FTM305 Input/output (I/O)
Input / output (I/O)
Search
Enter the keyword to search for the desired permanent I/O.
More Filters
It provides additional filter options such as Priority, Operand, and rows with currently available values.
View Columns
Filters the necessary tabs when making configuration changes or viewing. Priority, Operand, Low Level, High Level, and Event Only Options are available filters. The Input name and Current Values are permanent columns.
Current Value
If the device is connected to the Telematics Configuration Tool, then all the current I/O values can be seen here.
Units
Units of measurement.
Priority
This field allows the enabling of the I/O elements and sets them a priority so they are added to the data packet, which is sent to the server.
By default I/O elements with Low priority are enabled: Total odometer GSM Signal, Battery Voltage, Battery Current, PCB temperature, GNSS PDOP, GNSS HDOP, Ignition, Movement, External voltage.
These records made by FTM305 device are regular, and regular packets are sent as low priority records.
Priority level (AVL packet priority) can be:
None Priority
- The module doesn't make additional records.
Low Priority
- The module makes an additional record with an indication that the event was caused by an I/O element change (depending on Operands configuration).
High Priority
- The module makes an additional record with High priority flag and sends event packet immediately to the server using GPRS.
High and Low Level
These levels define I/O value range. If I/O value enters or exits this range, FTM305 generates an event.
Event Only
When this is selected, I/O element status value will be appended only to eventual records, otherwise I/O element status value will appear in each AVL record.
Operands
Defines when to generate event: On Exit, On Entrance, On Both, Monitoring, On Hysteresis, On Change or On Delta Change.
Operand Monitoring
No event at all. Values are recorded only when other triggers worked.
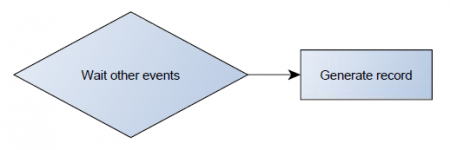
Operand On Change
Record is generated when input value changes.
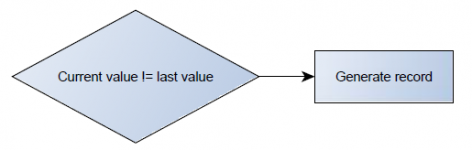
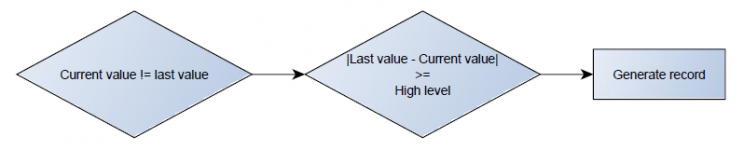
Operand On Exit
Record is generated when input value leaves a range between low and high level limits.
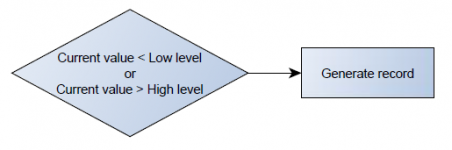
Operand On Entrance
Record is generated when input value enters a range between low and high level limits.
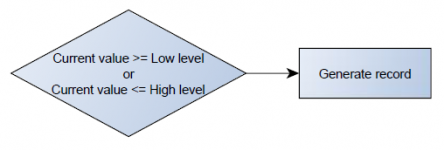
Operand On Both
Record is generated by both On Exit and On Entrance operands' logic at same time.
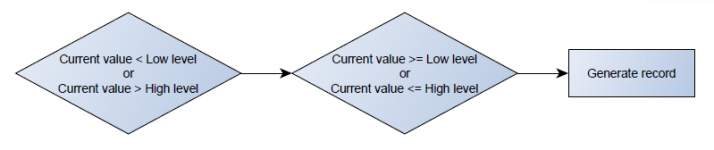
Operand On Hysteresis
Record is generated when input value crosses the high limit value from below the low limit value or vice versa.
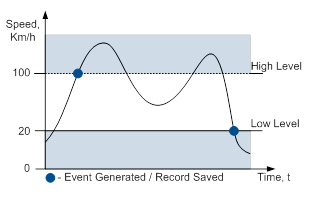
Operand On Delta Change
Record is generated when input value changes and the absolute change becomes equal to or higher than the limit value.
Permanent I/O
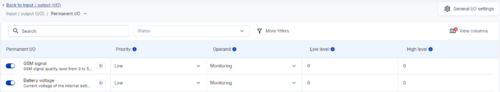
When no permanent I/O elements are enabled, AVL packet comes with GNSS information only.
After enabling I/O element(s) AVL packet contains current value(s) of enabled I/O element(s) along with GNSS information.
General I/O Settings

