Difference between revisions of "FMA202 Data acquisition mode settings"
(Created page with "{{Template:FM3612_Data_acquisition_mode_settings|model=FMA202|dataAcquisitionFoto=600px|center}}") |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Template:FM3612_Data_acquisition_mode_settings|model=FMA202|dataAcquisitionFoto=[[Image:FMAacquisition_conf.png|600px|center]]}} | {{Template:FM3612_Data_acquisition_mode_settings|model=FMA202|dataAcquisitionFoto=[[Image:FMAacquisition_conf.png|600px|center]]}} | ||
| + | [[Category:FMA202 Configuration]] | ||
Latest revision as of 07:48, 6 May 2019
Main Page > EOL Products > FMA202 > FMA202 Configuration > FMA202 Data acquisition mode settingsData Acquisition Modes are an essential part of FMA202 device, it is also highly configurable.
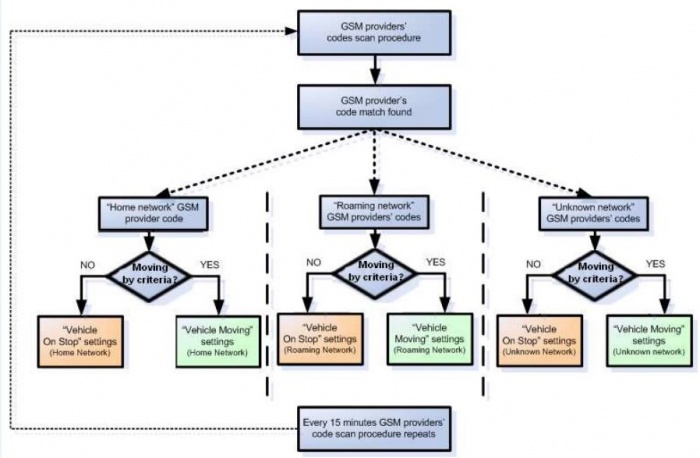
By configuration user defines how records will be saved and sent. There are three different modes: Home, Roaming and Unknown. All these modes with configured data acquisition and send frequencies depend on current GSM Operator defined in Operator list and are switched when GSM operator changes (e.g. vehicle passes through country boarder).
If current GSM operator is defined as Home Operator, device will work in Home Data Acquisition mode, if current operator is defined as Roaming Operator, device will work in Roaming Data Acquisition mode, and if current
operator code is not written in Operator list (but there is at least one operator code in the operator list), device will work in Unknown Acquisition mode.
This functionality allows having different AVL records acquire and send parameters values when object is moving or stands still. Vehicle moving or stop state is defined by Stop Detection Source parameter. There are 3 ways for FMA202 to switch between Vehicle on Stop and Vehicle Moving modes. FMA202 allows having 6 different modes.
| Note: If there are no operator codes entered into operator list, FMA202 will work in Unknown network mode ONLY. |
Data Acquisition Mode configuration
Operator search is performed every 15 minutes. Depending on current GSM operator, Home, Roaming or Unknown mode can be changed faster than every 15 minutes. This process is separate from operator search. Movement criteria are checked every second.
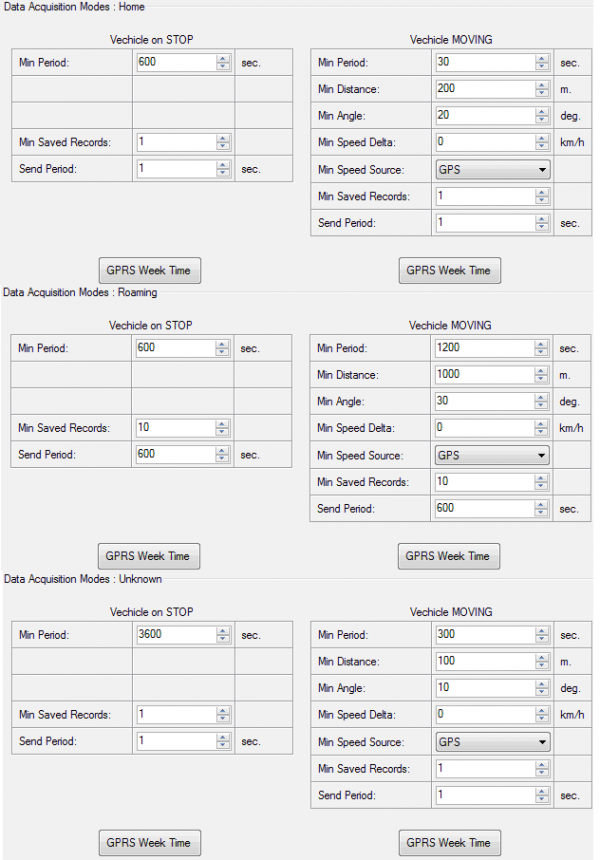
Min Period This parameter indicates time interval in seconds in order to acquire new record. If value is 0 it means no records by min period will be saved.
