GPS Electronic Logbook
Project description
If you are one of those drivers or fleet managers who find doing your logbook a tedious and time-consuming process, we have got good news for you. Thanks to Teltonika GPS trackers, you can automate nearly the whole process by using an accurate and reliable GPS electronic logbook.
Here You will find how to prepare and to test this solution.
What will You need for the solution?
- Teltonika FM device which is compatible with this use case. Recommended products are: FMB001, FMC001, FMM001, FM3001, FMB002, FMB010, FMB003 or FMB020.
- The SIM card in order to receive data to Your server.
- Teltonika Configurator to set up FM device correctly for the solution...
- FOTA WEB to remotely send the configuration to the device.
- BTAPP / Driver application for Private Mode or Business Mode selection.
Installation
All of recommended products are "Plug and Play" devices. It means that devices are directly plugged into vehicles OBDII socket and after configuration is complete - devices are set for use. Although, if plugged OBDII device is too hard to reach and vehicle parts are interfering with GPS signal or vehicle parts need to be removed/opened to access OBDII socket and afterwards parts no longer fit or close - Teltonika offers OBDII extension cable. [1]
Apart from device configuration (more later) and installation into vehicle, GPS electronic logbook doesn't require additional hands on work.
Configuration
1. Prerequisites:
1.1. Read through First start guide
2. Configuration of GPS electronic logbook scenario:
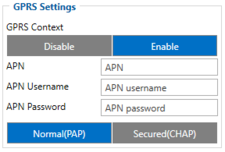
Parameter ID - Parameter name
- 2001 – APN
- 2002 – APN username (if there are no APN username, empty field should be left)
- 2003 – APN password (if there are no APN password, empty field should be left)
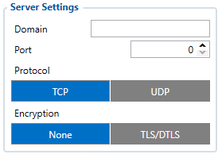
Server settings:
- 2004 – Domain
- 2005 – Port
- 2006 – Data sending protocol (0 – TCP, 1 – UDP
After successful GPRS/SERVER settings configuration, FMB920 device will synchronize time and update records to the configured server. Time intervals and default I/O elements can be changed by using Teltonika Configurator or SMS parameters.
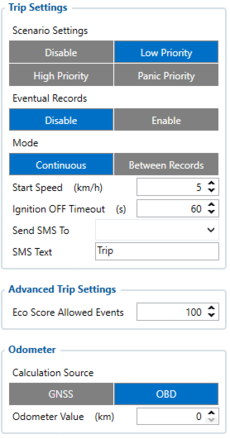
Configuration of Trip scenario:
- 11800 - Scenario priority (0 - Disable, 1 - Low, 2 - High, 3 - Panic).
- 11801 - Eventual settings (0 - Disable, 1 - Enable), if disabled - trip settings will come with periodical data.
- 11802 - Mode (0 - Continuous, 1 Between Records). If Between Records option is selected - distance will be counted until any record is made. Then odometer will be reset to zero and start counting until next record is made. If Continues option is selected - distance will continue counting between trip start and trip stop and odometer will not reset.
- 11803 - Start Speed (km/h).
- 11804 - Ignition OFF timeout (s).
- 7031 - ID of SMS recipient.
- 8031 - SMS Text.
- 700 - Eco Score Allowed Events.
- 11806 - Odometer Calculation Source (0 - GNSS, 1 - OBD).
- 11807 - current Odometer Value (km). Odometer data will be counted from provided value.
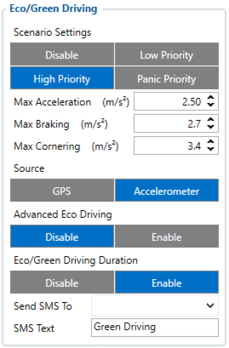
Configuration of Eco/Green driving scenario:
- 11000 - Scenario priority (0 - Disable, 1 - Low, 2 - High, 3 - Panic).
- 11004 - Maximum Acceleration (m/s2).
- 11005 - Maximum Braking (m/s2)
- 11006 - Maximum Cornering (m/s2)
- 11007 - Source (0 - GPS, 1 - Accelerometer). Green driving scenario according to selected data source.