When a device has at least one DOUT, the "General I/O Settings" menu button is displayed on the top right. This menu allows configuring general settings for DOUTS. Select a particular DOUT and configure its settings.
Overcurrent recovery
Parameter ID = 350
The feature will attempt to recover DOUT state when an overcurrent is detected in the circuit.
Principle of recovery: The DOUT is toggled to HIGH and the device checks whether the overcurrent event is still present. If yes, DOUT is toggled to LOW. This toggling to HIGH and LOW have the duration of ~2 ms and ~3 ms respectively, thus the whole cycle takes ~5 ms. This is repeated until the overcurrent event is no longer detected or the maximum number of attempts (1000) is reached (takes ~5 seconds in total).
Inversion
Parameter ID = 360
This feature inverts the digital output value. All scenarios and commands will have an inverted effect for the digital output. For example, when DOUT is inverted - it will be ON by default and triggering any scenario will turn it OFF.
Normal behavior: DOUT ON - HIGH (1), DOUT OFF - LOW (0).
Inverted behavior: DOUT ON - LOW (0), DOUT OFF - HIGH (1).
IMPORTANT! DOUT state I/O element that is sent in the records represents the real state of the DOUT pin.
Manual CAN

The user can configure 70 Manual CAN I/O element by setting Priority, CAN Type, CAN ID, Data Mask, Operand. Each CAN I/O has its own parameters and can be configured independentely.
When configuring CAN IO elements, each parameter (like priority, operand, CAN type, CAN ID, etc.) requires a unique configuration ID. These IDs follow specific formulas to ensure no overlap with other parameters in the system. This guide explains how to calculate them.
Formula:
Parameter_ID = 1,000,000 + (AVL_ID * 100) + OPTION Parameter_ID = 1,000,000 + (AVL_ID * 100) + OPTION
- 1,000,000: Base offset for CAN-related parameters.
- AVL_ID: The CAN AVL IO element identifier (within certain allowed ranges).
- OPTION: A small integer offset indicating which setting is being adjusted (e.g., priority or operand).
Valid AVL Ranges
- [10216:10235]
- [10298:10347]
Example: If AVL_ID is 10216 and the OPTION for “priority” is 1, then Parameter ID=1,000,000+(10216×100)+1=1,000,000+1,021,600+1=2,021,601
MCAN IO Parameter Calculation
For MCAN IO elements (e.g., MCAN0, MCAN1, MCAN2…), each has three specific parameters: CAN Type, CAN ID, and Data Mask. The MCAN IO number is the index of the MCAN entry (starting at 0, 1, 2, etc.).
Formulas 1. CAN Type Parameter ID=17,000+(10×MCAN IO number) 2. CAN ID Parameter ID=17,001+(10×MCAN IO number) 3. Data Mask Parameter ID=17,002+(10×MCAN IO number)
Examples
- MCAN0 (IO number = 0):
- CAN Type: 17000 + (10 × 0) = 17000
- CAN ID: 17001 + (10 × 0) = 17001
- Data Mask: 17002 + (10 × 0) = 17002
- MCAN1 (IO number = 1):
- CAN Type: 17000 + (10 × 1) = 17010
- CAN ID: 17001 + (10 × 1) = 17011
- Data Mask: 17002 + (10 × 1) = 17012
- MCAN69 (IO number = 69):
- CAN Type: 17000 + (10 × 69) = 17690
- CAN ID: 17001 + (10 × 69) = 17691
- Data Mask: 17002 + (10 × 69) = 17692
Putting It All Together
1. Check Your AVL ID Range
- If your CAN IO element has an AVL ID in [10216–10235] or [10298–10347], use the first formula for Parameter_ID = 1,000,000 + (AVL_ID * 100) + OPTION.
2. Identify Your MCAN IO Number
- If you have an MCAN entry (e.g., MCAN0, MCAN1), use the second set of formulas to find the corresponding CAN Type, CAN ID, and Data Mask parameter IDs.
3. Plug In the Numbers
- Calculate step by step, ensuring you add the correct base offsets and multipliers.
4. Configure Your Device
- Once you have the parameter IDs, set or modify them in your configuration tool to match the desired priority, operand, or other CAN-related settings.
Manual CAN Commands
Manual CAN Commands functionality allows user to send configurable commands to CAN BUS.
Note: Before using Manual CAN, make sure to select the correct CAN settings: FTM305 CAN settings.
Up to 10 Manual CAN Command I/Os can be configured:

Configurable settings:
- Command type - defines which CAN ID type will be used to send commands:
- Standard (11-bit) - a maximum value of 7FF.
- Extended (29-bit) - a maximum value of 1FFFFFFF.
- CAN ID – defines command CAN ID.
- If Command type is Standard (11-bit) - a maximum value of 7FF.
- If Command type is Extended (29-bit) - a maximum value of 1FFFFFFF.
- Data - defines command data.
- Data length - defines command data length in bytes.
- Send type - selects command send type:
- Once - command will be sent one time after it is triggered.
- Periodic - command will be sent periodically after it is triggered.
- Response - command will be sent once as a response to received Manual CAN I/O.
- Run on startup - if enabled, command will be triggered automatically on device startup.
- Response - if Send type is Response, defines Manual CAN I/O which will trigger command.
- Send period - defines command send period (in miliseconds) if Periodic send type is selected:
- Minimal command period - 100 ms.
- Period must be configured with a step of 100 ms.
- Send count - defines command sending count if Periodic send type is selected.
- If set to 0 - command will be sent infinitely until it is turned off by the user.
- Command Enabler - toggles command.
- If enabled - command will send CAN messages.
- If disabled, the command will not be available to trigger sending, even if configured.
After configuring, Manual CAN commands can be triggered with SMS/GPRS commands: FTM305 SMS/GPRS Commands.
