Speed Limiting Solution
Introduction
Due to the accidents caused by over speeding, corporate fleet businesses and insurance companies suffer from huge losses in most of the countries globally. This can often lead to a loss in productivity, reduction in revenue, paying insurance costs (if it’s the driver’s fault), as well as medical and collateral damage costs. To help resolve this major concern, here at Teltonika Telematics we have developed and manufactured a unique GPS tracker with the speed limiter feature.
Solution description
Utilizing a modern and comprehensive GPS tracking method allows you to monitor driver (including novice) behaviour, improve safety, and reduce the fleet running costs and legal liability. And that is where Teltonika MSP500 comes into the play.
Teltonika MSP500 is a special tracking terminal with GNSS/GSM/Bluetooth 4.0 connectivity, internal GNSS/GSM antennas, RS232 interface, internal Ni-Mh battery, and waterproof IP65 casing. The device has been specifically designed with the key feature – speed limiting control
What you need for a solution?
- MSP500 device
- The SIM card in order to get data to your server
- FOTA WEB to remotely send the configuration to the device.
Installation
It is important to install the tracker securely, hide it so that it would not be a simple task for the thieves to find and unplug it.
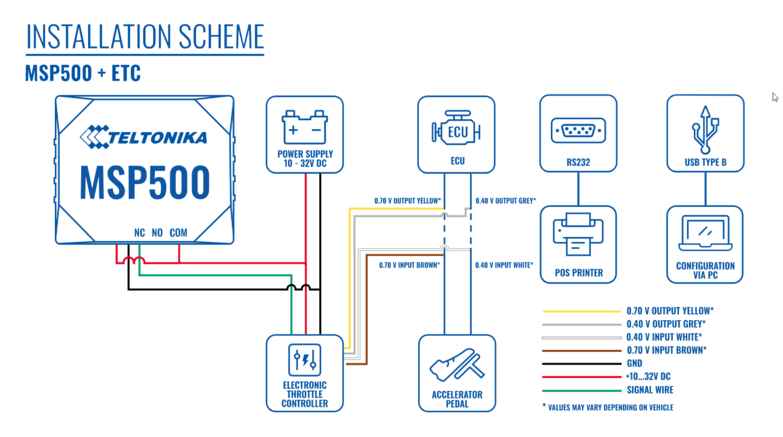
MSP500 tracker can be connected in 4 different ways based on the speed limiting scenario that will be implemented. It’s important to hide the tracker, so it would not be a simple task for the thieves to find and unplug it.
Although devices have high gain antennas it’s important to mount devices with stickers on top and in metal-free space. The device should be firmly fixed to the surface or cables. Please make sure, that device is not fixed to heat emitting or moving parts.
To have a working solution it’s important to properly wire the devices. In the picture below it's shown how to correctly wire the device.
During installation please follow recommendations in order to avoid damaging device and vehicle:
- Wires should be connected while the module is not plugged in.
- Be sure that after the car computer falls asleep, power is still available on the chosen wire. Depending on the car, this may happen in a 5 to 30 minutes period.
- When the module is connected, be sure to measure the voltage again if it did not decrease.
- The ground wire is connected to the vehicle frame or metal parts that are fixed to the frame.
Configuration
1. Prerequisites:
1.1. Read through First start guide
1.2. Understanding of possible Sleep modes.
2. Speed limiting configuration:
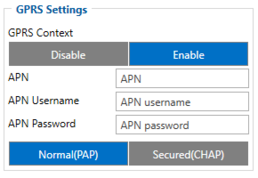
Parameter ID – Parameter name GPRS settings:
- 2001 – APN
- 2002 – APN username (if there are no APN username, empty field should be left)
- 2003 – APN password (if there are no APN password, empty field should be left)
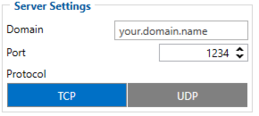
Server settings:
- 2004 – Domain
- 2005 – Port
- 2006 – Data sending protocol (0 – TCP, 1 – UDP)
After successful GPRS/SERVER settings configuration, MSP500 device will synchronize time and update records to the configured server. Time intervals and default I/O elements can be changed by using Teltonika Configurator or SMS parameters.