- 11019 - Advanced Eco Driving (0 - Disable, 1 - Enable). If enabled, Eco Driving Average (ID.: 11011) and / or Eco Driving Maximum (ID.: 11015) settings can be changed.
- 11008 - Eco/Green Driving Duration (0 - Disable, 1 - Enable).
- 7034 - ID of SMS recipient.
- 8034 - SMS Text.
Note: Maximum acceleration, braking and cornering values should be set according to vehicle type, power, weight and etc. Best values can be approached by practical testing. E.g. testing cornering parameters - take the same turn at different speed (30km/h, 20 km/h, 40 km/h) and check if Eco/Green Driving event has been triggered for cornering - if it feels as turning on 30km/h is harsh but event is not triggered - lower Max Cornering values and reattempt the test.
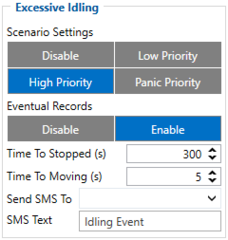
Configuration of Excessive idling scenario:
- 11200 - Scenario priority (0 - Disable, 1 - Low, 2 - High, 3 - Panic).
- 11203 - Eventual settings (0 - Disable, 1 - Enable), if disabled - excessive idling data will come with periodical data.
- 11205 - Time To Stopped (s). Represents how long vehicle should not move with engine ON.
- 11206 - To To Moving (s). Represents how long vehicle should be moving with engine ON, to exit idle state.
- 7033 - ID of SMS recipient.
- 8033 - SMS Text.
Quick start: From default configuration to GPS electronic logbook records in one SMS:
" setparam 2001:APN;2002:APN_username;2003:APN_password;2004:Domain;2005:Port;2006:0;11800:1;11801:0;11806:1;11000:2;11007:1;11200:2"
This SMS will set up Your device to send Trip, Eco/Green driving and Excessive idling data to Your previously provided server.
Note: Before SMS text, two space symbols should be inserted if no SMS username or password was set in SMS / Call settings.
3. BTAPP Mobile application

After making configuration for Your device, it is time to download BTAPP. Keep in mind, app and device connection is established via Blue-tooth. Devices by default come with Bluetooth enabled and visible. After pairing to device - You can change the trip type of Your trips by performing a long press on the icon and confirming the change.
Parsing GPS electronic logbook records
1. Prerequisites:
1.1. Open TCP/UDP port
1.2. Go to Java parser first start guide
2.Parsing example:
| Unparsed received data in hexadecimal stream |
|---|
| 000000000000005E08010000017716AE03D8010F0F22D720982E9C007E00120A002FFD1609E
F01F00150011505C80045010101FD03FE230BB5000BB60006423A0018002F430F8A4400000 901301100161200EC13FBD90F038402C7000003BD1003066802000100005F75 |
| AVL Data Packet Part | HEX Code Part |
|---|---|
| Zero Bytes | 00 00 00 00 |
| Data Field Length | 00 00 00 5E |
| Codec ID | 08 (Codec 8) |
| Number of Data 1 (Number of Total Records) | 01 |
