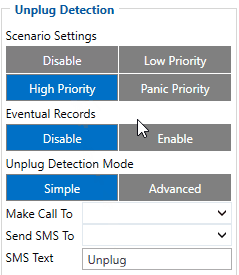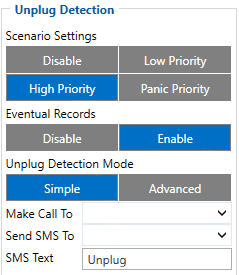
In 03.25.15.Rev.122 version:
If unplug detection scenario is enabled, conditions to determine unplug state are checked every second. Initially external power is checked to set device to appropriate unplug state. If external power is less than 5.25 volts, unplugged state is set, on the other hand, if external power is higher than or equal 5.25 volts, plugged state is set. There are two configurable (id: 11502) unplug detection modes: simple and advanced.
If simple mode is configured:
- Unplug scenario changes states from plugged to unplugged, when external power is less than 5.25 volts AND unplug detection pin is high (meaning that device is pulled out of holder).
- Unplug scenario changes states from unplugged to plugged, when external power is higher than or equal 5.25 volts OR unplug detection pin is low (meaning that device in pushed into the holder) OR these both conditions are true.
If advanced mode is configured:
- Unplug scenario changes states from plugged to unplugged, when unplugged detected by accelerometer flag is set to true AND unplug detection pin is high (meaning that device is pulled out of holder). This unplugged detected by accelerometer flag is set to true when external power is less than 5.25 volts and measured accelerometer threshold exceeds 0.31 mg. Once accelerometer threshold exceeds 0.31 mg it is not going to be measured again until external power will be higher or equal to 5.25 volts.
- Unplug scenario changes states from unplugged to plugged, when external power is higher than or equal 5.25 volts OR unplug detection pin is low (meaning that device in pushed into the holder) OR these both conditions are true.
In 03.27.02.Rev.160 version after base update to 03.27.02.Rev.01 additional condition was introduced when calculating accelerometer measured values in configured advanced mode. This workaround came from version 03.25.15.Rev.03, if no movement detected, z axis is ignored.
Towing Detection
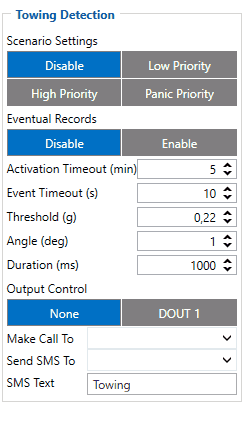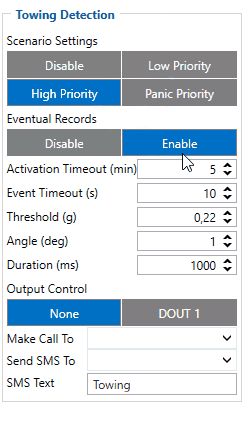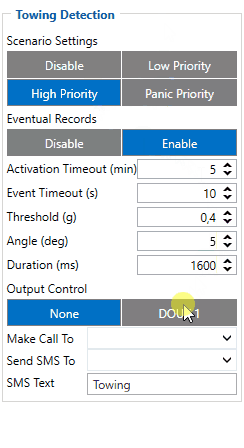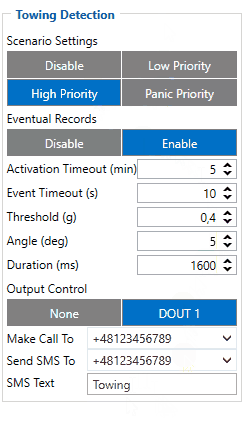
Towing Detection feature helps to inform the driver about unexpected car movement when it was parked. FMB1YX generates an event when a car is being towed or lifted, for example, in a case of vehicle evacuation. FMB1YX activates the towing function when the following conditions are met:
- Ignition (configured Ignition Source) is OFF.
- Activation Timeout is reached.
When the towing function is engaged FMB1YX monitors accelerometer data. If acceleration Threshold or Angle reach configured values for a configured Duration, and Ignition is still OFF for a period of time that is longer than Event Timeout, then an event is generated. When configured, Make Call To and Send SMS To functions make a call or send an SMS to a predefined phone number. The towing function will be reactivated after FMB1YX detects a change of Ignition state from ON to OFF or if the configured Activation Timeout is reached again.
The digital output can be activated for a period of time to warn the driver. Output on-time is configured separately for each featuring case. For more information please refer to DOUT controls.
NOTE: From 03.27.xx firmware version, when the Towing event is detected, the device starts to send data to the server as configured in "On Moving" mode in the "Data Acquisition" tab. This will help to track where vehicles are towed.
