Difference between revisions of "FMU126 Data acquisition settings"
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
{| class="wikitable sortable" | {| class="wikitable sortable" | ||
|+'''Table 1.''' Activation source enter/exit conditions | |+'''Table 1.''' Activation source enter/exit conditions | ||
| − | !'''Activation source''' | + | ! style="background: #0054A6; color:white" | '''Activation source''' |
| − | !'''Enter conditions''' | + | ! style="background: #0054A6; color:white" | '''Enter conditions''' |
| − | !'''Exit conditions''' | + | ! style="background: #0054A6; color:white" | '''Exit conditions''' |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |Unplug | + | |'''Unplug''' |
|Device unplugged based on Unplug scenario | |Device unplugged based on Unplug scenario | ||
|External power connected | |External power connected | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |Towing | + | |'''Towing''' |
| − | |Towing | + | |Towing occurred based on configuration |
|Towing is not active anymore (no movement for timeout amount of time reached or ignition activated) | |Towing is not active anymore (no movement for timeout amount of time reached or ignition activated) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |Autogeofence | + | |'''Autogeofence''' |
| − | |Device exited autogeofence zone or no fix with movement for activation timeout amount of time | + | |Device exited autogeofence zone or no fix with the movement for activation timeout amount of time |
|When deactivation source is triggered | |When deactivation source is triggered | ||
|} | |} | ||
[[Category:FMU126 Configuration]] | [[Category:FMU126 Configuration]] | ||
Revision as of 11:50, 20 April 2021
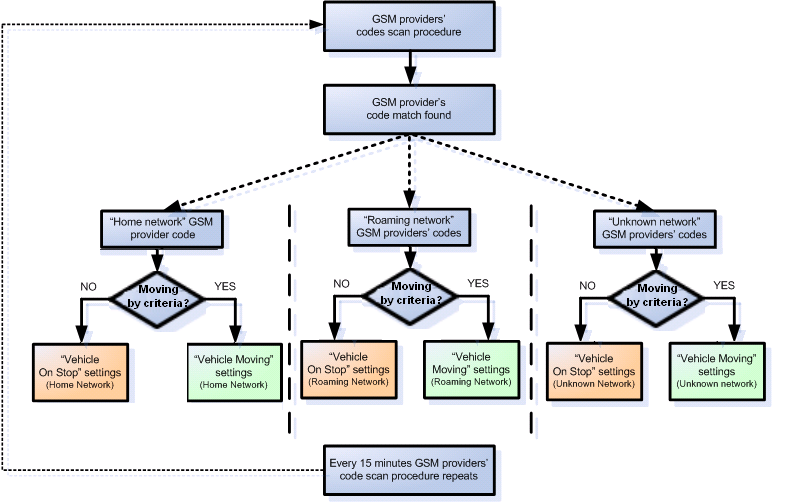
Main Page > EOL Products > FMU126 > FMU126 Configuration > FMU126 Data acquisition settingsData Acquisition modes are an essential part of FMU126 device, they are also highly configurable.
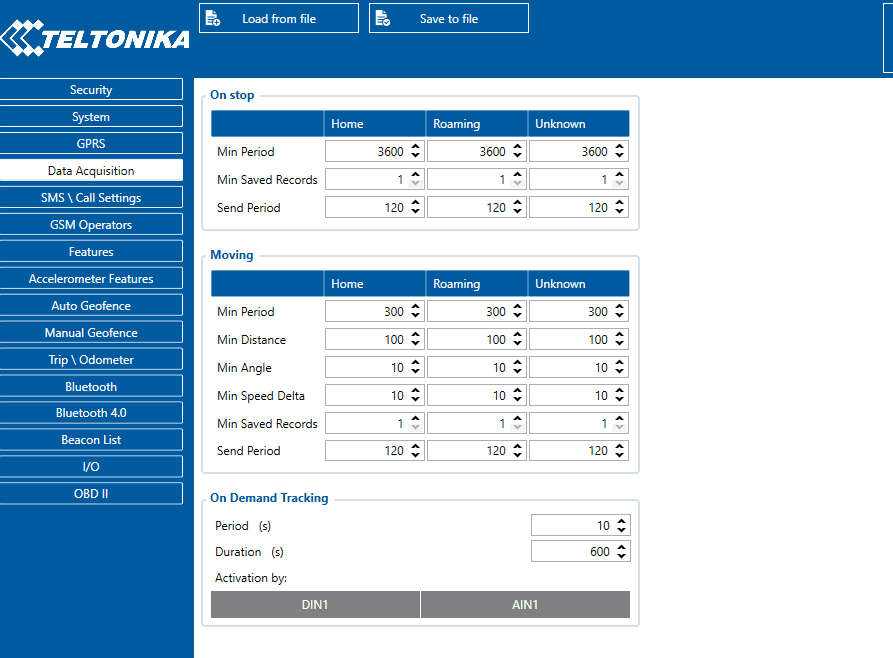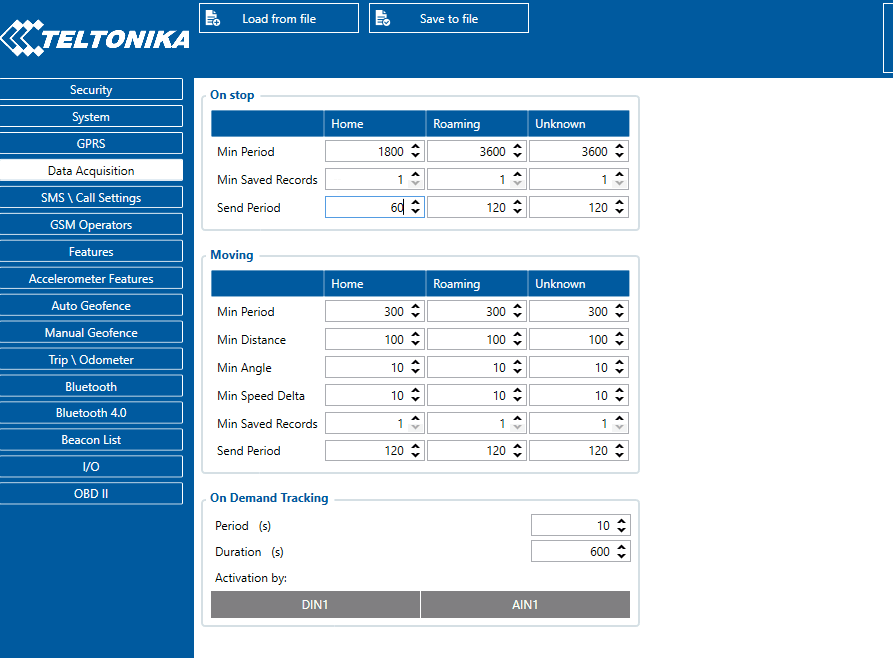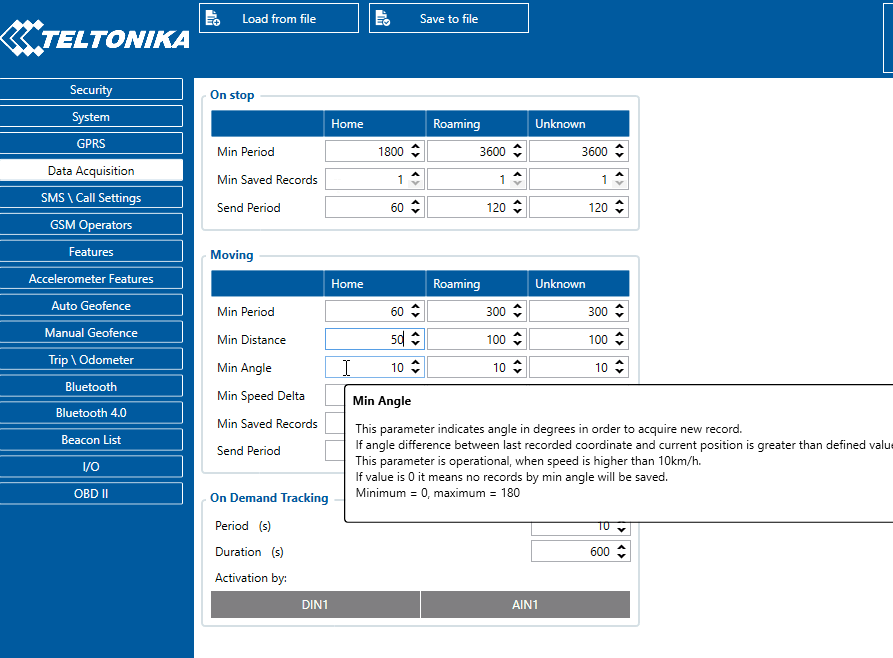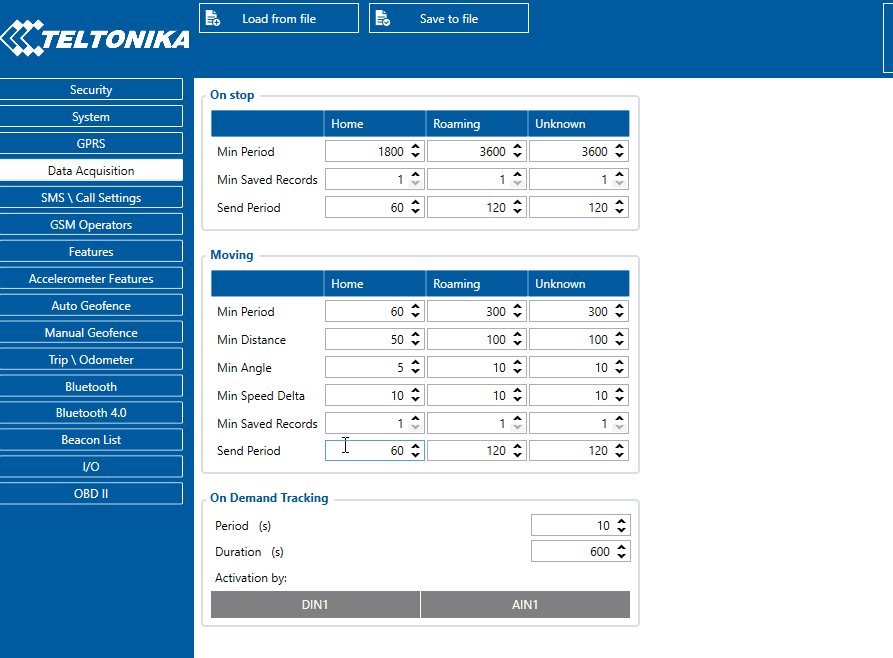
Through configuration user defines how records will be saved and sent. There are three different modes: Home, Roaming and Unknown. All these modes with configured data acquisition and report frequencies depend on current GSM Operator defined in the Operator list (see section GSM Operators settings) and are switched when GSM operator changes (e.g. vehicle passes through a country border).
If current GSM operator is defined as Home Operator, device will work in Home Data Acquisition mode, if current operator is defined as Roaming Operator, device will work in Roaming Data Acquisition mode, and if current operator code is not written in the Roaming Operator list, device will work in Unknown mode.
This functionality allows having different AVL records to acquire and send parameter values when object is moving or standing still. Vehicle moving or stop state is defined by Stop Detection Source parameter. There are 4 ways for FMU126 to switch between Vehicle on Stop and Vehicle Moving modes, please refer to the first table in System settings.
FMU126 has 6 different modes. Operational logic is shown in the figure below.
| If home operator is written to roaming operator list, it will still be detected as home operator. |
Operator search is performed every 15 minutes. Depending on current GSM operator Home, Roaming or Unknown mode can be changed faster than every 15 minutes. This process is separate from operator search. Movement criteria are checked every second.
Min Saved Records defines minimum number of coordinates and I/O data that should be transferred within a single connection to the server. If FMU126 does not have enough coordinates to send to the server, it will check again after a time interval defined in Send Period field.
Send period controls the frequency of data being sent to server over GPRS. Module makes attempts to send collected data to the server every defined period of time. If it does not have enough records (depends on the parameter Min. Saved Records described above), it tries again after the defined time interval.