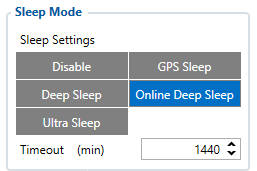
Sleep settings:
- 102 – Sleep settings(0 – Disable, 1 – Gps sleep, 2 – Deep sleep, 3 – Online Deep sleep, 4 – Ultra sleep)
Note: This scenario will not work with Deep Sleep and Ultra Sleep modes, since they disable the device's GSM module to save power.
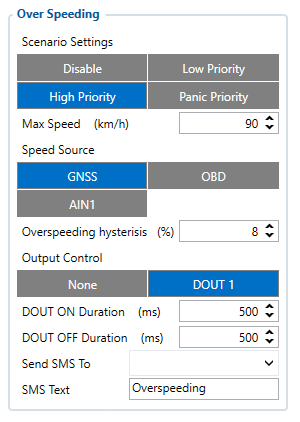
To setup the speed limiting feature in the configurator we should navigate to Features → Over Speeding where we would set a priority for the event, speed source and DOUT 1 for the relay to work properly.
Over speeding settings
- 11100 – Scenario settings(0 – Disable, 1 – Low Priority, 2 – High Priority, 3 – Panic Priority)
- 11104 - Max Speed (Default value - 90 km/h)
- 13217 - Speed Source (0 - GNSS (Default), 1 - OBD, 2 - AIN1)
- 13223 - Over speeding Hysteresis (Default value - 8%), value that determines what would be the threshold speed level that would activate the speed limiting feature
- 11103 - Output Control (0 - None (Default), 1 - DOUT1), DOUT1 needs to be enabled to use the speed limiting feature
Quickstart: From default configuration to Speed Limiting solution in one SMS:
" setparam 2001:APN;2002:APN_user;2003:APN_password;2004:Domain;2005:Port;2006:0;102:3;11100:2;11104:90;13217:0;13223:8;11103:1"
This SMS will set up your device to report the Speed Limiting scenario to the server.
Note: Before SMS text, two space symbols should be inserted if no SMS username or password was set in SMS \ Call settings.
Parsing information
1.Prerequisites:
1.1. Open TCP/UDP port
1.2. Read Java parser first start guide
2. Parsing example:
| Unparsed received data in hexadecimal stream |
|---|
| 00000000000000758E010000017CB7A57370000F0E53AE209AB86A007F00110D000000000014000800EF0100F00100500100150300C800004501000100011300000A00B5000A00B6000600423FC900180000004300000044000000
1100220012FFBA0013FC34000F0000000200F10000601A0010002D97E0000000000100007FCF |
| AVL Data Packet Part | HEX Code Part |
|---|---|
| Zero Bytes | 00 00 00 00 |
| Data Field Length | 00 00 00 75 |
| Codec ID | 8E (Codec 8 Extended) |
| Number of Data 1 (Number of Total Records) | 01 |
| Timestamp | 00 00 01 7C B7 A5 73 70 00 (Monday, October 25, 2021 4:30:46 PM GMT+03:00) |
| Priority | 00 |
| Longitude | 0F 0E 53 AE |
| Latitude | 20 9A B8 6A |
| Altitude | 00 7F |
| Angle | 00 11 |
| Satellites | 0D |
| Speed | 00 00 |
| Event IO ID | 00 00 |
| N of Total ID | 00 1F |
| N1 of One Byte IO | 09 |
| 1’st IO ID | EF (AVL ID: 239, Name: Ignition) |
| 1’st IO Value | 00 |
| 2’nd IO ID | F0 (AVL ID: 240, Name: Movement) |
| 2’nd IO Value | 00 |
| 3’rd IO ID | 15 (AVL ID: 21, Name: GSM Signal) |
| 3’rd IO Value | 04 |
| 4'th IO ID | B3 (AVL ID: 179, Name: Digital Output 1) |
| 4'th IO Value | 01 |
| 5'th IO ID | B4 (AVL ID: 180, Name: Digital Output 2) |
| 5'th IO Value | 00 |
| 6'th IO ID | 51 (AVL ID: 81, Name: Vehicle Speed) |
| 6'th IO Value | 00 |