Crash Detection
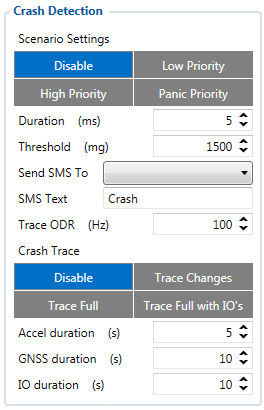
If Crash Detection is enabled, it monitors acceleration on each axis which helps to detect an accident. Threshold and Duration values are set depending on the impact magnitude that is required to be detected. FMT100 can detect events ranging between a slight tapping on the device and a severe accident.
If Crash Trace is disabled only one eventual crash record will be generated when Duration (ms) and Threshold (mg) values are exceeded.
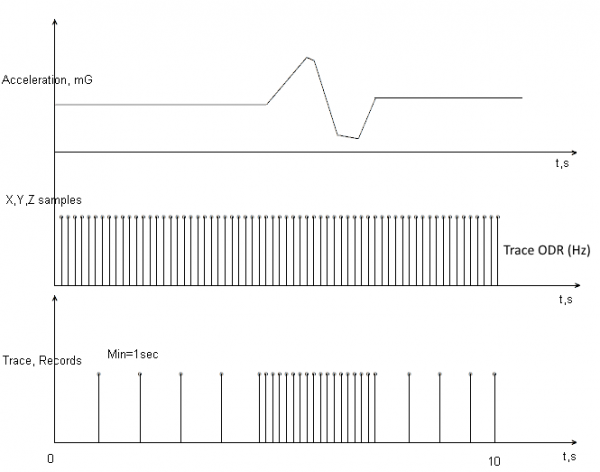
If Crash Trace is enabled, FMT100 will collect crash trace data with frequency defined by Trace ODR (Hz) parameter. Acceleration, GNSS and IO data monitoring duration during the crash event is defined by these parameters:
- Accel duration (s). Acceleration data duration can be set for up to 15 seconds before crash event and 15 seconds after;
- GNSS duration (s). GNSS data duration can be set for up to 30 seconds before crash event and 30 seconds after.
- IO duration (s). IO data duration can be set for up to 30 seconds before crash event and 30 seconds after.
There are three configurable Crash Trace modes:
Trace Full
- Data tracked: all GNSS and acceleration data
Trace Full with IO's
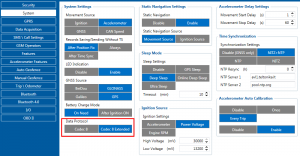
- Data tracked: all GNSS and acceleration data with IO's, configured in I/O settings as "Crash" parameter (see picture below)
Trace Changes
- Data tracked: GNSS and acceleration data, when acceleration values are changed by more then 50mG
NOTE: with Crash Trace mode enabled, it is recommended to use Codec 8 Extended Data Protocol. This helps to optimize crash trace data sending from device to server.
Each record will have accurate timestamps in milliseconds.
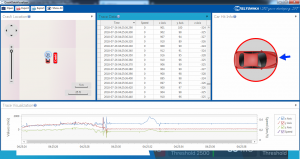
Crash Data Visualisation
With Teltonika CrashDataVisualizer tool you can analyze crash trace data visually: determine impact to vehicle direction, view crash trace on the map, also see the change of mG and speed values during crash time period. CrashDataVisualizer is dedicated to work with TAVL application, it means that only crash trace log files exported from TAVL is compatible. To have ability to export crash trace log files, device must be configured to send data by Codec8E.
To start using CrashDataVisualizer
Download and install TAVL (version 4.15.0.1 or later) + CrashDataVisualizer applications from here:
Link: https://drive.teltonika.lt/d/05369fc90d9744afb14f/
Password: TJEk24YApbRhWrQQ
To get crash data
Login to TAVL application (please contact your Sales manager for TAVL login information).
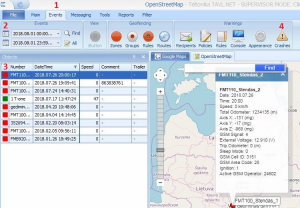
In TAVL application:
1. Go to Events
2. Set the date of event
3. Select the object you want to analyze
4. Press "Crashes" button
Crash event list window will show up. Press Download icon and save crash event file (.JSON).
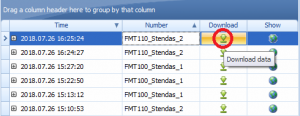
Viewing crash data in application
Open CrashDataVisualizer application. Drag and Drop or Browse crash data file (.JSON).

Use the Visualizer.