| Timestamp | 00 00 01 77 16 AE 03 D8 (Mon Jan 18 18:07:19 UTC 2021) |
| Priority | 01 |
| Longitude | 0F 0F 22 D7 |
| Latitude | 20 98 2E 9C |
| Altitude | 00 7E |
| Angle | 00 12 |
| Satellites | 0A |
| Speed | 00 2F |
| Event IO ID | FD (AVL ID: 253, Name: Green driving type) |
| N of Total ID | 16 |
| N1 of One Byte IO | 09 |
| 1’st IO ID | EF (AVL ID: 239, Name: Ignition) |
| 1’st IO Value | 01 |
| 2’nd IO ID | F0 (AVL ID: 240, Name: Movement) |
| 2’nd IO Value | 01 |
| 3’rd IO ID | 15 (AVL ID: 21, Name: GSM Signal) |
| 3’rd IO Value | 05 |
| 4'th IO ID | 50 (AVL ID: 80, Name: Data mode) |
| 4'th IO Value | 01 |
| 5'th IO ID | C8 (AVL ID: 200, Name: Sleep Mode) |
| 5'th IO Value | 00 |
| 6'th IO ID | 45 (AVL ID: 69, Name: GNSS Status) |
| 6'th IO Value | 01 |
| 7'th IO ID | 01 (AVL ID: 1, Name: Digital Input 1) |
| 7'th IO Value | 01 |
| 8'th IO ID | FD (AVL ID: 253, Name: Green driving type) |
| 8'th IO Value | 03 (01 - harsh acceleration, 02 - harsh braking, 03 - harsh cornering) |
| 9'th IO ID | FE (AVL ID: 254, Name: Green Driving Value) |
| 9'th IO Value | 23 ( Depending on green driving type: if harsh acceleration or braking - g*100 (value 123 ->1,23g). If Green driving source is "GPS" - harsh cornering value is rad/s*100. If source is "Accelerometer" - g*100. |
| N2 of Two Byte IO | 0B |
| 1’st IO ID | B5 (AVL ID: 181, Name: GNSS PDOP) |
| 1’st IO Value | 00 0B |
| 2’nd IO ID | B6 (AVL ID: 182, Name: GNSS HDOP) |
| 2’nd IO Value | 00 06 |
| 3’rd IO ID | 42 (AVL ID: 66, Name: External Voltage) |
| 3’rd IO Value | 3A 00 |
| 4'th IO ID | 18 (AVL ID: 24, Name: Speed) |
| 4'th IO Value | 00 2F |
| 5'th IO ID | 43 (AVL ID: 67,Name: Battery Voltage) |
| 5'th IO Value | 0F 8A |
| 6'th IO ID | 44 (AVL ID: 68, Name: Battery Current) |
| 6'th IO Value | 00 00 |
| 7'th IO ID | 09 (AVL ID: 9, Analog input 1 |
| 7'th IO Value | 01 30 |
| 8'th IO ID | 11 (AVL ID:17, Name: Axis X) |
| 8’th IO Value | 00 16 |
| 9'th IO ID | 12 (AVL ID:18, Name: Axis Y) |
| 9’th IO Value | 00 EC |
| 10'th IO ID | 13 (AVL ID:19, Name: Axis Z) |
| 10'th IO Value | FB D9 |
| 11'th IO ID | 0F (AVL ID: 15, Name: Eco score) |
| 11'th IO Value | 03 84 |
| N4 of Four Byte IO | 02 |
| 1'st IO ID | 02 C7(AVL ID: 199, Name: Trip Odometer) |
| 1’st IO Value | 00 00 03 BD |
| 2’nd IO ID | 10 03(AVL ID: 16, Name: Total Odometer) |
| 2’nd IO Value | 06 68 80 20 |
| Number of Data 2 (Number of Total Records) | 01 |
| CRC-16 | 00 00 5F 75 |
In platform
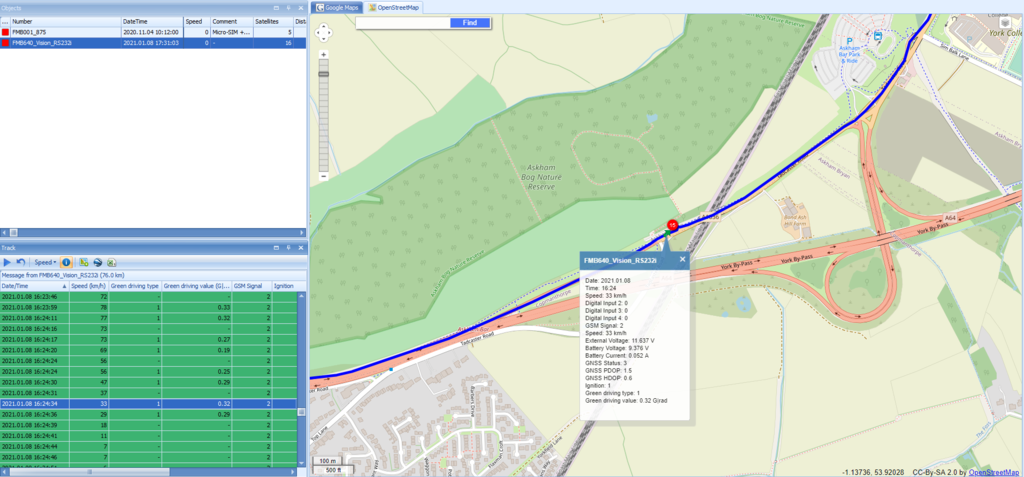
Packet information can be displayed visually. In the picture below, event location is displayed on the map. Dot on the map represents a record. By clicking on it, it is possible to see what kind of information is gathered in the particular entry.