| 7'th IO ID | 52 (AVL ID: 82, Name: Accelerator Pedal Position) |
| 7'th IO Value | 00 |
| 8'th IO ID | 59 (AVL ID: 89, Name: Fuel level) |
| 8'th IO Value | 00 |
| 9'th IO ID | 98 (AVL ID: 152, Name: Geofence zone 05) |
| 9'th IO Value | 00 |
| N2 of Two Byte IO | 0B |
| 1’st IO ID | 42 (AVL ID: 66, Name: External Voltage) |
| 1’st IO Value | 30 74 |
| 2’nd IO ID | 43 (AVL ID: 67, Name: Battery Voltage) |
| 2’nd IO Value | 0F 82 |
| 3’rd IO ID | 44 (AVL ID: 68, Name: Battery Current) |
| 3’rd IO Value | 00 00 |
| 4'th IO ID | 11 (AVL ID: 17, Name: Axis X) |
| 4'th IO Value | 00 18 |
| 5'th IO ID | 12 (AVL ID: 18,Name: Axis Y) |
| 5'th IO Value | 0F 8A |
| 6'th IO ID | 13 (AVL ID: 19, Name: Axis Z) |
| 6'th IO Value | FF E8 |
| 7'th IO ID | 54 (AVL ID: 84,Name: Fuel level) |
| 7'th IO Value | 00 BE |
| 8'th IO ID | 55 (AVL ID:85, Name: Engine RPM) |
| 8’th IO Value | 00 00 |
| 9'th IO ID | 5A (AVL ID:90, Name: Door Status) |
| 9’th IO Value | 00 00 |
| 10'th IO ID | 97 (AVL ID:151, Name: Battery Temperature) |
| 10'th IO Value | 00 00 |
| 11'th IO ID | A8 (AVL ID: 168, Battery Voltage) |
| 11'th IO Value | 00 00 |
| N4 of Four Byte IO | 0A |
| 1'st IO ID | F1 (AVL ID: 241, Name: Active GSM Operator) |
| 1’st IO Value | 00 00 60 1A |
| 2’nd IO ID | 53 (AVL ID: 83, Name: Fuel Consumed) |
| 2’nd IO Value | 00 00 00 00 |
| 3’rd IO ID | 57 (AVL ID: 87, Name: Total Mileage) |
| 3’rd IO Value | 03 CB 6B 98 |
| 4’th IO ID | 64 (AVL ID: 100, Name: Program Number) |
| 4’th IO Value | 00 00 2E 97 |
| 5’th IO ID | 66 (AVL ID: 102, Name: Engine Worktime) |
| 5’th IO Value | 00 00 00 00 |
| 6’th IO ID | 69 (AVL ID: 105, Name: Total Mileage (counted)) |
| 6’th IO Value | 02 3B 33 85 |
| 7’th IO ID | 6B (AVL ID: 107, Name: Fuel Consumed(counted)) |
| 7’th IO Value | 00 00 65 B2 |
| 8’th IO ID | 7B (AVL ID: 123, Name: Control State Flags) |
| 8’th IO Value | 00 00 00 00 |
| 9’th IO ID | 7D (AVL ID: 125, Name: Harvesting Time) |
| 9’th IO Value | 00 00 00 00 |
| 10’th IO ID | BD (AVL ID: 189, Name: Cruise Time) |
| 10’th IO Value | 00 00 00 00 |
| N8 of Eight Byte IO | 01 |
| 1'st IO ID | 84 (AVL ID: 132, Name: Security State Flags) |
| 1’st IO Value | 00 80 00 00 30 00 00 05 |
| Number of Data 2 (Number of Total Records) | 01 |
| CRC-16 | 00 00 5C 92 |
Security State Flag Examples:
- 1) Locked doors 00 80 00 00 30 00 00 05
- 2) Unlocked doors 00 80 00 00 00 00 00 05
Convert HEX value to BIN value:
Then count 28'th BIT from the back (28'th bit value shows locked/unlocked states)
- 1) 10000000000000000000000000110000000000000000000000000101
- 2) 10000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000101
If car is locked value is 1 and if car is unlocked value is 0
To test the car unlocking and locking use these GPRS commands
- 1) To unlock all doors use this command: "lvcanopenalldoors"
- 2) To lock all doors use this command: "lvcanclosealldoors"
//