Min Saved Records defines minimum number of coordinates and I/O data that should be transferred with one connection to server. If FMA202 does not have enough coordinates to send to server, it will check again after time interval defined in Sending Period
Send period – GPRS data sending to server period. Module makes attempts to send collected data to server every defined period. If it does not have enough records (depends on parameter Min. Saved Records described above), it tries again after defined time interval.
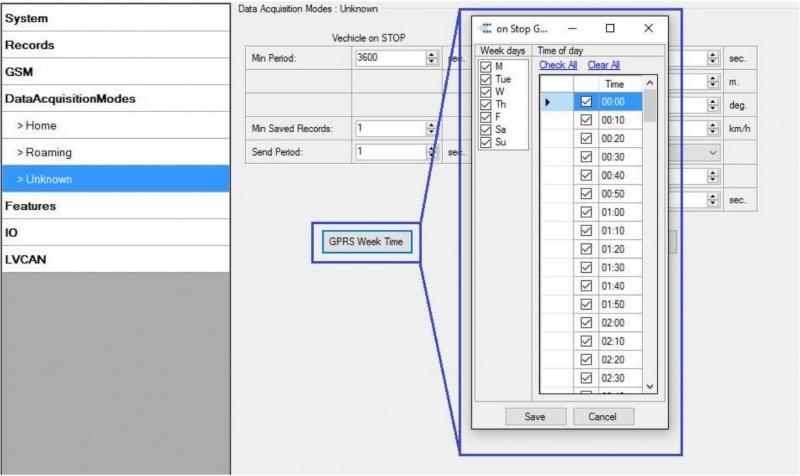
GPRS Week Time configuration
GPRS Week Time tab – most GSM billing systems charge number of bytes (kilobytes) transmitted per session. During the session, FMA202 makes connection and transmits data to a server. FMA202 tries to handle the session as much as possible; it never closes session by itself. Session can last for hours, days, weeks or session can be closed after every connection in certain GSM networks – this depends on GSM network provider. GPRS Context Week Time defines session re-establish schedule if session was closed by network. New GPRS context is opened if time is 10 minutes till time checked in table. Therefore if all boxes are checked, FMA202 is able to open new connection anytime. At scheduled time match FMA202 checks for GPRS session activity. If GPRS session is alive, FMA202 sends data to server according to Send period parameter. If it is not, FMA202 checks if it is able to re-establish the session.
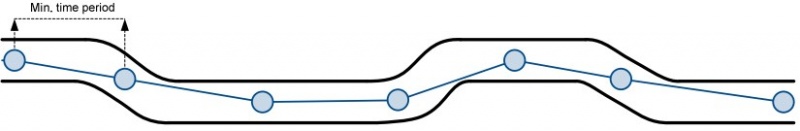
Device checks if the time between last saved record and current time is equal or higher than Time based acquire interval. If so, FMA202 saves record to memory. If not, FMA202 checks if the distance from last record to current record is equal or higher than Distance based acquire interval. If so, saves the record to memory. If not and speed is higher than 10km/h, then FMA202 checks if angle difference between last record and current record is equal or higher than Angle based acquire value. If so, saves the record to memory. These checks are performed every second.
| Note: Keep in mind that FMA202 operates in GMT:0 time zone, without daylight saving. |
FMA202 is able to collect records using four methods at the same time: time, distance, angle and speed based data acquisition:
Time based data acquiring (Min. period) – records are being acquired every time when defined interval of time passes. Entering zero disables data acquisition depending on time.
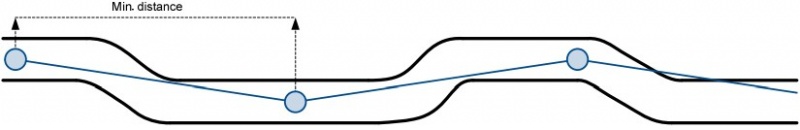
Distance based data acquiring (Min. distance) – records are being acquired when the distance between previous coordinate and current position is greater than defined parameter value. Entering zero disables data acquisition depending on distance.
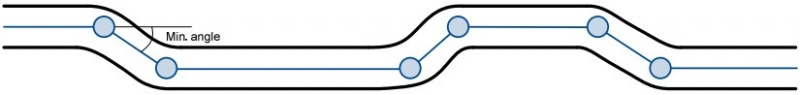
Angle based data acquiring (Min. angle) – records are being acquired when angle difference between last recorded coordinate and current position is greater than defined value. Entering zero disables data acquisition depending on angle.
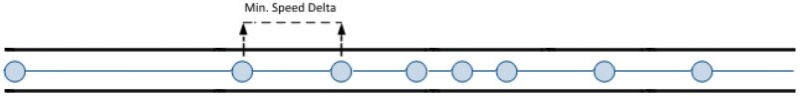
Speed based data acquiring (Min. speed delta) – records are being acquired when speed difference between last recorded coordinate and current position is greater than defined value. Entering zero disables data acquisition depending on speed.