In order to visually see received information on the platforms:
TAVL: Open TAVL → select client → select Street Map → select device → choose the date from which to which to show the records → push advanced → push show button and then you will see in left down corner all information.
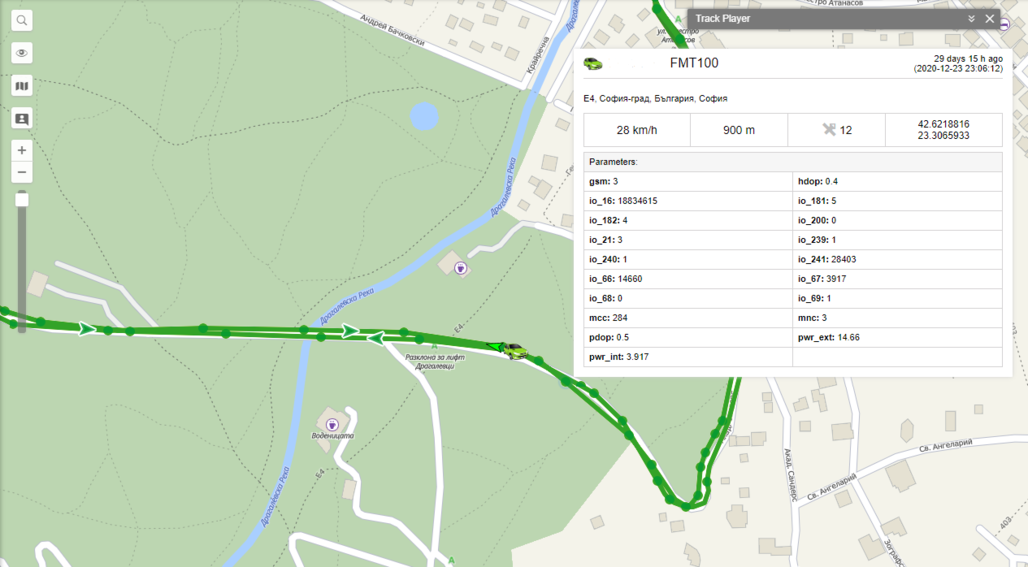
WIALON: Open WIALON → open messages → push unit ( select your device) → choose the date from which to which to show the records → select message (data messages) → push execute button and you will see all information. (Note: Figure below is an example and doesn't represent the actual visualization of the packet in the parsing example).
BTAPP:
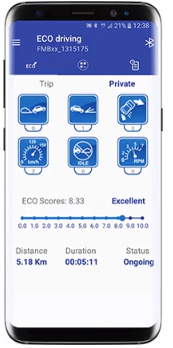
Bluetooth connection to monitor and score driver behavior. Real time events notifications about harsh acceleration, braking, cornering, overspeeding, idling and RPM. Solution designed to improve driver behavior and productivity.
- You must connect to the FMB device by clicking Bluetooth icon, and selecting your FMB device.
- Each event that was detected by the FMB device will be displayed in the application as well. Users can be notified visually, event icon will turn yellow and event count will be increased accordingly, and by sound alert as well (can be optionally enabled in application settings).
- Eco score is calculated by FMB device depending on total event amount and trip distance.
Eco score, distance, and duration is being updated periodically automatically.
- Trip status can be Ongoing and Finished. The trip finish is decided by FMB configuration. If the application will be connected to FMB device during an ongoing trip – the application will update event count, score, distance, and trip duration for an ongoing trip.