| Keep in mind that FMU126 operates in GMT:0 time zone, without daylight saving. |
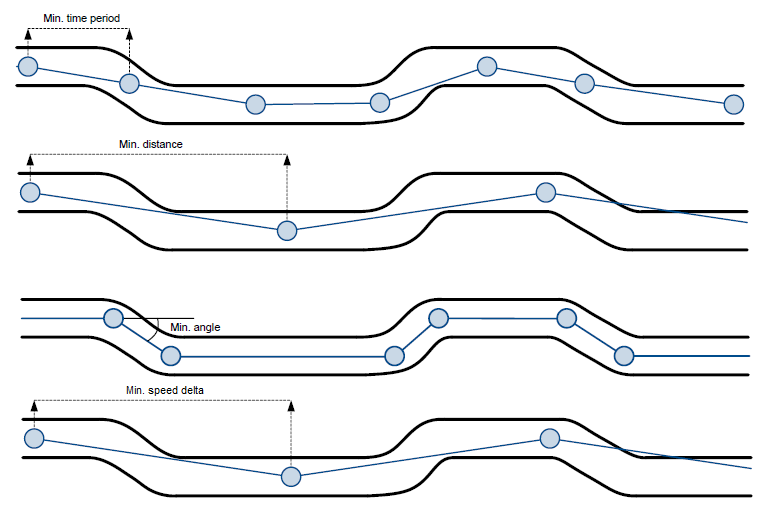
FMU126 is able to collect records using four methods at the same time: time, distance, angle and speed based data acquisition:
- Time based data acquisition (Min Period) – records are acquired every time when a defined interval of time passes. Entering zero disables data acquisition based on time.
- Distance based data acquisition (Min Distance) – records are acquired when the distance between previous coordinate and current position is greater than a defined parameter value. Entering zero disables data acquisition based on distance.
- Angle based data acquisition (Min Angle) – records are acquired when the angle difference between last recorded coordinate and current position is greater than a defined value. Entering zero disables data acquisition based on angle.
- Speed based data acquisition (Min Speed Delta) – records are acquired when the speed difference between last recorded coordinate and current position is greater than a defined value. Entering zero disables data acquisition based on speed.
On Demand Tracking
This functionality was made global (for all FMB devices) from 03.25.06.Rev.00. Tracking on Demand can be activated using commands. After device receives SMS/GPRS command " on_demand_trackingX" where X is a number from 0 to 2.
Possible X values are:
- X = 0 – Stops Tracking on Demand functionality.
- X = 1 – Starts Tracking on Demand functionality.
- X = 2 – Generates one high priority record and initiates data sending to the server.
After that, the device starts to generate high priority records and initiate data sending to the server. This
feature is configurable via SMS/GPRS commands only.
From version 03.25.11.Rev.00 tracking on demand can be triggered by multiple IO Events. To enable functionality at least one activation source must be selected and an appropriate IO Event (in I/O tab) should be enabled (Low/High/Panic priority, the operand must NOT be “Monitoring”). When IO Event is generated and if the event is enabled in activation sources, tracking on demand will be started. THE new IO event will not interrupt or restart tracking on-demand until the Duration period has expired. If tracking on demand is already running, SMS/GPRS command will restart tracking on demand. If tracking the on-demand period is lower than the normal record acquisition period, only high priority records will be created. If tracking the on-demand period is larger than the normal record acquisition period, low priority records will be created according to data acquisition configuration and high priority records will be created after configured tracking on-demand period. Some new Tracking on Demand parameters are introduced in devices.
There are three available options for the activation source of tracking on demand - DIN/AIN or both (devices that support multiple DINs/AINs allow choosing which DINs/AINs to use). Note that, these inputs will work as buttons, rather than switches, and are used to trigger the functionality, the duration of tracking on demand will not be extended if the activation source status is high for a period of time.
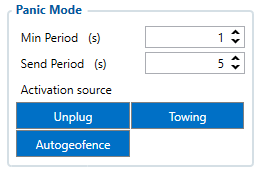
Panic Mode
Panic mode was introduced from FW version FMB.Ver.03.27.01.Rev.160+.
This mode has 3 main parameters:
- „min period"
- „send period“
- „activation source“
Parameters are located in the „Data acquisition“ tab. It works by checking the configured activation sources for events. If any one of them occurs, it changes the minimum acquisition period for records as well as starts to try to send records to the server at a different rate. When in panic mode, exiting is possible once all of the configured activation source exit conditions are met.
Sending to the server is tried every „send period“ parameter amount of seconds both to main and backup server. The selected activation source scenarios should be configured as not “none priority” in order for them to work.
| Activation source | Enter conditions | Exit conditions |
|---|---|---|
| Unplug | Device unplugged based on Unplug scenario | External power connected |
| Towing | Towing occurred based on configuration | Towing is not active anymore (no movement for timeout amount of time reached or ignition activated) |
| Autogeofence | Device exited autogeofence zone or no fix with the movement for activation timeout amount of time | When deactivation source is triggered |